Table of Contents
A research methodology is the overall plan that guides how the study is carried out. It explains why the specific designs are chosen. It understands how the designs are used in research. It shows how the designs connect with the research aim. It ensures the study is organised, accurate and suitable to achieve goals. Because methodology defines the structure and credibility of academic work, many students rely on structured research writing support to ensure their approach aligns with university expectations.
Methodology is the strategy.
A strong methodology is like a recipe for your research. Without it, even your interesting findings have no value. In US universities, methodology convinces your reader fully. It helps to trust the results of research. It helps them to understand that your research is not based on guesswork. Rather, it has a clear and logical process to get outcomes.
Across the United States, from Ivy League institutions to larger institutions, professors give a strong importance on methodology. This is because it helps students to develop strong research skills . A clear, well-written methodology shows how the learner knows how the knowledge is created. It explains the overall planning of research. It shows how and why the research approach is chosen. It explains how the study aligns with research objectives. It focuses on how approach fits with the research question. With reading methodology, whether the research is carefully deigned or not. This becomes even more critical in large academic projects such as dissertations, where the methodology section carries significant weight in grading.
A strong methodology leads to creating more meaningful findings. Good planning helps to improve credibility. It gives the overall justifications of the research design. It aligns with the objectives of the research. In many cases, a strong methodology can be helpful to get valid findings. That helps to improve the quality of research.
To write a perfect methodology, you can follow these 5 steps:
Methods are the tools
It consists of specific techniques to carry out the methodological strategy. This explains what the researcher actually wants to collect and analyse data. This helps to fulfill exact needs of research. There are several common methods like
This consistes of set of techniques that interpret the data. These includes statistical testing or thematic coding. These gives importance on implementation to get a valid results.
In short, it can be stated that methodology demands an overall plan of the study. But a method is the set of actions that carry out the plan. For example, adopting a methodology focuses on the strategic choices. It helps researchers to understand the experiences more deeply. On the other side, a semi-structured interview is the method that focuses on practical actions and is used to collect data. It helps to implement the strategy. Methodology and methods both ensure that the research is organized, clear and trustworthy.
Comparisons between strategy and tools
| Aspect | Methodology (Strategy) | Method (Tools) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It identifies the overall research plan and rationale. | Focuses on specific techniques of data collection and analysis. |
| Focus | Explains why and how the research is conducted. | Explains what is conducted within the research. |
| Level | Based on concepts and theories. | More practical in nature. |
| Academic Role | Justifies the design of the research. | Applies the research design in practice. |
| Examples | Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods. | Surveys, interviews, observations, experiments. |
Positivism is based on the knowledge that is valid only if it is facts and reasoning. It focuses on measurable data of research. It explores people’s experiences. It is based on scientific facts. Most students face the challenge to collect those facts. This approach is centralized with generalisation. It aligns with research questions. This way, it highlights research findings strongly.
Interpretivism refers to the understanding of social phenomena through subjective experiences. It explores different points of view of human beings. That helps to analyse behaviour. This approach focuses on how individuals gain experiences from their surroundings. For this reason, intervies is the best way to collect data from individuals. This way, depth data helps to get better research outcomes. The detailed analyses of data help to answer research questions.
Deductive vs. Inductive Reasoning: A brief explanation of how you approach your hypothesis.
An inductive research approach moves from specific to broad theory. It starts with observation, using specific data and ends with creating a new theory. It is used in exploratory research. On the other side, the deductive approach tests existing theories. It begins with general principles and leads to specific outcomes. Inductive is more flexible than deductive. In simple, inductive, create a new theory and deductive tests that theory.
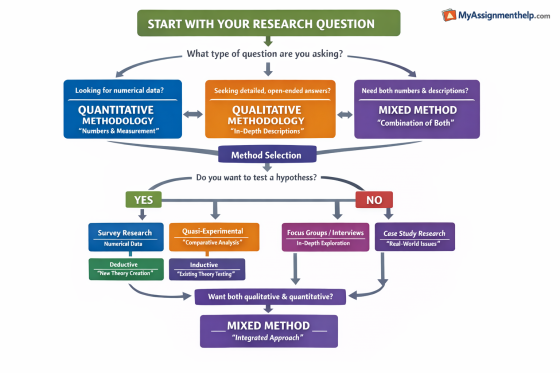
The first step of writing a methodology is to focus on the methodological approach. It helps to explain how the research is conducted. The choice of methodology is always based on research questions and objectives. Students need to understand all methods to choose a suitable one.
Qualitative research: It focuses on understanding the experiences of people. It is used while it needs to prove how and why a particular phenomenon can happen. It relies on several methods. These include interviews, observation and focus groups. The collected data will be analysed with thematic analysis. It offers more depth of context. Rather, measures numerical way. It is used to collect data from a small sample.
Quantitative research: This approach helps to analyse numerical data in research. It analyses the research goals that are tested with a hypothesis. It establishes a common link between the variables detected in the study. By using a survey, the researcher collects research data. In a survey, researchers develop a questionnaire. It is the set of questions that is designed to align with research questions. It is suitable for large samples.
Mixed method: It combines qualitative and quantitative methods. That helps to describe a single study. It analyses the deeper understanding of data in a qualitative way. Also, it analyses numerical data in the same study. It is used to make a stronger approach to research findings. This way, it makes a deep understanding of the research problem.
Data collection is the method of gathering data for research. Choosing right data collection helps to ensure desired outcomes. There are two types of data collection method is used in research.
It collects data directly from the field. For example, surveys and interviews are used in research. These two help to gather the experiences of participants. In both methods, samples play a vital role. For instance, inteview is generally applicable for a small sample. A survey is used in large samples. It offers more authentic data due to direct collection. It requires lots of time to collect data. Before conducting research, you need to make proper plans. The planning helps to design proper questions. That helps to get high-quality data.
Secondary data collection: It uses data which is already exists. Here, the data is collected by other researchers. This type of data is cited properly to prove authenticity. For example: academic literature, archives, and scholarly databases. This type of data understands the theories and ideas. It supports the concrete data. This research takes less time to manage data. It spends a low cost. This data collection method is fast.
In quantitative research, researcher uses statistical method to analyse data. Here, survey is used to collect numerical data. The collected data is analysed with following ways:
Here, specialised software such as SPSS is used to analyse large datasets and conduct statistical tests accurately. It uses large data samples. This data is used to conduct statitical test.
Collected data is analysed with thematic analysis. The researcher gives more descriptive data than numerical one. The technique, such as thematic coding, is used to create themes. Here, interview transcripts are divided into clear themes. Each theme relies on research objectives. Software like NVivo is used here to track codes. It is used identify patterns of variables. It explains the detailed review of participants’ experiences.
This will start with a research approach. This explains the exact type of data and the main purpose of the study. For instance, a qualitative research approach is used to explore in-depth views of people. A quantitative approach offers numerical evidence. It helps to measure trends in data.
Next, to justify the methods. It focuses on the sampling techniques. You need to add the reasons of choose sampling and other techniques. For better justification, you can add the advantages of the chosen method. You need to add the accuracy level and the efficiency of the method. Along with this, it is better to acknowledge alternative methods. In this case, you need to explain the reasons for not choosing other methods. This way, it strengthens the overall justification.
Ethics are a vital part of research methodology. This especially gets importance in US institutions. Our experts follow all the strict rules of the Institutional Review Board (IRB). This ensures conducting research with participants with special care and without any harm.
Key ethical standards:
Informed consent: A researcher must get permission from participants before collecting data. You can clearly explain the research objectives. Participants will decide if they take part or not. They are free to leave anytime if they do not feel comfortable.
Confidentiality means to keep personal information private. Researchers make sure all data is safely stored. They ensure not share information with others. In interviews and surveys, participants often share sensitive information. Keeping information private helps participants to feel safe while sharing data. Along with ethical compliance, students must also ensure their methodology writing is original and properly verified before submission.
Anonymity: It means the researcher does not reveal the names of participants. It helps to protect their identity. Instead, you can use any fake name. It allows people to share information freely.
No harm: A researcher must design the questionnaire in a way that never harms the participants’ sentiments. They avoid creating any discomfort. They freely share all the data. In US universities, these all align with IRB guidelines.
The most common limitation is sample constraints. The size of the sample is restricted due to time and resources. A small sample imposes limitations to get high quality findings.
A case study is used in a qualitative study to explore the experiences of participants. It understands the perceptions of the participant in depth. A case can focus on a single organisation, community or group to gain a detailed understanding of a specific occurrence.
Data collection
The data can be collected from a semi-structured interview method. It uses a flexible approach to gain data from participants. In this method, the researcher can use open-ended questions. The questions are designed in such a way that helps to make a comfortable environment for participants. In these questions, every research question can be addressed. In this type of question, participants describe answers without limitation. The interview transcripts are analysed with developimg of themes. The thematic analysis understands participant responses. This helps to manage in depth interpretaion of meanings and experiences.
A scientific lab report is a quantitative research method. It involves to test hypothesis using numerical data. This helps to test hypotheses of research. This analysis results from using statistical techniques. It allows us to understand the cause and effect of variables.
For example, 1000 person digital survey is one of the best quantitative methods. In this survey, a researcher can collect a large amount of numerical data. This uses structured questions. This mainly uses closed-ended questions. The making of lab reports on 1000 people helps to analyze cause behind phenomena. Here, participants need to choose fixed options from questions. A large sample size is not able to provide any specific answers. It gets very general answers. The survey measures the behaviour and opinions of participants.
Writing a perfect methodology is challenging due to some pitfalls. As a result, students can lose marks. Understanding these errors is important to improve the quality of writing in methodology.
Being too descriptive: In many cases, students simply make a list of steps. They face issues in explaining the best fit in their writing. They fail to explain how the methods align with objectives. A perfect methodology must give proper justification of choices and avoid adding flat descriptions.
Weak reliability: Failing to detect reliability can weaken the study. Professors expect the result to be trustworthy. If the method is not clearly explained, the study cannot be reliable. It is important to discuss the reason behind the choice of method.
Ignore the sample frame: Students just give the sample numbers. But they fail to explain the reason for choosing the population size. Also fail to describe the inclusion criteria or the choice of the selection. The generalised explanations make the explanation weak.
Avoid ethics: In most cases, the appropriate justifications of ethics can be missing in the writing. The breaking of IRB standards affects the quality of research.
Inappropriate research question: The lack of explanation of proper research questions weakens the structure of the writing. Students fail to align methods with research objectives. The poor alignment makes the overall justification very weak. It affects the quality of writing. A student can lose marks in this way.
The reproductive test: The reproductivity test asks whether other researchers can recreate your study or not. The steps of writing must be clear. The details of the study can create a challenge to directly replicate the research. US professors give importance to the value of this. It shows how the research is systematic and credible. It demonstrates whether your research is ethically sound or not!
The PEEL framework
This framework helps to make a structure of methodology paragraphs.
Point: It simply starts with a clear statement regarding the choice of methods.
Evidence: It makes a detailed description of methods. The presentation of data is supported by proper references. It makes the research reliable.
The overall methodology section outlines the research approach. The methodology is designed to align with research objectives. To choose a specific research design, a study ensures to choose the suitable data collection method. The overall analysis is focused on aligning with research questions. The approach ensures the research can generate valid and reliable findings.
The justification in writing highlights why the approach is most appropriate. The overall methodological approach is focused on different factors. Like research aim, data types, scopes of study and validity of data. It strengthens the authenticity of the research. It makes a logical connection between research questions and method.
To apply a specific data collection method, the ethics of research maintain the participants’ privacy. Addressing ethics offers safeguards to participants. It ensures the creation of a trustworthy relationship with them. A researcher can follow ethics like informed consent, anonymity, and focus on securing data. The ethically sound research supports the objectives of the research. It helps to make valid and meaningful results. As a result, this will develop a better research paper.
A methodology should be 10-15% of the total word count of the research. It depends on the assignment level. Also, focus on the complexity of the study.
In US academia, both styles are widely accepted. You can observe that there are many instructors who follow the active voice (That is, ‘I’ conducted). Also, many prefer to use passive voice (eg, data are collected). To understand this, you can follow the specific guidelines of the course. It will tell you which voice is perfect for the writing.
Data triangulation is the use of multiple data sources. It highlights the methods to manage valid research findings. The multiple sources are used to validate the single result. It uses different kinds of data to examine a single research question. It is commonly used on mixed and qualitative data colection method. It ensures all research findings are well-supported. It is not based on a single source.