Table of Contents
People often think the greenhouse effect is only a bad thing. We usually hear about it when we talk about climate change. However, have you ever thought about the advantages of the greenhouse effect? While too many gases can cause global warming, these same gases make Earth a place where we can live. Without them, our planet would be a frozen wasteland.
The greenhouse effect is vital for our ecosystems and human life. It acts like a warm blanket for the planet. It keeps our temperatures steady so that plants can grow and water stays liquid. By learning about these benefits, you can better understand how our environment works. This balance is key for any academic study or research on our climate.
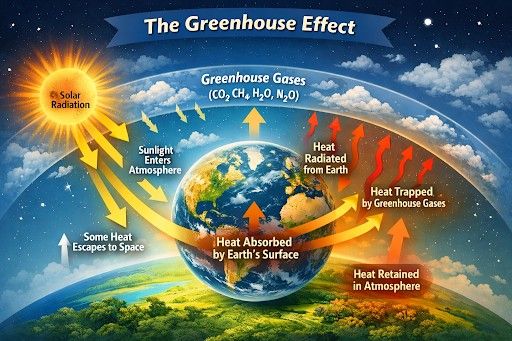
The greenhouse effect is a natural process. Certain gases in the air trap heat around the Earth. These gases are mainly carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and nitrous oxide. They act like a blanket for the planet. This keeps our world at a temperature that supports life.
Without this effect, Earth would be a frozen wasteland. Average temperatures would drop well below freezing. One of the key advantages of the greenhouse effect is that it keeps our planet warm enough for us to live.
Example: Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth’s average temperature would drop to around –18°C (0°F) instead of the current 15°C (59°F). Oceans would freeze over, plants would die, and human survival would be impossible. Even the tropics would experience frost year-round.
Understanding this idea is important for students and researchers. It is also vital for those who love the environment. If you want to find deep examples or turn in an essay, you can look at an essay help. This service gives you help with how to build your papers. It covers hard topics like the greenhouse effect. It also makes it much easier for you to share scientific facts in a clear and simple way.
Greenhouse gases play a pivotal role in maintaining Earth’s energy balance. They absorb infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s surface and re-emit it in all directions, keeping the planet warm enough for plants, animals, and humans to thrive.
For instance, the presence of greenhouse gases allows crops to grow in temperate climates, ensuring food security. Without this natural heating mechanism, many regions would face harsh winters, making agriculture impossible. Students who are studying chemical interactions and the role of gases may benefit from Chemistry Assignment Help to deepen their understanding of how these gases interact in the atmosphere.
Example:
After sunset, greenhouse gases prevent rapid heat loss, allowing temperatures to remain livable. Without them, daytime heat would escape into space, and night temperatures would plummet—just as they do on the Moon, where temperatures can swing from 127°C (260°F) during the day to –173°C (–280°F) at night.
The greenhouse effect helps nature by keeping the climate steady. Plants are the base of the food chain. They need the right heat to grow and make food. This helps the animals that eat plants and the hunters that eat those animals.
Think about the Arctic tundra. This is a delicate place. The greenhouse effect keeps these areas from getting too cold. This allows foxes, reindeer, and birds to stay alive. If you are working on a school project, you can use Biology Assignment Help. They can help you study how this process keeps life going in different places.
Example:
The Amazon Rainforest creates 20% of the world’s oxygen. It grows well because the Earth stays at a middle temperature. Even small changes in heat could stop the rain. This would hurt all the plants and animals there. In the same way, foxes and caribou in the North need stable winters to survive. Greenhouse gases help keep those conditions safe for them.
Humans directly benefit from the greenhouse effect in multiple ways. By keeping the Earth warm, it ensures that water remains liquid in most regions, supporting agriculture, drinking water supplies, and sanitation. Moreover, moderate temperatures help maintain human health and comfort.

Example:
If the greenhouse effect were not functioning properly, major cities like New York, Tokyo, or London would face extreme cold, freezing water supplies and halting agriculture. Even equatorial nations would experience dramatic temperature swings between day and night, making life difficult.
Students researching the role of greenhouse gases in human survival can consult Environmental Science Research Topics for case studies and academic resources.
The greenhouse effect contributes to Earth’s energy retention, ensuring a balanced climate. Without this natural mechanism, the planet would lose heat too rapidly at night, causing extreme temperature fluctuations.
This balance supports not only agriculture but also energy systems. Heating and cooling needs would skyrocket in a world without greenhouse gases, increasing human dependency on natural resources. For students studying physics or energy systems, Law of Conservation of Energy provides insights into how energy flows through ecosystems and the atmosphere.
Example:
In Scandinavia, where winters are long, the greenhouse effect helps moderate cold spells, reducing energy consumption for heating. Meanwhile, the absence of this effect on the Moon results in wildly fluctuating temperatures unsuitable for any life form.

Learning about the good sides of the greenhouse effect has many uses in our world. It is not just a topic for a classroom. It helps us make big decisions about our future. Scientists and world leaders use this knowledge every day. They use it to plan for clean energy that does not hurt the air. By knowing how gases trap heat, they can choose the best ways to power our homes.
For students preparing research projects or environmental studies, Environmental Research Proposal Help offers guidance on crafting detailed proposals that explore the benefits and applications of greenhouse gases in real-world scenarios.
Example:
In places like Scandinavia, winters are very long. The greenhouse effect helps by making the cold less harsh. This means people use less energy to heat their homes. On the other hand, the Moon has no greenhouse effect. This causes its temperature to swing from very hot to very cold. Because of this, no life can survive there.
Several climate studies have highlighted the necessity of greenhouse gases for maintaining life-supporting temperatures. For instance, controlled greenhouse experiments show that increasing carbon dioxide levels within limits can enhance plant growth by improving photosynthesis efficiency.
Example:
Scientists did a test in greenhouses in California. They gave the plants a bit more $CO_2$. They found that the plants grew 25% faster and made more fruit. NASA also uses a special climate model. NASA’s GISS Climate Model shows how the right amount of greenhouse gas keeps Earth’s heat steady. This helps the whole world grow more food for people to eat.
Here are some key advantages:

[ALT Text: Greenhouse farming demonstrating benefits of controlled greenhouse effect]
The agricultural sector is heavily dependent on the stable climate created by the greenhouse effect. Warm winters and moderate temperatures prevent crop failure and promote biodiversity.
For example, wheat and rice production are highly sensitive to temperature changes. The greenhouse effect ensures these crops have a suitable growing season, supporting global food supply chains. Students interested in ecology and agriculture can refer to Ecology Research Topics for research ideas.
Example:
In India’s Punjab region, consistent temperatures maintained by greenhouse gases ensure two major harvests a year. Similarly, in California’s Central Valley, mild winters maintained by the greenhouse effect support year-round fruit and vegetable production.

Urban environments benefit indirectly from the greenhouse effect. Stable temperatures reduce energy costs, lessen heating and cooling demands, and support green urban spaces that rely on consistent climatic conditions.
By understanding these effects, city planners and environmental engineers can develop sustainable cities. Students preparing urban environment assignments may consult Environmental Science Assignment Help for practical examples.
Example:
Singapore’s green architecture, which includes rooftop gardens and eco-friendly buildings, takes advantage of the steady tropical climate maintained by greenhouse gases. This reduces the city’s carbon footprint while enhancing energy efficiency.
Teachers often assign essays exploring the balance of greenhouse gases and their effects. Students may be asked to analyze how these gases help sustain life while considering their role in climate change.
A useful resource for essay topics is Research Essay Topics, which provides structured ideas for academic research and writing exercises.
Example:
A student researching this topic might write a comparative essay showing how controlled greenhouse systems in the Netherlands mimic Earth’s natural process. These case studies reveal how humans replicate the greenhouse effect to improve food production sustainably.
The greenhouse effect indirectly supports the adoption of renewable energy. Stable global temperatures reduce the unpredictability of weather-dependent energy sources like solar and wind power.
Students writing about renewable energy can link greenhouse benefits to sustainability projects, helping illustrate real-world applications of scientific concepts.
Example:
Countries such as Germany and Denmark rely on consistent temperature and wind patterns, made possible by the greenhouse effect, to optimize renewable energy production. Stable atmospheric conditions also enhance the efficiency of solar farms across southern Europe.
By preventing extreme temperatures, the greenhouse effect ensures that a variety of species can coexist in multiple climates. Coral reefs, rainforests, and grasslands all rely on specific temperature ranges to sustain biodiversity.
Example:
Coral reefs like Australia’s Great Barrier Reef require stable ocean temperatures to survive. Even a slight increase of 2°C can cause coral bleaching. Similarly, African savannas depend on moderate climates sustained by greenhouse gases to support elephants, lions, and antelopes.
1. Know the Two Types You must show the difference between the natural and the enhanced greenhouse effect. The natural one is good and helps us live. The enhanced one is caused by humans and can be harmful.
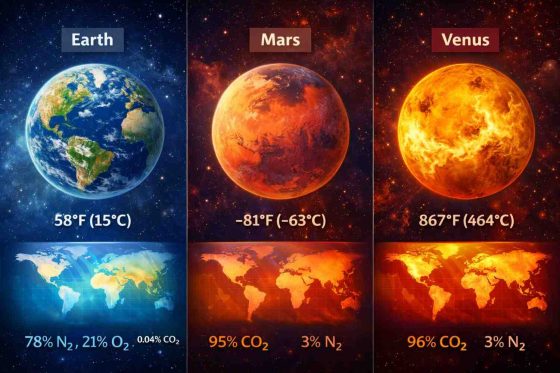
2. Use Comparisons Use analogies to help people see the facts. Compare Earth to Mars or Venus. This helps readers picture why the right amount of gas is so important.
3. Show Both Sides When you write an essay, talk about the good and the bad sides. This makes your work look fair and well-planned. It shows you have studied the topic deeply.
4. Use Real Examples Mention real stories to make your point stronger. You could talk about greenhouse farming in the Netherlands. You could also mention official climate models.
5. Add Pictures Use charts or simple maps. Visuals help people understand hard ideas much faster than just words.
6. Focus on the Future End your paper with ways to help the planet. Talk about planting trees, using clean energy, and cutting down on waste.
7. Keep It Simple Check your work for mistakes. Use a plagiarism checker to be safe. Avoid using big words that might confuse your readers.
Writing a detailed essay on the greenhouse effect or climate science can get tricky—don’t let grammar mistakes weaken your arguments. Catch every error before submission using our advanced grammar checker and make your environmental essay shine.
Check Grammar NowMany people do not fully understand the greenhouse effect. Too many gases can be a risk, but we need them to live on Earth. They help by keeping temperatures steady and helping crops grow. These gases also keep our nature in balance.
Students and researchers can find help for their work. You can also look up Climate Change Research Topics for your papers.
When we see the good side of the greenhouse effect, we see how it keeps us alive. We must still work to manage the bad parts, but we can also value how it protects our world.
Understanding the advantages of the greenhouse effect is essential, but acknowledging its potential risks helps create balanced insights. Check out our article on Disadvantages of Greenhouse Effect for more information.
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial emissions, increase greenhouse gas concentrations. This enhances the natural greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change.
Yes, changes in greenhouse gas levels can influence regional temperatures, precipitation patterns, and the frequency of extreme weather events, affecting agriculture and urban planning.
No. While CO₂ is most abundant, gases like methane and nitrous oxide are much more effective at trapping heat per molecule, making them critical in climate studies.
Yes. The natural effect is good, but too many gases can be a problem. This leads to global warming and extreme weather.
Stable temperatures maintained by greenhouse gases support ocean circulation patterns, which in turn regulate marine ecosystems, nutrient distribution, and fish migration patterns.
Yes. Greenhouses and controlled-environment agriculture artificially replicate the greenhouse effect to optimize plant growth, using CO₂ enrichment, temperature control, and humidity regulation.
Experts use it to study the climate. It also helps with green farming and planning for clean energy.
Satellites measure atmospheric gas concentrations, heat radiation, and surface temperatures, helping scientists monitor greenhouse gas impacts and model climate scenarios accurately.