Types of Flow Meters for Measuring Different Fluids
Q 1 (a) Specify an instrument, in each case listing its operating features and benefits, which is suitable for measuring the following:
(i) the flow-rate of fruit juice in the range 5-25 m3/hour
(ii) the flow-rate of sea water in the range 150-1000 m3/hour
(iii) the flow-rate of steam in a 50 mm nominal bore pipe
(iv) the flow-rate of oil in the range 8-20 m3/hour
NOTE, that differential pressure devices and variable area flow-meters are not allowed, and that in each case, the instrument is to be installed in a fully automated plant, and a 4-20mA output signal is required.
(b) Describe briefly, the measuring principle used in the flow-meter specified above for the measurement of the flow-rate of fruit juice in the range 5-25 m3/hour, and for this instrument only, list the questions you would ask the end user prior to ordering the instrument.
(c) Specify two instruments suitable to detect the presence of flow during normal process operation, and list the benefits and disadvantages of each type
(d) Specify a device describing briefly its principle of operation, that is typically installed downstream of a bursting disc as an indicator of disc rupture,
(e) A flip switch can be used to detect the presence of flow. What are the benefits and disadvantages of this type of switch? Suggest a better alternative.
Q 2
(a) The filtrate flow from an upstream process must be transferred to a downstream unit operation a substantial distance away. To achieve this the filtrate is passed to a 1000 L buffer tank and pumped to the downstream operation. The filtrate flow-rate is not constant and must be maintained (the flow cannot be stopped) as any back pressure would damage the upstream filter unit.
On completion of the operation the tank is cleaned using a hot water flush via a spray ball with the flush water directed to drain.
Based on the specification that the process plant is fully automated and hygienic, sketch a P&ID of the tank and any associated equipment required to achieve this duty and explain the principle steps and basis of operation.
(b) On/off air driven valves are purchased, with the specification, normally closed or normally open (spring to close or spring to open), and with single or double feedback. Explain the above statement, and the principle of operation
(c) An inductive proximity switch is a device used in valve feedback, describe its construction, operating principle and beneficial features
Q 3
(a) In an automatic process plant four communication signals are used to interface with the main control unit. With the use of an appropriate example in each case, outline the function of each of these four signals.
(b) In continuous process control a ‘PID controller’ is installed which uses a combination of proportional, integral and derivative action. Why are these three modes of control used in conjunction?
(c) Give an example of a process situation where PID control is used and a further example where on/off control would suffice.
Instruments for Detecting the Presence of Flow
(d) In an automatic process plant software and hard-wired interlocks are used. With the use of an appropriate example in each case explain the difference.
Q 4
(a) Thermocouples, RTD’s (resistance temperature devices) and thermistors are used to measure temperatures on process plants, for each device:
(i) sketch the typical response characteristics,
(ii) the range of temperature measurement,
(iii) the advantages and disadvantages,
(iv) the principle of operation.
(b) In certain instances change of state temperature sensors are used, for these:
(i) discuss the advantages and disadvantages,
(ii) and give two examples of their use.
Q 5
(a) Discuss the factors that have to be considered on deciding whether a process plant should be designed to be fully automated, and specify the operating benefits.
(b) Explain why an FDS (Functional Design Specification) is an important document.
(c) In an automatic process plant four kinds of signal are used to interface with the main control unit. With an appropriate example in each case outline the function of each of these four signals.
(d) If you were to purchase a rack type PLC (programmable logical controller), list the items required, and what determines their specification, and with an appropriate sketch show its typical construction.
Q 6
(a) It is imperative to use a Tag number to identify an individual plant item, explain why this is.
(b) You have been appointed the lead engineer on the design of a process plant that is used to manufacture a cosmetic product. Part of that plant is the supply and installation of a pressurized vessel on a concrete mezzanine floor, which allows the mixing of two ingredients which are put into the vessel one after the other in a set ratio by mass from an upstream unit operation. The ingredients are pumped and have the consistency of pastes. The mixing must be performed at a set temperature of 90ï‚°C and maintained at that temperature and for this reason the mixing tank is jacketed with a sealed unit using water which is re-circulated through a plate and frame heat exchanger supplied with steam as the heating medium. After mixing for a set period of time the contents are transferred to an adjacent pressure reaction vessel for further processing. The vessel is finally cleaned using hot water on completion of the transfer of the mixed ingredients.
Propose a design to achieve the requirement specified above. Consider in your design the following criteria:
- The medium must never be in contact with air.
- The water jacket is sealed and must not be subjected to a pressure increase in the temperature control process.
- The method used to transfer the mixed product to the second vessel if pigging or pumping is not possible, as the vessel is in close proximity to the first.
- The mixed product must not cool down during the transfer between vessels
- The plant is fully automatic.
In your answer you should include a P&ID and briefly explain the function of the design and the reason behind any equipment used.
(c) On commissioning of the unit operation designed in part (b) the end user has asked if the plant can be modified such that after the mixing period the contents can be cooled prior to transfer. Suggest a possible solution and explain the method of operation, including a simple sketch of the relevant section of the P&ID.
Q 7
a)Identify the options available to the process engineer when measuring the flow-rate of liquid in pipelines that are to be installed as part of a new fully automated process plant. Your answer should include four types of flow-meter each with a different operating principle, and in each case you should list the operational and installation advantages and disadvantages. Differential pressure devices should not be included.
Valve Types and Principles of Operation
b) Identify a choice of options available to the process engineer when ‘measuring’ the level of a liquid in a vessel, which is installed as part of a fully automated process plant, give the advantages and disadvantages of each method
(c) Identify a choice of options available to the process engineer when ‘measuring’ temperature, in the case of each instrument, briefly describe their operating principle
(d) If you were required to supply an instrument to a Pharmaceutical Company in the context of liquid flow measurement what questions would you ask the end user.
(e) If you were required to supply a flow switch to a Pharmaceutical Company specify two options that would meet the duty, and in each case, explain the device’s operating principle.
(f) If you were required to supply a device to be installed downstream of a bursting disc, in order to indicate rupture of the disc, suggest a device that would meet the duty, and explain the operating principle of the device.
(g) Automatic air driven valves are supplied normally open, normally closed or air/air driven with single or double feedback. Explain these terms.
(h) Automatic control valves can be specified to control flow or pressure upstream of the valve, explain why. What problem can occur if there is an excessive pressure drop across a control valve?
(i) If you were required to supply a flow control valve to a Pharmaceutical Company, what questions would you ask the end user to fully specify the valve?
(j) Explain the principle of operation of a control valve and discuss the options available to the valve manufacturer. In your answer include the valve opening characteristics, direct and reverse acting, function of a positioner, use of a cam, and fitting of mechanical stops.
Q8 (a) List the factors that have to be considered prior to specifying a pump for a given duty.
(b) Centrifugal pumps can be split into various designs. Identify the options available.
(c)With the use of appropriate graphs, for centrifugal pumps only explain the relationship between pressure and volumetric flow, and power consumed and volumetric flow.
(d) Positive displacement pumps require in certain instances the inclusion of additional equipment. If a positive displacement pump was fitted in a fully automated plant, what equipment is essential and why, and what equipment is required in certain cases and why?
(e) An instrument is to be installed in a storage vessel to act as a low level switch, in order to protect a discharge pump from dry running. Describe two devices that would meet this duty.
(f) If a device cannot be fitted to the storage vessel, suggest a suitable instrument, and the point of installation, which would prevent the dry running of the discharge pump.
Q 9
(a) Discuss the importance of certification in the manufacture and supply of instrumentation. Your answer should include the following certificates: IP, 3A, EHEDG, ATEX, FM, CSA, calibration, material and conformity.
(b) Instruments are in certain cases certified as suitable for installation in pipe-work systems that undergo pigging. What is pigging, what is involved and how is the pipe-work design adapted for pigging?
Introduction to Process Controls and PID Controller
(c) The following contact materials PEEK, PFA, PTFE, and EPDM are used in hygienic process plants. In each case, listing the beneficial properties, explain why?
(d) Instruments can be purchased to specifically measure the following parameters: ORP; Redox; Brix; and conductivity. Define each parameter.
Q 10
(a) A Tag number is imperative in the identification of an individual plant item, explain why this identification is necessary.
(b) Multi-national companies operate under global standards, using preferred suppliers, outline the benefits and disadvantages of this policy
(c) Accreditation is important, what certificates are typically required to ensure a process plant is accredited.
(d) Instruments can be supplied as intrinsically safe. What certificate would be supplied with an intrinsically safe instrument, and what methods could the manufacturer use to design a device to be intrinsically safe.
Q11
(a)Many companies insist on named manufactures, this is not only for instruments but also for the supply of all equipment, to maintain global standards. What are the reasons behind this policy, outline the possible advantages and disadvantages in your answer, considering not only the company itself, but also any other organisation who are designing or supplying process plant to the company.
(b) Describe the operating mechanism of a Bourdon Tube pressure gauge. How is this instrument adapted for use in a modern automated hygienic plant? Suggest an alternative device, outlining its measuring principle and it benefits.
(c)You are the lead engineer in the design of a process plant that produces a cosmetic product, a suitable method to ensure that at the end of a production run the surface hold up in the transfer pipe-work is minimised is pigging. What is pigging and how is the design adapted to account for this.
d) Differential pressure transmitters can be used to determine the level in a pressurized vessel, or the pressure drop across a filter installed downstream of a pump. Discuss any problems if this type of instrument is used.
e)With the use of appropriate graphs, for centrifugal pumps only explain the relationship between pressure and volumetric flow, for pumps operating in series and for pumps operating in parallel. (Your answer should include the plant system curve, the individual pump curves and the combined pump curve)
f) If centrifugal pumps are installed in series, for the downstream pump what additional information must be supplied to the pump manufacturer.
Q12
(a)Compare and contrast, with the aid of drawings, where appropriate, the design characteristics of orifice plates and venturi tubes.
(b) It is desired to measure the flow-rate of a process fluid (density 1000 kg/m3) in a 100 mm internal diameter pipe. The normal operating mass flow-rate is approximately 200,000 kg/hr and the maximum anticipated flow-rate is 250,000 kg/hr. It is proposed to use an orifice plate to measure the flow-rate, but for process reasons the pressure drop across the meter must not exceed 0.15 bar.
(c) Calculate the diameter of the orifice bore to achieve this.
(d) What is a reasonable figure for the minimum flow-rate that can be measured with this orifice plate installed?
Temperature Measurement Devices
(e) Based on your knowledge of the operating characteristics of orifice plates and venturi tubes in the measurement of flow-rate, suggest an alternative use (apart from the measurement of flow-rate) for each item.
(f) Describe the measuring principle used in the operation of electromagnetic flow- meters and vortex-shedding flow- meters. What applications are these types of instruments suitable for, and why?
g)The measurement of flow-rate in an open channel can be determined using a rectangular notch (weir), and applying the ‘Francis’ formula:
h) If Q represents the volumetric flow-rate (m3/s), what do the letters B, n and D represent?
i) Water flows in an open channel, across a rectangular weir, which occupies the full width of the channel. The width of the weir is 0.5 m and the height of water flowing over the weir is 100 mm. Calculate the volumetric flow-rate m3/s.
j) What would be the height of the water flowing over the weir if the water flow-rate was increased to 0.04 m3/s?
k) Specify an instrument, which is to be installed in a fully automated plant, which is suitable for measuring the following, noting that differential pressure devices are not allowed, and in each case list the instruments features and benefits:
(i) Fruit juice at a flow-rate of 20m3/hour
(ii) Carbon dioxide at a temperature of 50ËšC, and a flow-rate of 40m3/hour
(iii) Steam at 2 barg in a 25 mm ID tube.
(iv) Ultra pure water at a flow-rate of 180m3/hour
(v) Suspensions at a flow-rate of 36m3/hour
l) Describe the measuring principle used in the instrument specified to measure the flow-rate of ultra pure water above.
m) Flow switches can be used to detect the flow of liquid, describe three different devices that can be used for this purpose. In each case outline their advantages and disadvantages, their principle of operation, their typical use and point of installation. Do not include devices used downstream of bursting discs.
n) You are the lead engineer on an expansion of an existing process plant, and in this capacity you are organising a HAZOP. The plant is fully automated. The members of the HAZOP team must have an understanding of how the plant operates. What two documents must be distributed to the HAZOP team prior to the day of the HAZOP exercise? Explain the importance of each document.
o) If it was not possible to fit a device to the storage vessel suggest an alternative instrument, and its point of installation, which would prevent the dry running of the pump.
p)Identify a choice of options available to the process engineer when ‘measuring’ temperature, in the case of each instrument, briefly describe their operating principle.
q) Four temperature measuring devices are commonly used, thermocouples, RTD’s, thermistors and radiation pyrometers. In each case give an indication of a typical temperature response, state the general measuring range of the instruments, and list their advantages and disadvantages.
r) Based on your knowledge of instruments specify two methods to prevent the drying running of a centrifugal pump, if the pump is being used to empty a vessel in an automated process plant. In each case sketch a simple P&ID showing the position of any instrument used and explain your reasoning.For measuring flow rate of fruit juice in the range 5-25m^3/hour magnetic meter instrument can be used.
Process Plant Automation: Benefits and Considerations
a) i) Operating features of magnetic flow meter
Magnetic flow meter transmitter has several kinds of operating features. It provides unparallel process of magnetic capabilities with the help of its coupled class performance. Its operating features are summarized below;
- An electrochemical emf is formed during the action which results the electrolytic reaction between the process of ion conducting and the metal electrode.
- When the conductors situated in the magnetic field inductive coupling are formed which can be also referred to as the quadrature of the a.c voltage.
- The operating principles run on the faraday’s law of induction.
Benefits
- Various advanced diagnostics provides information of the unparallel that can enhance the performance of the meter.
- Isolated local operator interface make dist easy to design and makes it safe.
- It is also available for designing of the remote mount.
ii)
For measuring flow rate of sea water in the range 150-1000 m3/hour helical gear instrument can be used.
Operating features and benefits of helical gear
- The helical gears may be used in several kinds of applications as it can be mounted in two types of shafts such as either 900 shafts of non-intersecting or parallel.
- The operating characteristics are smoother than any other instrument.
- The concentricity of the close connection between the diameter of the outside and the diameter of the patch which are smooth and easy to operate.
- The strength of the tooth is better due to the wrap of the helical around it.
Nutating disk flow meter can be used for flow-rate of steam in a 50 mm nominal bore pipe.
Operating features and benefits of Nutating disk
- Power source is not required for this type of measurement.
- The cost of the operating subsystem is low.
- It can be used for measuring the follow meter of the fuel.
iv)
For measuring the flow-rate of oil in the range 8-20 m3/hour magnetic meter instrument can be used.
The operating features and the benefits of the magnetic meter instrument have been discussed previously
Operating principle of magnetic flow meterThe operating principle of magnetic flow meter is based on the principle of laws of Faraday’s electromagnetic induction. An electric current is applied to the package coil of the flow meter. The magnetic field (B) is generated in the coil due to this electromagnetic induction. When the flow of the liquid is applied to the instrument a very small voltage is induced in the coil. The induced voltage is proportional to the velocity of the flow of the liquid. Two electrodes of the coils are connected to the input of the circuit. The microprocessor then calculates the flow of the volumetric of the liquid and control of the input. The operating principle can be written by, u= K*B*v*d, where u is the induced voltage in the coil, B is the field of the magnetic strength between the two electrodes, d is the distance between the two different electrodes of the coil, v is the liquid velocity and k is the calibration factor.
- How can it measure the flow of a liquid?
- What are the capacity factor and size?
- How can it different from flow meter?
- What is the power used by the measurement instrument?
c)
Two types of instruments are proportional counter and the GM detector which can be suitable for detection the presence of flow during normal process operation.
The advantages of GM detector
- This kind of detector is reliable and very useful for several kinds of indoor applications.
- Very easy to use and available in various kinds of shapes and sizes.
The advantages of proportional counter
- It can be used in various kinds of applications.
- There is no dead time for the various activity sources.
d)
Burst disc indicator device can be installed in the downstream of a bursting disc as an indicator of the disc rupture.
Operating principle of Burst disc indicator device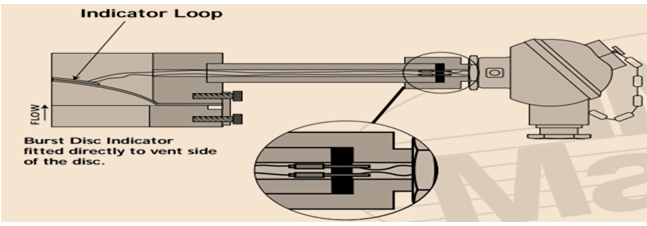
Once the burst disc indicator has ruptured, it can be beneficial for shutting down of the plant. Burst is special kind of indicator circuit which is installed to the downstream of the burst disc during the breaking of the disc rupture. The input signal is frequently received by the control room of the plant.
e)
Advantages of the flip switch
- Installation process is easy.
- Long lasting.
- Versatility.
Disadvantages of the flip switch
- Resetting is required.
- Loss of the temporal information.
The better alternative switch is the magnetic switch as it is easy to use as well as to operate.
2
a)
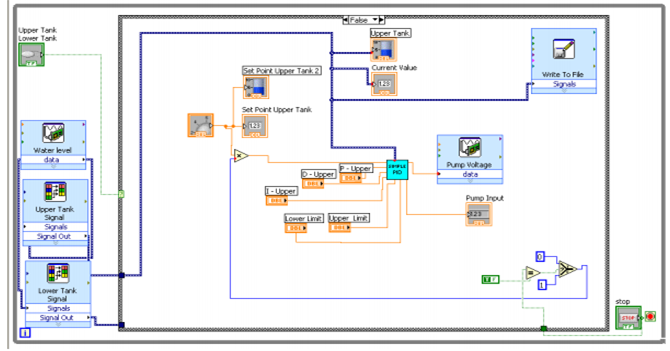
Operating principle of the PID tank controller
Plant
This part of the controller system is to be controlled.
Feedback
The feedback part devices are used to measure the several kinds of variables which can be used to control.
Error signal
Error signal is measured during the operation of the PID controller.
Disturbances
Disturbances can be defined as such kinds of systems which can cuase the disturbance of the normal flow of the program. For example, the electrical intereference.
Controller
The controller is most important part of this system which is used to set the point, for processiong of the error and provides an accurate output of the signal.
b)
Principle of operation of on/off air valves
- This kind of valve can be referred as the modulating pilot valve. The main valve a affecting the downstream valve b in different ways which are summarized below;
- When the valve of the pilot ‘a’ is closed then no water can be passed through the downstream to the main valve that is closed by pressure of the upstream and after that the valve is introduced the chamber a.
- When the valve b is open then it can allow passing the drainage pressure to the chamber of the downstream. At this point the pressure of the water is controlled by the control chamber which is nearly equal to the downstream of the chamber.
- The throttling valve b is flowing through a fixed volume of the water to the control chamber.
c)
Operating principle of inductive proximity switch
Detection of the inductive proximity sensors
The inductive proximity sensor can detect the loss of the magnetic due to its eddy current which is generated at the time of external magnetic field. The magnetic AC field is produced on the coil of the detection which can change the impedance due to the loss of eddy current. Several kinds of pulse response sensors are used to generate the eddy current which can detect the change of the time. Proximity sensor is used to detect the change of the capacitance between the object and the sensors.
Advantages of proximity switch
- Switching rate is high.
- It is capable for working in any kind of environment condition.
- Very accurate.
3
a) The four types of communication signals are actuator, controller, and sensors and the feedback which are used in automatic process plant.
- The actuator responds to the sensors with the help of various command of the responder. For example, the gas flow in the heating system is used to monitor the pump.
- The controller signal is sued to control the overall process of the system and can embed with the computers.
- Sensors are used for measuring the physical state of the level like liquidity level.
- Feedback is used to control the error signal.
b) Proportional mode is used in PID controller for getting continuous variables output which are used to provide the error signal between the set point and the variable process. Integral mode is used in PID controller to reset the output bias automatically which is used for processing of the adjustment of the process error. Derivative mode is used in PID controller to change the output as per the rate of the change of the error in the output.
c)
The example of a process situation where PID control is used is the electrical resistance furnace. The PID loop control is used to control of the temperature resistance and it is used to stabilize the system. The example of the on/off control is thermostat which is used for measuring the temperature
d)
Differences between the Hardwired and software
- The hard wired interlocks provide intrinsic type protection of several kinds of equipments.
- The example of hard wired interlocks is Fuse.
- The hard wired interlocks provide inventory of the class for using of the sub detector.
- In software the protection is normal level.
- The example of the software is switched on /off of a system.
- It provides the several kinds of requirements as per the requirements of the actions.
4
a)
Response characteristics of thermistor 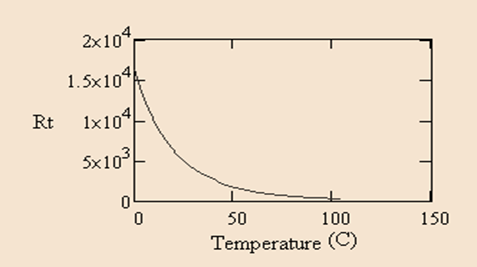
Response characteristics of thermocouple
Response characteristics of RTD
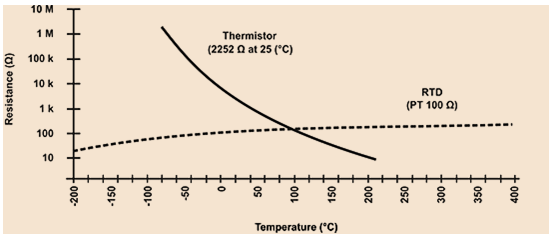
Range of temperature for measurement of the thermocouple
-2670 C to 23160 C
Range of temperature for measurement of the thermistors
-100°C to 500°C
Range of temperature for measurement of the RTD
-240°C to 649°C
The advantage of the thermistors
- Accuracy is high.
- High sensitivity.
The advantage of the thermocouple
- Linearity is better.
- Temperature range is high.
The advantage of the RTD
- Accuracy is better.
- Linearity is high.
The disadvantage of the thermistors
- Temperature range is low.
- Not highly linear.
The disadvantage of the thermocouple
- The operating cost is high.
- Accuracy is not so good.
The disadvantage of the RTD
- The range of the temperature for operating system is medium.
- Sensitivity is not so good.
Operating principle of thermocouple
Two different types of wire are joined at the end of the junction point which can be called as the thermo elements. Two types of thermo elements are denoted as the positive and negative element. One end of the junction is immersed in the air which is to be measured and other end is called the tail.
Operating principle of Thermistors
The resistance of the Thermistor can be determined by, R = Ro ek and K = β(1/T – 1/To) where R is the resistance of the thermistor at different temperatures of T and e can be denoted as the Naperian logarithms and β is the constant range.
Operating principle of RTD
RTD operating system can be determined by, Rt= R0[1+α(t-t0)] where Rt is the temperature of the resistance, R0 is the temperature of the resistance at t0 and α is the temperature coefficient.
b)
Advantages
- Cost
Disadvantages
- Self heating
- Non linearity
Examples of the temperature sensor
The example of temperature sensors are Thermocouple, full thermometer system, bimetallic thermometer and RTD.4
5
a)
The factors are the actuator, controller, feedback and the sensors
b)
Importance of FDS
- Development can know the exact develop.
- Quality can be assured in accordance with the testing process.
- Tracking numbers are requirements.
- The client can be assured about the testing.
c)
The four types of communication signals are actuator, controller, and sensors and the feedback which are used in automatic process plant.
- The actuator responds to the sensors with the help of various command of the responder. For example, the gas flow in the heating system is used to monitor the pump.
- The controller signal is sued to control the overall process of the system and can embed with the computers.
- Sensors are used for measuring the physical state of the level like liquidity level.
- Feedback is used to control the error signal.
d)
Specifications for PLC
- Input port and output port.
- Maximum number of channel.
- Computer interface.
- Power supply.
- Operating temperature.
6
a)
Tag number is important for labelling the plant item because it provides a record of the all items in the database of the plant; it keeps a record of the item with the help of the number ID system.
b)
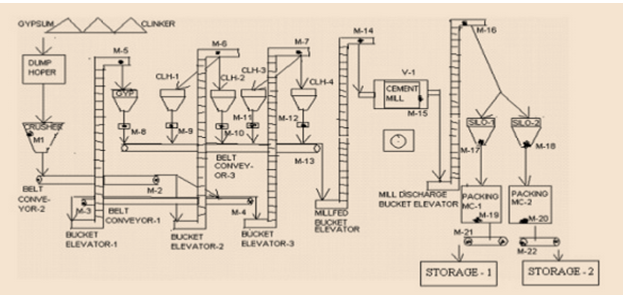
The above figure showcases the process of the plant of cosmetic products which maintains the above all criteria given in the assignment
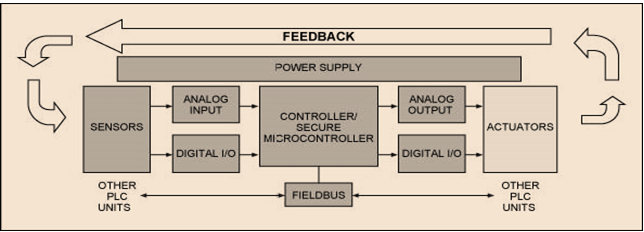
7
a)
The four types of flow meters are turbine, nutating disk, rotary vane and coriolis which can be installed for measuring of the flow rate of liquid in pipelines that are to be installed as a part of fully automated plant.
Operating principle of turbine
A pick up sensor is installed above the rotor of the flow meter. Hall Effect sensor can be used for this kind of flow meter. The differences between the Hall Effect and inductance pick up sensor are that the inductance type sensors provide a voltage pass in each time of the rotor. Pre amplifier may be dependent on the receiving signal at the input section. The turbine flow meter consists of the stainless steel body and a rotor at the end of the supports.
Advantages
- Volumetric flow plot is continuous as the turbine is constantly roataing at a constant speed.
- Response rate is fast.
Disadvantages
- Installation cost is high.
- Loss of accuracy due to accumulation of the viscosity.
Operating principle of nutating disk flow meter
A multi pole solenoid is used to rotate with the help of a driver and a switch. The streaming of the liquid causes a rotation on its own axis. The number of the pulse determined the volumetric flow rate.
Advantages
- Accuracy is high.
- Little maintenance is required.
- Cost effective.
Disadvantages
- Corrosion by water.
Operating principle of rotary vane
The rotary vane is made of a kind of circular rotor which is mounted to the sliding vane. The sliding vanes are isolated and based on the liquid of fixed volume between the compartment of the wall and the rotor. In normal state the centre of the rotor is in offset condition. More vanes in the rotor make the higher accuracy of the flow meter.
Advantages
- Pressure drop is low.
- Choice of the construction of materials is wide.
- Accuracy is high.
Disadvantages
- Design process is very complex.
- Maintenance cost is high.
Operating principle of coriolis mass flow meter
The cotriolis meter consists of a vibrating tube which is used to change of the frequency of the flow of the liquid. The signal of the sensor is installed to the pc board. The output signal is fully proportional to the rate of the mass flow.
Advantages
- Mass flow rate.
Disadvantages
- High pressure loss.
- Highly sensitive.
b)
Capacitance level measurement and continuous level sensor can be used for measuring the level of a liquid in a vessel.
Advantages of capacitance level measurement
- No moving part is required.
Disadvantages of capacitance level measurement
- Below 20lb/ft^3 particle size can cause problem due to process of dielectric constant.
Advantages of continuous level sensor
- Accuracy is high.
- High sensitivity.
Disadvantages of continuous level sensor
- Not very reliable.
- Installation process is costly
c)
Temperature measuring instruments are thermocouples and resistance temperature detector.
Operating principle of thermocouple
Two different kinds of wire are installed at the end of the point of the junction which can be termed as the thermo elements. There are two types of thermo elements are used for measuring the temperature of an object such as the positive and negative element. The measuring end is immersed in the air and other end is called the tail.
Operating principle of RTD
RTD operating system can be determined by, Rt= R0[1+α(t-t0)] where Rt is the temperature of the resistance, R0 is the temperature of the resistance at t0 and α is the temperature coefficient
d)
The questions will be asked to the end users are;
- What is the rating of the switches?
- What is the required voltage?
- Applications of that kind of switch?
e)
Two types of switches are pressure switch and the electronic regulators which can be used in Pharmaceutical Company. Operating principles of two types of switches Electronic regulators are the smaller in size the output of the signal fed to the LED display. Pressure switch consist of various kinds of options such as fluid switch, IP65 protection and various high purity options.
f)
Operating principle of Burst disc indicator device. Once the burst disc indicator has ruptured, it can be beneficial for shutting down of the plant. Burst is special kind of indicator circuit which is installed to the downstream of the burst disc during the breaking of the disc rupture. The input signal is frequently received by the control room of the plant.
g)
The normally open valves are used to pass the air through it when it is not actuated with the feedback. The normally closed valves are used to pass the air through it when it is actuated with the feedback.
h)
The automatic control valve can be specified to control flow or pressure upstream of the valve because it allows the different types of fluids in one way direction. If there is an excessive pressure drop across the valve then the diaphragm automatically back to the original position.
i)
The questions are:
- Does it maintain the constant flow?
- How adjustable flow setting can be used?
- How it can maintain the pressure drop
j)
Principle of operations of a control valve. Pressure relief valve is such kind of control device which is used for emergency in any overpressure events. A spring is used in pressure relief valve to set the piston in the seat.
8
a)
The specifications factors of a pump are summarized below;
- Flow rate of the pump.
- Pressure head of the pump.
- Elevation head of the static pump.
- Friction head of the pump.
b)
The centrifugal pumps can be categorized into several kinds such as radial flow pumps, axial flow pump, mixed flow pump and multistage centrifugal pumps
c)
Relationship between the pressure and volumetric flow
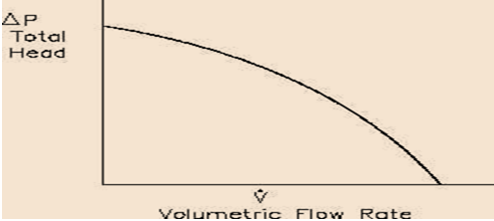
The above graph depicts the relationship between the volumetric flow rate and the total head. The pump head is the differences between the back pressure of the syrttem and the pressure of the inlet of the cenrtifugal pump. The vertical axis showcases the total head pressure of the centrifugal pump and the horizontal axis shocases the rate of the violmuteric flow in the centrifugal pump.
Relationship between the pressure and volumetric flow
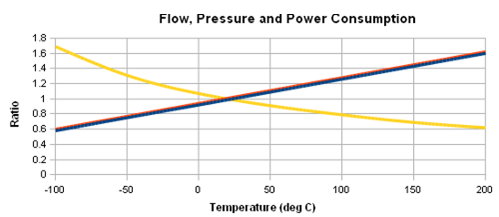
The above diagram depicts the relationship between the pressure and volumetric flow. The vertical axis showcases the ratio of the power consumption and the pressure and the horizontal axis showcases the temperature of the experiments.
d)
Reciprocating type equipments are needed such as piston is essential which can be fully fitted in the automated plant because it can expand the cavity in the end of the suction and also it can minimize the cavity in the side of discharge. The positive displacement can be categorized into two classes such as the rotary and the reciprocating.
e)
The two devices are centrifugal pump and the vertical turbine pump.
f)
The suitable instrument is electric macerator pump which cannot be fitted to the storage vessel and which can prevent the dry running of the discharge pump.
9
a)
Importance of certification in the manufacture and supply of instrumentation
- The certification should be authenticated so that various specifications of the instruments can be known.
- Several kinds of essential information of the instruments can be understood from the certifications.
- The certification is needed for authentication of the data provided by the manufacturer.
b)
Pigging is the background of the pipeline which can be referred to as such kind of device that is used to perform the maintenance operation of the pipeline. This process can be done by preventing the product flow of the pipeline
c)
Beneficial properties of PEEK
- Spinal fusion, which is used to implants of the metal.
- Fusion surgery which is used to spine surgery.
Beneficial properties of PFA
- It can reduce the bleeding.
- It can reduce the heat of the hydration.
Beneficial properties of PTFE
- Friction constant is very low.
- Maintenance is free.
- Form factor is low.
Beneficial properties of EPDM
- Suitable for all types of operation.
- Environment friendly.
d)
ORP can be termed as the oxidation reduction potential which is used to minimize the substance of the chemical materials.
The combination of oxidation and the reduction process is termed as the REDOX process.
BRIX can be defined as then scale which is used to determine the amount of lights which is passing through the liquid.
Conductivity can be defined as the degree by which a material can conduct through the electrically. In other word it can be defined as the ratio between the current density to the electrical field.
10
a)
Need for the identification of the tag
Tag number is important for labelling the plant item because it provides a record of the all items in the database of the plant; it keeps a record of the item with the help of the number ID system
b)
Advantages of the multinational companies
- Financial benefits.
- Upgraded with latest technologies.
Disadvantages of the multinational companies
- Loss of the expertise.
- Dependency on the suppliers
c)
NPCA and NRMCA accreditation certification are needed for processing of a plant.
d)
ATEX certification is needed for intrinsically safe instrument. The methods for designing a device to be intrinsically safe are summarized below;
- Explosion proof.
- Pressurized and purge method.
- Encapsulation method.
11
a)
The reason behind to maintain global standards is the brand value because the company is renowned which can maintain the brand value of the product.
Advantages
- It can help to enhance the brand value.
- Suppliers get the right amount of money at the right time.
Disadvantages
- Delay in the supply of the instruments due to long network
b)
Working principle of Bourdon Tube pressure gauge
The Bourdon Tube pressure gauge is such kind of instrument which is used to measure of the fluid pressure. When the pressure is applied to the tube the stress is generated in the tube. The linear motion in the tube is converted to the circular motion which is parallel to the axis of the link. This device consist a high ranges of pressure measurements like 100,000 psi and it is a one kind of pressure transducer. The alternative device is thermometer.
Advantages of thermometer
- It is used to measure the temperature of the human body.
- It is user friendly
c)
True size of opening method can be used which can minimize the pigging. Pigging is the background of the pipeline which can be referred to as such kind of device that is used to perform the maintenance operation of the pipeline. This process can be done by preventing the product flow of the pipeline.
d)
Limitations of differential pressure measurements transmitter
- Error can be found during the operation.
- It can work with the clean liquids only
e)
Relationship between the pressure and volumetric flow
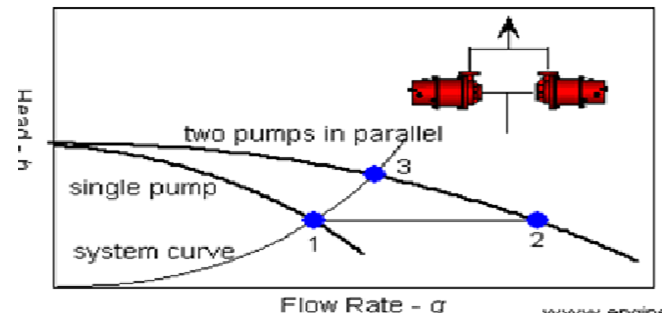
The above graph showcases the relationship between the pressure and volumetric flow for the pumps which are operating in series and in parallel.
f)
If the centrifugal pumps are installed in series then additional information which must be supplied to the pump manufacturer are described below;
- The differences between the pump performances of the individual pump.
- For different kinds of flows the operating features are different.
12
Comparison between orifice plates and venture tube
- Venture tube takes may times to install and very expensive but venture tube is cheap.
The head lost of the orifice meter is greater than venture meter
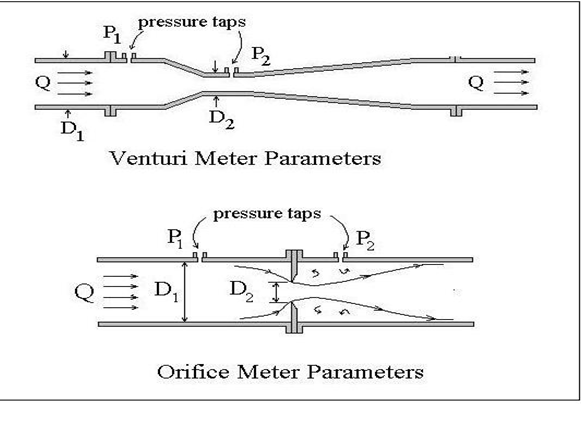
b)
The pressure drop equation is given by, ½ P v2^2 – ½ Pv1 ^2 , the internal diameter of the pipe is 100 mm, so, the pressure drop is 0.115 bar
c)
Orifice bore diameter can be calculated by, d= D where D is the internal diameter of the bar which is 100 mm and m is the mass flow rate which is 250000 kg/hr. so, the diameter is 50000 mm.
d)
Minimum flow rate is 200,000 kg/hr.
e)
The alternative use of orifice plate is V cone and the alternative use of venture tube is flow nozzle
f)
The application of electromagnetic flow meter is it can be used to determine rates of the flow of the liquid. Vortex-shedding flow- meters are used to measure flow rate of the gases, steam and the viscosity liquids
g)
The flow rate can be measured by q = 2/3 cd b (2 g)1/2 h3/2 where q is the flow rate, h = head on the weir (m)
b = width of the weir (m)
g = 9.81 (m/s2) - gravity
cd= discharge constant for the weir - must be determined.
h) b is the width of the weir. D is the diameter of the weir and n is the head on the weir.
The equation is given by, q = 3.33 (b - 0.2 h) h3/2 where, b is 0.5 m, h is 100 mm. so, q= 0.050 m^3/s
i) The height of the water can be calculated by, 0.09= 3.33(0.5-h)h^1.5 , so, h= 0.054 m.
j)
- Magnetic meter instrument can be used for flow rate 20m^3/hr.
- Nutating disk can be used.
- Helical gear instrument can be used.
- GM detector instruments can be used.
- Magnetic meter instrument can be used.
k)
Wet benches instruments are used for measuring the flow rate of ultra pure water above.
l)
Three types of devices are Thermal meters, Coriolis meters and KOBOLD instruments which are used to detect the flow of the liquid
m)
Capacitance level measurement and continuous level sensor can be used for measuring the level of a liquid in a vessel
n)
Temperature measuring instruments are RTD, thermocouple and thermistor. Operating principle of thermocouple
Two different types of wire are joined at the end of the junction point which can be called as the thermo elements. Two types of thermo elements are denoted as the positive and negative element. One end of the junction is immersed in the air which is to be measured and other end is called the tail.
Operating principle of Thermistors
The resistance of the Thermistor can be determined by, R = Ro ek and K = β(1/T – 1/To) where R is the resistance of the thermistor at different temperatures of T and e can be denoted as the Naperian logarithms and β is the constant range.
Operating principle of RTD
RTD operating system can be determined by, Rt= R0[1+α(t-t0)] where Rt is the temperature of the resistance, R0 is the temperature of the resistance at t0 and α is the temperature coefficient.
o)
The advantage of the thermistors
- Accuracy is high.
- High sensitivity.
The advantage of the thermocouple
- Linearity is better.
- Temperature range is high.
The advantage of the RTD
- Accuracy is better.
- Linearity is high.
The disadvantage of the thermistors
- Temperature range is low.
- Not highly linear.
The disadvantage of the thermocouple
- The operating cost is high.
- Accuracy is not so good.
The disadvantage of the RTD
- The range of the temperature for operating system is medium.
- Sensitivity is not so good
p)
The suitable instrument is electric macerator pump which cannot be fitted to the storage vessel and which can prevent the dry running of the discharge pump. The sketch diagram is depicted below in the figure.
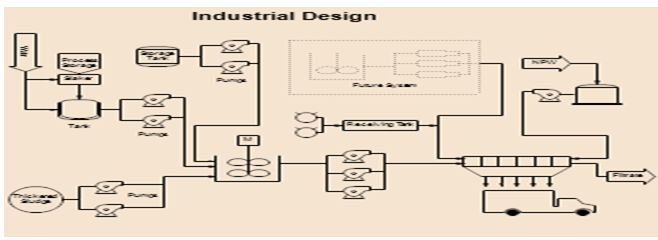
References
Bagajewicz, M. (2001). Process plant instrumentation. Lancaster, Pa.: Technomic Pub.
Bartholomew, D. (2006). Measurement. London: SAGE.
Bolton, W. (2004). Instrumentation and control systems. Oxford: Newnes.
Brown, D., Harrold, D. and Hope, R. (2004). Control engineering. Amsterdam: Newnes.
Butz, J. and Kottenstette, J. (1985). High energy gas fracturing pressure profile transmission. Chicago, Ill.: Gas Research Institute.
Corballis, T. (2002). Measurement. Wellington [N.Z.]: Victoria University Press.
D'Azzo, J. and Houpis, C. (1991). Linear control system analysis and design. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Doebelin, E. (2010). Instrumentation design studies. Boca Raton: CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group.
Dowdy, P. (2009). Measurement. New York: Crabtree Pub.
Ellis, G. (2004). Control system design guide. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press.
Gensler, W. (1996). Advanced agricultural instrumentation. Dordrecht: M. Nijhoff.
Goodwin, G., Graebe, S. and Salgado, M. (2001). Control system design. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
Horowitz, L. and Vernon, J. (1996). Measurement. Dubuque, Iowa: W.C. Brown.
Levine, W. (2000). Control system fundamentals. Boca Raton, Fla.: CRC Press.
Lewis, H. (2000). Advanced telescope and instrumentation control software. Bellingham, Wash.: SPIE.
Lockhart, P. (2012). Measurement. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press.
McCall, W. (1939). Measurement. New York: Macmillan.
Olsson, G. (2005). Instrumentation, control and automation in wastewater systems. London: IWA.
Padmanabhan, T. (2000). Industrial instrumentation. London: Springer.
Pistoia, S. (2003). Measurement. Chanhassen, MN: Child's World.
Pluckrose, H. and Fairclough, C. (1992). Measurement. Franklin Watts.
Prutchi, D. and Norris, M. (2005). Design and development of medical electronic instrumentation. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Interscience.
Stollon, N. (2011). On-chip instrumentation. New York: Springer.
Suter, A. (1991). Measurement. Chicago: Contemporary Books.
Webster, J. and Clark, J. (1998). Medical instrumentation. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Whitt, M. (2004). Successful instrumentation and control systems design. Research Triangle Park, NC: ISA.
Wrigley, W., Hollister, W. and Denhard, W. (1999). Gyroscopic theory, design, and instrumentation. Cambridge, Mass.: M.I.T. Press.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2015). Instruments And Principles For Process Plant Automation. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/instrumentation-and-control-engineering.
"Instruments And Principles For Process Plant Automation." My Assignment Help, 2015, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/instrumentation-and-control-engineering.
My Assignment Help (2015) Instruments And Principles For Process Plant Automation [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/instrumentation-and-control-engineering
[Accessed 31 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Instruments And Principles For Process Plant Automation' (My Assignment Help, 2015) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/instrumentation-and-control-engineering> accessed 31 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. Instruments And Principles For Process Plant Automation [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2015 [cited 31 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/instrumentation-and-control-engineering.
