Table of Contents
Research assists people in gaining new information, understanding, and generating new concepts or ideas.
Any research project should be carried out with utmost care, diligence, serious research, and investigation. This helps find the accurate interpretation of facts during the final discovery.
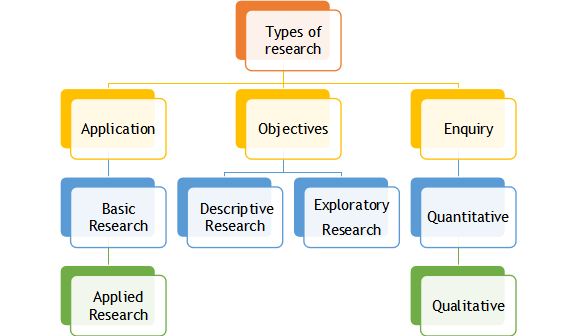
These are a few different types of research, but here we will learn some facts about basic vs. applied research and its examples.
Basic and applied research is differentiated depending on their purpose and utility. These approaches have several meeting and departure points; researchers must comprehend them thoroughly.
ALL ABOUT BASIC RESEARCH
Basic research writing is an entirely theoretical strategy intended to advance or broaden the body of knowledge in a particular field of study. It is also known as pure research or fundamental research. It is intended to learn more in-depth information about a research topic or phenomenon and is depending on a systematic investigation.
In order to fill voids in science’s societal utility, the idea of basic research emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Exploratory, descriptive, and explanatory types of basic research are all possible. This research strategy’s main objective is to gather data in order to comprehend a problem and then use that data to suggest solutions.
The basic research method can be done in the following ways:
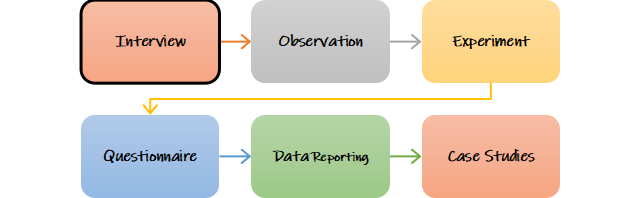
An interview is a technique of data collection that includes interacting with an individual one-on-one to gather relevant information about a phenomenon. Depending on the research method and objectives, interviews can be structured, unstructured, or semi-structured.
Observation is the process of closely observing a phenomenon for a predetermined amount of time in order to learn useful information about its characteristics. The researcher may need to spend a specific amount of time watching the research subject interact with its natural environment when conducting basic research.
A type of quantitative data collection method is called an experiment. It is used to test theories and validate or disprove hypotheses. In this data collection technique, the researcher manipulates dependent and independent variables to achieve measurable research outcomes.
It is a data collection tool composed of a sequence of questions to which research subjects respond. This tool is a cost-effective data collection method because it lets you simultaneously collect large data samples from group members.
In data reporting, a researcher gathers relevant data and computes them for research analysis to arrive at a particular conclusion. The foundation of this method depends on all the data that has been gathered.
In order to gather factual data about the characteristics and behaviors of the research subject, a case study is a type of data collection technique that involves a thorough examination of a specific subject matter. Although primarily qualitative, this method of data collection can also be quantitative or numerical.
New educational theories which explain the various behaviours of teachers and students in the learning environment are developed in education using basic research.
Examples of fundamental studies in education consist of:
Medical professionals can learn more about various health issues from basic research, such as the causes and signs of illnesses and infections, which can help search for a treatment.
Examples of basic health research include:
Basic psychological research is used to understand various psychological conditions in order to better understand these behaviours.
Examples of applied psychology research include:
Mastering the intricacies of the methodologies associated with basic and applied research can be overwhelming and not to forget time-consuming. Go through our below-given basic vs. applied research samples to comprehend both theoretical frameworks and research in action, gaining crucial insights in your research pursuits.
ALL ABOUT APPLIED RESEARCH
The process of conducting applied research entails evaluating how successfully we applied the knowledge we gained from basic science to a given problem. Although the techniques used here are similar to those in basic research, the objectives of the study are different.
Applied research can systematically comprehend and measure how successfully an engineered system addresses the issue for which it was created. System design, implementation, and testing are all included in applied research.
Although applied research frequently employs experimental rigor, its main goal is to comprehend how a system or application works, such as the true/false positive rate of an intrusion detection algorithm.
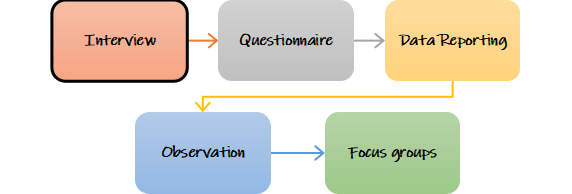
In applied research, both quantitative and qualitative data collection techniques are used to collect experimental proof that is then investigated to extract at valid research outcomes. In applied research, these data collection techniques are used:
The interview is a research technique where the researcher asks questions to the participants to collect information. Interviews in applied research can include 5 – 10 participants in which a one-on-one session is conducted and the answers are noted down or recorded in a video.
A questionnaire is also used to collect data for applied research. It aids in collecting pertinent information that leads to more informed choices. However, it is susceptible to bias because the person or group collecting the data can easily exaggerate it.
It is the procedure of gathering pertinent data about a research topic that can be used for more research. Non-profit reports, newspapers, online articles, and medical records can all be used for this. It aids in collecting pertinent information that leads to more informed choices. However, it is prone to bias because the person or group collecting the data can easily exaggerate it.
The observation help in the collection of empirical data; it serves as the basis for the formulation of a hypothesis. Several observation methods include participant as an observer, participant as a participant, complete observer, and complete participant.
A focus group is a research technique that assembles a small group of individuals to respond to questions in a controlled environment. The questions are intended to shed light on an interesting topic, and the group is selected based on predetermined demographic characteristics.
By offering workable solutions to pedagogical issues, applied research in education enhances teaching and learning techniques.
Following are some instances of research in education:
Applied research can help health and medical professionals to create evidence-based solutions to urgent medical problems.
Instances of applied health research comprise:
It is extensively used to improve solutions for organizational behavior, policies, and hiring procedures.
Examples of psychology research are:
The following are examples of applied research topics. You can see that each of these topics covers a real-world problem.
The following list of 15 differences between basic and applied research:
| S. No. | Terms | Basic | Applied |
| 1. | Definition | · Basic research aims to increase the perimeters of knowledge by developing new theories by revising the old ones. · Secondly, by gathering and examining empirical data, applied research focuses primarily on developing solutions to issues to produce reliable research findings. | · While basic research is an approach to research that seeks to advance knowledge in a field of study, applied research is a methodology that develops practical solutions for particular problems. · In contrast to basic research, which is knowledge-specific, applied research is solution-driven. |
| 2. | Characteristics | · The focus of basic research is theory. · Basic research focuses on specific problems and is primarily concerned with knowledge expansion rather than the practical application of research findings. | · Applied research primarily focuses on offering a workable solution to a predetermined problem. · While basic research is explanatory and analytical, applied research is goal-oriented and synthetic. |
| 3. | Uses | · Basic research is beneficial for learning a concept, any type of phenomenon, or field of study. · This research investigates the functions and characteristics of recently discovered occurrences to develop understanding of these concepts. | · Applied research can help you find practical solutions to problems. · Applied research contributes to developing new technologies and solutions to specific problems. |
| 4. | Alarmed With | · The creation of new information and principles that are extensions of existing theories. | · Applied Research is meant to expand new tools and technology for industrial applications. |
| 5. | Environment | · Basic research is carried out in confined spaces such as laboratories. | · Applied research is carried out in an open world with many unexpected variables. |
| 6. | Advantage | · Basic research has a subjective methodology. · Basic research is usually objective because it derives conclusions by subjecting empirical data to accepted scientific practices, which makes it a more reliable research method. | · Without offering answers to on-going issues, applied research assists groups and individuals in finding solutions to particular issues. · However, this does not change the fact that results from applied research can be used to suggest solutions to issues. |
| 7. | Scope of research | · Basic research is more universal than conceptual research because it deals with various concepts across numerous subject areas. · Fundamental research examines knowledge in various dimensions to learn new things and advance the body of knowledge. | · Compared to basic research, applied research is more constrained in its application. · This is because, unlike basic research, which can be applied to various concepts, applied research primarily focuses on a single subject, with its research findings using principally to this subject. |
| 8. | Theory formulation | · Basic research aims to develop theories that clarify research results, to improve a body of knowledge. · Principles and theories are the main topics of basic research. · Basic research aims to develop theories and generalizations that completely explain a concept, subject, or phenomenon. | · Findings from applied research are intended to address real-world issues. · The goal of applied research is resolution. · Applied or conceptually oriented research examines empirical data to connect its conclusions to a particular issue. |
| 9. | Research outcomes | · Basic research can develop new theories, improve existing theories and advances the knowledge of the people. · Basic research results do not help to provide practical solutions to a real-world issue. | · The researcher reaches valid discoveries that support or refute the research theories after conducting applied research and challenging the experimental proof. · These conclusions frequently provide specific research questions with answers, which is the purpose of the applied research. |
| 10. | Research approach | · The basic research is more theoretical. · In this way, basic research advances previously developed theories to add to the body of existing knowledge. | · Applied research is more descriptive and practical. · It is concerned about the utility of research outcomes, i.e. how they can be used to solve the problems and find solutions. |
| 11. | Nature of Research | · Basic research has a theoretical design based on previously established ideas and theorems. · Basic research is more hypothetical because it generates conjectures and looks into data that might not be immediately applicable. · Additionally, it is focused on advancing current academic concepts. | · Nature is fully practical and implied to develop strategies for applications in industrial use cases in applied research. · Since applied research aims to reduce and solve problems in various fields. · It is typically concerned with end-utilization, as it is more practical and graphic. |
| 12. | Efficacy | · Basic research serves a universal purpose and has a broad scope of application. | · Applied research’s main benefit is constrained and has a practical issue. |
| 13. | Purpose | · Fundamental research highlights knowledge extension over problem-solving. · Basic research typically done to satisfy the urge of a person to learn more. | · Applied research aims to identify a solution to a practical problem. · Here researchers often try to help the companies or a person to find a solution to their challenges. |
| 14. | Achievement | · Basic research contributes to society’s knowledge of a particular subject. · It explains why the occurrence of certain events is more common in disciplines like sociology, biology, astronomy, philosophy, and theology. | · Applied research typically yields greater financial rewards. · Applied research can aid in developing new products and may result in financial gain. · Governments and businesses frequently prefer applied research to basic research. |
| 15. | Research context | · Basic research is done in a controlled environment, such as a laboratory or restricted real-life setting. · The sterile research environment in basic research enables researchers to observe the research subjects’ behaviours and attributes. | · In applied research, the independent and dependent variables are allowed to interact spontaneously in an open setting with other variables. · This enables the researcher to comprehensively understand the research problem and arrive at valid and practical solutions. |
| Similarities | Basic | Applied |
| Data Collection Techniques | Use qualitative and quantitative data collection techniques including questionnaires, surveys, case studies, and interviews | Use qualitative and quantitative data collection techniques including questionnaires, surveys, interviews and focus groups. |
| Intersection | Basic research is done to find the problems or challenges. | These problems are then assessed to via applied research to find the solution |
| Deductive and Inductive Argumentation | Uses inductive and deductive reasoning. In deductive reasoning, the researcher transitions from idea to observation and in inductive reasoning, the observation is transitioned to idea. | In applied research also, a researcher uses the same inductive and deductive reasoning for his observations. |
Summing up,
Researchers must understand the applied and basic research methods by looking at the instances of basic vs. applied research in psychology. As previously stated, the primary difference between applied and basic research is done to accomplish the intention of the research.
Aside from the purpose of the research, both type types of research differ in terms of outcomes, nature, and context. Nonetheless, both of the research methods use similar data collection processes, such as inspection and interviews, to find the appropriate results.
Yes, applied research is mainly subjective as it is used to understand human behaviour and the reasons behind it. In this type of research, researchers drown themselves in the subject matter at an emotional level.
Researcher always chooses applied research as it is a very important tool for them. This type of process helps a researcher investigate the problems in a certain environment and find a solution.
The primary intent of applied research is to design or develop new goods or products and improve services to satisfy specific markets. It determines the market’s requirements. Finding new ways to enhance products that already satisfy the needs of an organization is its main objective.
Efforts to find practical solutions to the problems, such as infrastructure or conversation, are called applied research.
Basic research experiments are performed to gain further scientific knowledge without any benefit. This research is done to know the function of newly discovered molecules, cells or any phenomena.
Information that is found through basic research will help to develop theories. On the other hand, applied research can collect data by solving specific problems. As the problem-solving method is always effective, applied research is more important than basic research.
The difference in the goals of both types of research is – basic research aims towards the discovery of new knowledge or improvement of the existing knowledge. On the other hand, applied research aims to verify social or conventional problems and find a solution.
Yes, while researching, one first needs to find the problem. Then perform basic research on one hand to develop or improve theories and applied research on the other hand to find a practical solution to improve the condition.
In the medical field, basic research is done to understand how the cells work to know the fundamental problem. Then applied science is applied to the basic scientific knowledge for solving the problem.
Yes, applied science uses the information collected from basic research to solve practical problems.
Basic science is the support system of scientific theory. All the researchers use their basic knowledge to perform any examination or processes needed for the development.
Read Some Trending Blogs-