Table of Contents
There is a saying “ One who has own the small wars will win the Battle Royale”. Same is the case of antibodies. Those armies in your bodies are better than any military in the world. They have strategies and tactics that inspires even the best warriors. Lets know in depth about these fighters in your body.
Same is the case of antibodies. Those armies in your bodies are better than any military in the world. They have strategies and tactics that inspires even the best warriors. Lets know in depth about these fighters in your body.
Antibodies are blood proteins which kills the foreign particles like viruses, bacteria and hordes of microorganisms and keep your body healthy. The foreign particle is called as antigen. The ability of an organism to resist a particular infection, disease or illness caused by antigens is called as immunity. Any time an antigen enters the blood stream, the organism produces lot of antibodies to counter them.
It is a much greater battle than tuhe Star Wars or Avengers you may have seen.
Each antibody is specific to the disease it restricts. That means the body produces different kinds of proteins for countering different diseases. Antibodies produced in response to one disease cannot help in resisting other disease. Ex: An antibody of measles will not protect you from mumps and this statement hold true the other way round as well.
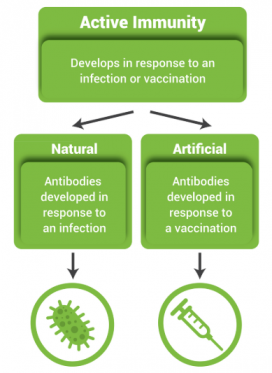
Every human body has two types of immunity: active and passive
A prime difference between active and passive immunitylies in the method or the process by which you acquire it.
Active immunity refers to the process of introducing antigen in small amounts in an organism and let the organism produce antibodies in response to that. These antibodies activate other immune cells to certain pathogens. Once the body learns the art of countering this antigen in small amount, any further disease cause by influx of large amount of same antigen can be stopped or better say,
In case of active immunity, a person’s immune system produces several antibodies that activate other immune cells to certain pathogens. On future encounter with the pathogen, the long-lasting immune cells are already primed to fight it and save you from falling ill.
It is called an adaptive immune response. The body adapts to the antigen or learns to counter the antigen effects.
In real world it is like practice tests. Before exams, you do a quite number of practice tests so that when the final exam or term paper is given , you are able to succeed.
While taking practice tests before exam, you are not accorded grades, but in the final exam you get grades. Similarly, small antigens do not provide you disease but if large influx of antigens are there, the body must know the defense mechanism to counter the disease or the long-lasting immune cells are already primed to fight it and save you from falling ill.
In Passive immunity, antibodies for a specific antigen is passed from one organism’s body to other.
A child , when he/she is born is not capable of producing good amount of antibodies to counter diseases. Then how does the child survive?
Well, your mother’s love protects you.
When you are breastfed milk by your mother, large amount of antibodies already present in your mother’s body passes on to you .
Passive immunity uis generally provided to chiildren and adults with weak immune system.
Here, antibodies are collected from a donor and a highly concentrated solution of that antibody is then injected to the patient. There are two types of passive immunity: artificial and natural. Naturally gained Passive Immunity takes place when antibodies are passed from the mother into the foetal bloodstream and from breast milk of the mother to a child.
You can acquire immunity in several ways. In case of diseases like measles and chicken pox, you acquire a lifelong immunity, once you are infected with the disease. You can also vaccinate yourself to protect from illness in future. Both forms of gaining immunity, either by vaccination or due to illness from a disease are examples of active immunity.
At times, weak immune systems do not let the antibodies function properly. Routine vaccinations might fail to protect the person from a disease organism. Once you have the antibody present in your body, it shields you from the disease-causing organism.
A newborn baby acquires passive immunity through the placenta of the mother. You can also acquire passive immunity through a blood containing antibody. Immune globulin can be induced in blood to generate immediate protection from a specific disease. For example, passive immunisations of hepatitis A (a gamma globulin) is given to travellers when they visit a hepatitis prone region. Passive immunisation called “rabies” (rabies immune globulin) is given if you get bitten by any wild animals.
In each case, the protection is immediate and the antibodies work instantly to prevent the disease. This is one of the major advantages of passive immunity as compared to active immunity, which takes several weeks or months to develop.
This protection is extremely short-lived and supports the child for only for six months.
Artificial passive immunity
Artificial immunity is an immediate but short-term immunisation process. Antibodies such as gamma globulin, are first developed in another individual or animals and is then injected into the recipient. They are normally administered during a sudden outbreak of any particular disease or during emergency treatment for toxicity. E.g. tetanus.
Some of the artificially acquired immunity are:
Natural Active Immunity/Active Immunity: Definition and its features
Source: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/understanding-hiv-aids/glossary/5/active-immunity
In case of direct exposure to a disease, our body triggers the immune system to produce antibodies. An active immunity results from exposure to the disease organism. This last for almost a lifetime for every individual. This is also called natural active immunity as you come in direct contact with the actual disease.
As soon as the microbes penetrate your skin, mucous membrane or other primary defences, it interacts with the immune system. The B cells of our body quickly produce antibodies and respond to fight against the invading microbes. The adaptive immune system may take days or weeks to develop, but once its generated, you get along lasting or lifelong protection against it.
Typically, when virus/bacteria enter an individual and it starts causing damage through its constant reproduction. The damaged cells then release a signal to immune cells to trigger that something is wrong. The immune cells then engulf the foreign bodies by surrounding them from all sides. At the same time, antibodies acquire information about the details of the disease-causing pathogens that helps them to identify and restrict these organisms during a future attack.
It becomes a daunting task to understand the intricate details of each antibody or different blood groups on the last day of the exam. The experts of MyAssignmenthelp.com guide you with excellent study materials and explain the vital concepts in easy language. Take help from our experts to improve your understanding of any aspect of Biology.
The tutors of MyAssignmenthelp.com are proficient in their respective fields. Most of them hold PhD and Post Doc degrees in Microbiology, Botany, Physiology and several other disciplines of biology. Are you stuck with a difficult assignment on vaccinations or circulation of blood? Call our experts and finish your assignments like a pro. We provide help in all these areas:
We have a hassle free and student-friendly order placing facility as well. Visit myassignmenthelp.com, click on the ‘order now’ or Free Assistance icon and fill the form. In case of any difficulty, you can ask our 24×7 customer support team to call you as per your convenience. Hire our experts to get A+ scores in all your assignments this semester.