Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered why we instinctively rub our hands together the moment we feel a bit cold? That action heats up your skin and provides immediate comfort. But if you look at the law of energy behind it, you’ll discover a fundamental truth about our universe.
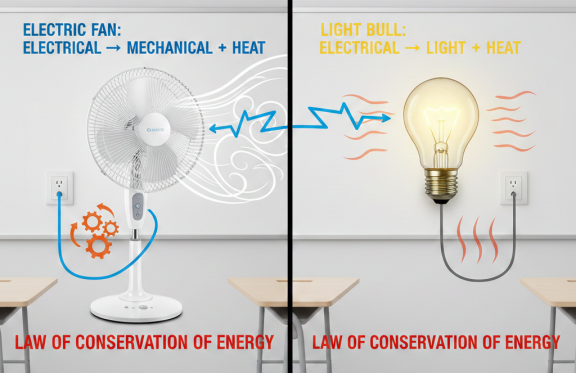
When we rub our hands, we use mechanical energy to create friction, which generates heat. This heat doesn’t appear out of thin air; you are converting mechanical energy into thermal energy. This is a perfect example of the law of conservation of energy.
To define law of conservation of energy, we must look at the stability of the universe. In physics, the definition of law of conservation of energy states that energy in an isolated system remains constant.
The most common way to state the law of conservation of energy is:
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another.
When someone asks, “What is the law of conservation of energy?” they are referring to the principle of conservation of energy. Whether you call it the law of energy conservation or the law of conversation of energy (a common typo!), the core meaning remains the same. If you find these conceptual definitions tricky to apply to your coursework, seeking professional science assignment help can help clarify the relationship between energy, matter, and the universe.
The law of conservation of energy characteristics include:
Pro Tip: In academic writing, use the law of conservation of energy in a sentence like this: “The roller coaster’s descent is a classic demonstration of the law of conservation of energy, as gravitational potential energy transforms into kinetic energy.”

To understand the conservation of energy equation physics students use, we must break energy down into its two primary components: Kinetic Energy (K) and Potential Energy (U).
The standard energy conservation formula for a closed system is:
K_1 + U_1 = K_2 + U_2
Where:
If you are struggling to balance these equations or apply them to specific dynamics problems, getting specialized physics assignment help can ensure your calculations are accurate and follow the correct laws of motion.
To solve a law of conservation of energy science problem, you often need to know how to calculate potential energy. The formula for gravitational potential energy is:
U = mgh
The conservation of kinetic energy formula (often used in elastic collision problems) is derived from:
K = ½ mv^2
Where K=kinetic energy
M=Mass
V=Velocity
In a perfectly elastic collision, the conservation of kinetic energy equation ensures that the sum of kinetic energies of the objects before the crash equals the sum after the crash.
Understanding how is energy conserved is easier when you see it in action. Here are detailed examples of the law of conservation of energy across different fields.
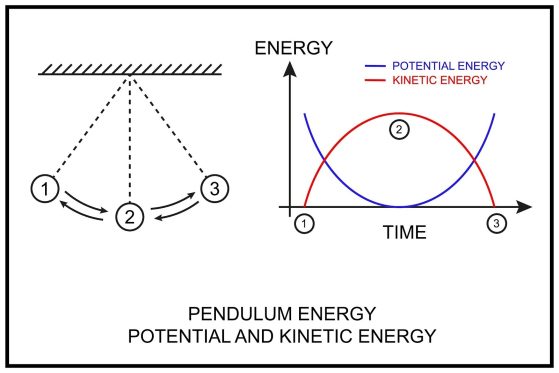
If you look at a law of conservation of energy picture of a pendulum, you see energy in constant flux. At the highest point, the pendulum has maximum potential energy. As it swings down, that energy becomes kinetic. This is a primary example of conservation of energy.
From pendulums to friction losses, we help you explain the “why” behind your data with scientific precision.
Green plants provide a biological example of the law of conservation of energy. They take light energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy stored in glucose. This conversion of light to chemical energy is a fundamental concept often explored within biology research topics.
“Educational infographic showing photosynthesis: a plant converting light energy from the sun into chemical energy (glucose), with an inset showing CO2 and H2O intake and Oxygen release.”
When you stop a ball, its kinetic energy doesn’t vanish. It is transferred into your hand as a tiny amount of heat and sound energy. This explains what the law of conservation of energy states regarding “disappearing” energy.
Pro Tip: When looking for a law of conservation of energy icon or conservation of energy clipart for a presentation, look for images of a “Newton’s Cradle.” It is the most recognizable law of conservation of energy visual.
To properly explain the law of conservation of energy, we must define the “system.”
An isolated system is like a “vault.” It is completely cut off from its surroundings. Neither matter (stuff) nor energy (heat/work) can enter or escape. In this perfect scenario, the total energy remains absolutely constant forever.
In a closed system, the “walls” are sealed tight so no matter can get in or out, but energy can still pass through. The container might get hot or cold, but the amount of material inside stays the same.
An open system is the most common type we see in our daily lives. It has no “walls” or barriers. Both matter and energy can move freely across the boundary between the system and its environment.
In a law of conservation of energy lab, students often struggle because they forget about the “environment.” For instance, air resistance is an external force that takes energy out of a system and turns it into heat. If you are currently drafting a report on your findings, professional lab report writing services can help you explain these energy “losses” and environmental factors with scientific precision.
The law of conservation isn’t limited to basic mechanics. It evolves as we move into higher physics and global issues. Because energy conservation affects everything from global warming to renewable technology, it serves as a critical pillar for many environmental science research topics.
The law of energy is actually the foundation of the First Law of Thermodynamics:
ΔU = Q – W ,Where Δ U is the change in internal energy, Q is heat added, and W is work done.
Albert Einstein updated our understanding of the laws of conservation of energy with his famous energy conservation equation:
E = mc^2
Where E=Energy
M=Mass
C= Speed of Light
This reveals that mass itself is a form of energy. In nuclear reactions, a small amount of mass is destroyed to release a massive amount of energy, leading to the broader “Law of Conservation of Mass-Energy.”
It is helpful to compare the law of conservation of energy with its sibling, the Law of Conservation of Mass.
In a chemical conservation of energy experiment, such as burning a candle, the mass of the wax and oxygen equals the mass of the CO2, water vapor, and remaining ash. Simultaneously, the chemical energy in the wax is conserved as it transforms into heat and light.
Pro Tips for Physics Students
If you need to explain these concepts orally for a class project, checking out these ideas for a science speech can help you communicate the laws of thermodynamics effectively, follow these steps:
| Process | Initial Energy | Final Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Rubbing Hands | Mechanical | Thermal (Heat) |
| Battery Usage | Chemical | Electrical |
| Hydroelectric Dam | Potential (Water height) | Electrical |
| Car Braking | Kinetic | Thermal (Friction) |
Physics is fascinating, but the conservation of energy equation physics problems can be incredibly complex. If you are struggling with a law of conservation of energy lab report or need to calculate potential energy for a difficult project, don’t stress!
MyAssignmenthelp.com is the premier destination for students globally. With over 4,500 PhD experts, we provide:
The law of conservation of energy science provides the framework for everything from engineering fuel-efficient cars to understanding how stars burn. Whether you are looking for images of law of conservation of energy for a project or trying to state the law of conservation of energy for an exam, remember that the total energy of the universe is a constant, beautiful balance.
Ans- The law of conservation of energy states that the total amount of energy in an isolated system never changes. While energy can move from one object to another or change its form (like from motion to heat), it cannot be created from nothing or completely destroyed.
Ans- In physics, people often refer to the “three laws of conservation” as the conservation of Mass, Energy, and Momentum. Within the specific context of energy, it is primarily governed by the First Law of Thermodynamics, which acts as the definitive law of energy conservation.
Ans- A perfect example of the law of conservation of energy is a swinging pendulum. At its highest point, it has maximum potential energy. As it swings down, that potential energy converts into kinetic energy (motion). At the bottom of the swing, its kinetic energy is at its peak.
Ans- To define law of conservation of energy for younger students: “Think of energy like a set of building blocks. You can build different things with them, like a tower (potential) or a car (kinetic), but you always have the same number of blocks at the end of the day.”
Ans- The conservation of kinetic energy formula is used primarily in elastic collisions where K_1 = K_2. The formula for kinetic energy itself is K = ½ mv^2. In a system where only kinetic energy is conserved, the sum of the energies of all participating objects remains constant.
Ans- Energy is never truly “lost,” but it can be transferred out of a specific mechanical system. In a law of conservation of energy lab, friction often turns kinetic energy into thermal energy (heat). This heat radiates into the environment, so while the machine might slow down, the energy still exists in the universe as heat.
Ans- To understand how to calculate potential energy, use the formula U = mgh. By knowing the mass (m), gravity (g), and height (h) of an object, you can determine how much energy is stored and ready to be converted into kinetic energy.
Ans- Yes, in classical physics, it is a fundamental truth. However, Einstein’s law of conservation of energy updates this by including mass. In nuclear reactions, mass can be converted into energy (E=mc^2), so we now refer to the “Law of Conservation of Mass-Energy.”
Ans- It states that energy is only conserved if the system is closed or isolated. If a system is “open,” energy can be added (like a battery charging) or taken away (like heat escaping), which changes the total energy of that specific system, though the energy still exists elsewhere.
Ans- A scientifically accurate law of conservation of energy sentence would be: “When a diver jumps off a board, their gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, illustrating that the total energy remains constant throughout the fall.”