Table of Contents
In the modern data-driven age, computers are no longer constrained by fixed limitations. They now learn from experience. Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) are two major technologies that have contributed to this change and are crucial branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Although they are commonly applied to prediction and automated decision-making, they vary in their data processing and complexity. This blog by My Assignment Help, curated around deep learning vs machine learning, will help you explore which technique should be used for a specific problem-related issue, especially resource utilisation for accurate and practical outcomes in real-world applications.
Machine Learning (ML) is one of the fundamental fields in AI, which allows systems to learn directly from data and make choices without any direct embedding of instructions to accomplish the task. ML algorithms do not follow rigid guidelines and instead process large amounts of structured data, discover patterns that matter and apply them to make predictions or recommendations.
These models will improve themselves with every piece of data they process. The real-life applications that are best served with ML include the detection of fraud, a recommendation engine and demand prediction.
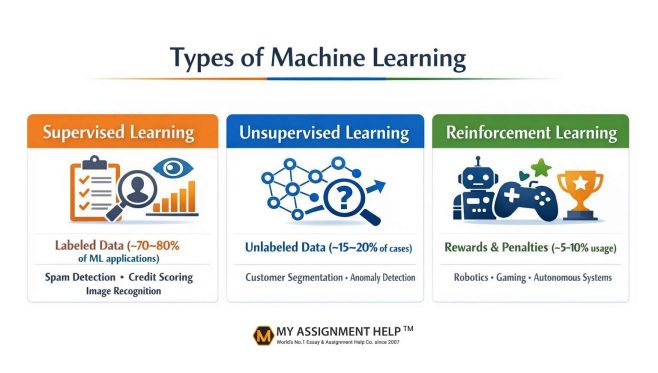
Supervised Learning: It is based on the usage of labelled datasets in which the correct output is available. This model learn through comparison between its predictions and real outcomes and then makes adjustments in the final results. The examples of common uses are email spam detection, credit risk assessment, and image classification.
Unsupervised Learning: The unsupervised learning is designed to operate with unstructured data. It works by revealing hidden patterns or relationships. It is also extensively applied in customer segmentation, market basket analysis and anomaly detection. Moreover, it enables businesses gain insights without predefined categories.
Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning works by training the models by trial and error using a reward-based system. The algorithm learns optimal actions by maximising rewards over time, which makes it ideal for applications such as robotics, autonomous vehicles, gaming, and real‑time decision‑making systems.
Deep learning (DL) is an advanced branch of machine learning which resembles the way the human brain processes information. It relies on the artificial neural networks (ANNs) developed using multiple hidden layers. It is a structure that enables systems to learn complex attributes automatically on large quantities of unstructured materials, including images, videos, speech and text. Unlike traditional ML, deep learning reduces the need for manual feature engineering by learning representations directly from raw data.
Deep learning stands out well on activities that are high in abstraction and precision. It drives technologies such as speech recognition, image classification, face recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems, in which natural patterns are critical to comprehend.
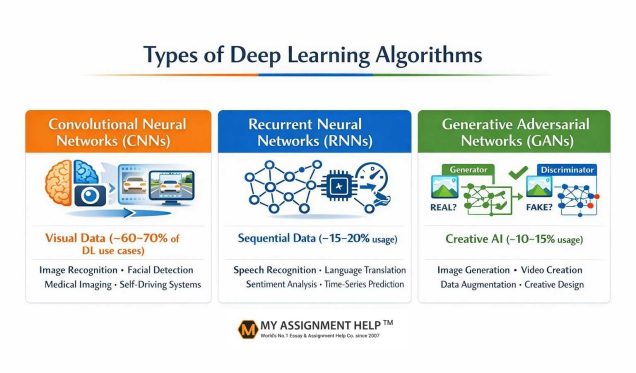
Convolutional Neural Networks: CNNs process visual data. They are also good at identifying spatial patterns and are widely used in computer vision, facial recognition, object identification, medical imaging, and autonomous car driving.
Recurrent Neural Networks: RNNs are trained on sequential and time-dependent data. They are usually used for time series prediction, speech recognition, language translation and sentiment analysis by retaining information from previous inputs.
Generative Adversarial Networks: GANs are made up of two neural networks, a generator and a discriminator, which work together to produce new, realistic data. They are commonly used in generative AI, such as image creation, video creation, data augmentation and creative design.
Deep learning and machine learning may seem similar, but they play different roles in academics. Online AI courses help students understand both, but the complexity often becomes overwhelming, especially for beginners. In such cases, turning to professional and reliable online class help not only clears doubts but also helps students complete coursework on time with confidence.
Refer to the table below to know the difference between machine learning and deep learning.
| Aspect | Machine Learning (ML) | Deep Learning (DL) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Concept | Uses algorithms that learn patterns from data and improve over time. | A specialised form of ML that relies on deep, multi-layer neural networks. |
| Data Needs | Performs well with limited or moderately sized datasets. | Needs large volumes of data to deliver accurate results. |
| Feature Handling | Requires human experts to identify and define key features. | Automatically extracts and learns features from raw data. |
| Training Speed | Trains quickly and uses fewer system resources. | Takes longer to train and demands high computational power. |
After the deep learning vs machine learning comparison, now it’s time to explore some related examples concerned with both technologies.
Machine learning is used to classify emails as spam or not spam based on predefined features.
The machine learning validates each incoming email and establishes a classification category as spam or not spam based on predefined features.
A machine learning model predicts house prices using historical data.
Machine learning helps identify suspicious purchases.
Deep learning is used to automatically recognise a person in a picture.
Deep learning converts human speech into text.
Deep learning enables cars to drive autonomously.
Professions in Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) are gaining popularity rapidly as companies in all fields are implementing AI solutions. Skilled professionals in these fields are in high demand and often rewarded with competitive salaries and strong career growth opportunities. This is the reason why Gen Z Learning Habits are more inclined towards learning technological skills rather than hard skills.
| Role | Key Responsibilities | Average Salary (USA) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Scientist | Develops and applies machine learning models to analyze data and solve complex business problems. | $122,738 per year |
| Machine Learning Engineer | Designs, builds, and deploys scalable machine learning systems for real-world applications. | $128,769 per year |
| Computer Vision Engineer | Specializes in processing and interpreting images and videos using advanced deep learning techniques. | $130,000 per year |
One of the advantages of deep learning is its ability to handle unstructured data such as images, audio, video and text without the manual feature engineering. The larger the data sets, the more accurate and better the deep learning model will be; they are ideal when it comes to large-scale, modern-day use.
That is the reason why they drive technologies like speech recognition, facial recognition, autonomous vehicles, and advanced recommendation systems.
While machine learning remains useful for simpler and cost-effective solutions, deep learning is the better choice for building intelligent, future-ready systems that demand precision and adaptability. If you are a student pursuing your academic degree in AI courses and need help with your assignments, you can always refer to our assignment help service to get expert help with your subjective queries and make your learning fun and interactive.
With the deeper penetration of the digital age, machine learning and deep learning will become increasingly popular. These technologies are making changes in the way we live, work, and find solutions to real-life challenges, and are transforming the nature of smart robots and individualised health care.
It is high time to enter this rapidly developing sphere, if you are willing to participate. Today, there are several online programs related to ML and DL that can help you have future-ready AI skills and practical knowledge. With the right training, you will be able to lead in the sphere of innovation in 2026 and beyond.
Get expert help from qualified engineering tutors. We’ve got you covered with 24/7 support!
Engineering Class HelpIn today’s technological environment, it’s crucial to understand machine learning and deep learning. Machine learning is most effective when it has structured information, smaller data, and definite rules. It is quick, economical, and suitable for an easy task.
Deep learning, on the contrary, addresses data-intensive, complicated issues. It can learn directly from raw data, hence it can learn from images, speech, video, and text. Speech recognition and Self-driving cars are built on deep learning.
In making the decision based on preference between the two, the correct one will depend on which issue we are dealing with. Machine learning is able to meet simple needs, whereas deep learning is able to drive the sophisticated, advanced and scalable AI applications in contemporary industries today.
The primary distinction lies in the way they extract the knowledge from data. Machine learning needs to be guided by humans in selecting features, whereas deep learning learns automatically by using neural networks.
Yes. Machine learning models run on regular computers, whereas deep learning consumes much more computing power, sometimes consisting of GPUs.
Absolutely. Machine learning is the place where most beginners begin, as it can be learned more easily and offers a background upon which deep learning can be taught.
Machine learning is best suited to smaller datasets, and deep learning to larger amounts of data and more complex problems.