McKinsey 7-s framework analysis
1. Produce a McKinsey 7-s framework analysis of Virgin Atlantic and explain how sure an approach to the organisation might assist in changing the organisation strategy.
2. Identify what comprises strategic capabilities in terms of organisation resources and competencies and apply the VRIN frame work to assess the capabilities in terms of providing a basis for achieving sustainable competitive advantage.
3.Outline and evaluate the present global corporate strategy through the Bowman's Strategy Clock
4. Potter 5 forces -Identify, analyse and give examples
5. With reference to Stakeholders Mapping: The Power/Interest Matrix, Identify and critically evaluate the impact of company's stakeholders on strategy development.
Strategic management is the planning for both predictable as well as impracticable possibilities. The identification and description of the strategies that are carried by managers in order to achieve better performance as well as competitive advantage is termed as strategic management. An organization is said to have competitive advantage if profitability is more than average profitability for all companies belonging to the same industry. The bundle of decision and acts undertaken by the manager is also termed as strategic management. Strategic management is a permanent procedure that evaluates and controls the business in which the organization is involved. In other words, it evaluates the competitors and set objectives in order to meet potential competitors (Hill et al. 2013).
Virgin Atlantic is a trade name of Virgin Atlantic Airways Limited that is a British airline. Virgin Atlantic mainly uses a mixed fleet of airbus as well as Boeing wide-body aircraft. In terms of passenger volume, Virgin Atlantic became the seventh largest UK airline for carrying more than 54 million passengers in the year 2012. Virgin Atlantic also holds a license that permits it to carry passengers, cargo as well as mail with more than 20 seats. The US and the UK authorities investigated suspected price fixing between Virgin Atlantic and British Airways over passenger fuel surcharges. The company is known to sell a 49 percent stake in the Singapore airline. In the year 2010, Virgin Atlantic had appointed Deutsche Bank in order to begin a planned review of choice for airline (ABUBAKAR 2016).
Virgin Atlantic McKinsey 7-s framework illustrates how the seven elements of airline business are associated to augment the overall efficiency of the business. The elements are divided into hard and soft groups. The hard elements include strategy, structure and systems, whereas soft elements include shared values, staff, skills and style (Mitchell et al. 2015).
Application of VRIN framework on strategic capabilities of Virgin Atlantic

Figure: McKinsey 7-s framework analysis
(Source: Jurevicius 2013)
Strategy – Virgin Atlantic pursues the business strategy of service discrimination. The airline mainly differentiates its services through a wide-ranging dependence on digitization as well as information technology. The Virgin Atlantic airline also depends on a high level of customization of service provision. They also have the strategy to fly a profitable airline that customers love to fly. Their strategy is to improve the services of the customers to improve their business. The strategy is also to ensure that they provide the best business product in the air. The Virgin Atlantic team also needs to consider all the major stakeholders to monitor the ever-changing external environment while building future strategy. Effective strategic management is required in order to stave off failure. Virgin Atlantic has been able to execute an effective strategic management by understanding the airline industry properly and changing customer needs.
Structure – Virgin Atlantic was first painted with a Euro white design with a red stripe through the centre of the main deck windows. The business structure of Virgin Atlantic is hierarchical that in turn reflects the large size of the business (Malbašić and BrÄÂić 2012). For example, Virgin Atlantic makes the use of mixed fleet of Airbus and Boeing aircraft with an average age of 9 years. Virgin became the first airline to function the Airbus A340-600. It also operates with a three-class cabin configuration: Economy, Premium Economy, and Upper Class. This has helped Virgin Atlantic an established business with an effective strategic management.
Systems - Virgin Atlantic maintains an industry-specific system in which the company has introduced Google Glass Innovation. The travelers of Virgin Atlantic will be the first air passengers to experience the advantage of pioneering Google Glass technology. It also includes industry-specific system for example; it operates a number of offices and call centres all over the world, with a big office in Swansea, Wales that deals with reservations and sales, baggage claims.
Staff – The staffs are mainly customer-friendly with a positive attitude. They authentically enjoy helping the travelers and solving their queries.
Style - Virgin Atlantic believes in flying in style as it was the first airline to offer personal entertainment for all passengers. For example, Virgin Atlantic provides preflight champagne that is known as the upper class dining. The Upper class features a seat that changes into a completely flat bed and access to chauffeur drive. These features are bound to attract the travelers.
Evaluation of present global corporate strategy through the Bowman's Strategy Clock
Skills - Virgin Atlantic is building on great skills as well as experience that occur in favor of the company. For example, the company had gained skills related to trading over the years that helped the company to gain profit.
Shared Values – The core part of the value of the business is the strong reputation and loyalty that is endangered by Virgin Atlantic airline limited.
The strategy of the organization can be changed, as shared values will help to shape how the organization behaves. Shared values are what stimulate trust. Structure is that organizational chart that will help to divide the task equally among the employees. Strategy will help Virgin Atlantic airline limited to reach the identified goal. The cultural style of Virgin Atlantic airline limited will be defined with the help of style (Burns and Cowlishaw 2014).
VRIN framework is useful technique for the analysis of comparative advantage of the firm regarding resources. The VRIN analysis has four components, which are presented below. This framework critically analyses efficiency of firms in resource utilisation (Rothaermel 2015).
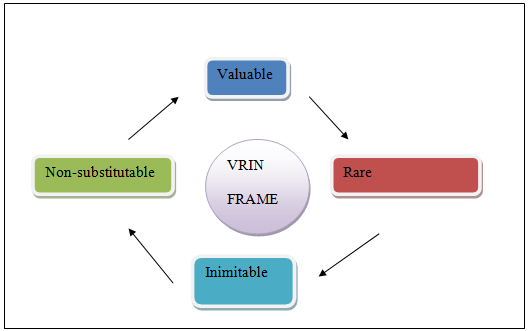
Figure: VRIN framework
(Source: Rothaermel 2015)
VRIN analysis of Virgin Atlantic
|
Resources |
Valuable |
Rare |
Inimitable |
Non substitutable |
|
Flight accommodation |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Use of cleaner fuel |
Yes |
yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
In-flight alignment |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
|
The customer Bill of Rights |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
Valuable resource:
In order to get competitive advantage in the market, the firm requires using resources of greater value in production. A resource is said to be valuable if it can provide the firm an opportunity to get sustainable competitive advantage in business. The value of resource utilised by Virgin Atlantic rises, if it can improve consumer perception. The valuable assets may be assets, information and knowledge, strategic capabilities of the firm. The valuable resources enhance the activity of the firm in the competitive market (Agarwal et al. 2012).
Virgin Atlantic provides two different class systems to the passengers such as economy class and upper class. Differentiated service is a part of price discrimination strategy of the firm. The economy class is also divided between two categories such as premium economy and economy, which cover other coaches other than premium economy (Simão and Diaz 2012). Sustainability strategy of this firm includes carbon efficiency and new cleaner fuel to reduce wastage of resources. Strategic use of resources makes the resources of Virgin Atlantic valuable. As the value of resources tend to change overtime according to changing environment of business, the value of resources needs to be reviewed overtime (Peng 2013).
For example, Virgin Atlantic carried 3.8 million travelers in the year 2003. This increased to 4.6 million in the year 2006. Virgin Atlantic also operated a compassionate aid charter flight to Islamabad, Pakistan, with 55 tonnes of aid for the people affected by the 2005 Kashmir earthquake. This helped the company to gain opportunity to get sustainable competitive advantage in business. Virgin Atlantic had been successful in terms of flight accommodation and as a result, it was placed seventh largest UK airline in terms of accommodation.
Analysis of Potter 5 forces
Rare resources
Resources are considered rare very few firm in the market holds these. Use of rare resources gives competitive advantage to the firm. The leader firm in the industry has advantage of using rare resources. Use of rare resources gives short term competitive advantage in the market. As airline industry in UK is a competitive industry, there is medium threat of new entry. Air line companies operate in large scale with having economies of scale. The sunk cost of operation is huge in this industry (Lin et al. 2012). Therefore, without having economies of scale, new entrants cannot operate in the industry successfully. Huge finance is needed in the operation. Therefore, losing competitive advantage to the new entrants regarding rare resources is less likely. However, other existing firms follow the strategy of leader firm. Hence, when the rival firms come to know about the rare resources, they can use the same in the production process in order to gain the competitive advantage (Grant 2016). Use of cleaner fuel is valuable as well as rare resource. Use of cleaner fuel is relatively costly. Therefore, it is not yet used widely. In future this may not be rare resources if the use of cleaner fuel becomes common in airlines. Hence, the firm has to identify new resources to get strategic advantage in the industry.
For example, Virgin Atlantic volunteered a Boeing 747 for a test of bio fuels that was planned to reduce emissions of greenhouse gas. The reduction of emission was mainly carried out by cutting weight of aircraft as well as consumption of fuel. Virgin Atlantic also decided to use algae-based bio fuels in the future. This is the part of rare resources since there are very few airlines who will take the risk to make the use of algae-based bio fuels to reduce greenhouse emission.
Inimitable and non-substitutable resources
The resources are inimitable if the utilization of resources is costly for other organization. The imitation can be in two ways such as direct imitation or duplication and applying comparable resources. According to Kerzner (2013), resources can be costly to imitate if the resources have historical background of usage. If the firm uses a resource for a long time, it gains natural monopoly over the resources and can use the resource at low cost due to having economies of scale (Agha et al. 2012). New firm may not get the advantages. Moreover, if the resource is dependent on firm’s organizational cultural, resource becomes inimitable and non-substitutable.
Analysis of Stakeholders Mapping: Power/Interest Matrix
For example, Virgin Atlantic added Boeing 747 to start a route from Gatwick to Miami. The company also has an order for the Airbus A380-800, with delivery due in 2018. The company had decided to make use of A380-800 as become less efficient to run. With the help of this costly resource, Virgin Atlantic will be able to gain to competitive advantage.
Low Price/ Low Value – The Company will not prefer to compete in this category. This category is known as the bargain basement bin. Virgin Atlantic will not prefer to be in this position. This is a position in which the company feels the pressure to compete with its competitors. In this position, Virgin Atlantic will not be able to win the loyalty of the customers but they will be able to sustain themselves. Under this strategy, the products provided by Virgin Atlantic will not be of great quality, however the customers will be convinced enough to purchase the product (Radut 2015). For example, if Virgin Atlantic provides a low upper class features in that case the travelers will lose faith on the airline.2. Low Price - Virgin Atlantic is not a low cost leader and as a result, the company will not be a part of this strategy. The companies under this category drive their prices down in order to bare minimum. However, Virgin Atlantic faced a challenge as with the falling fuel prices. With the falling fuel prices, the company faced a downward pressure on charges. As a result, in order to please the customers Virgin Atlantic needs to trigger price wars to benefit the customers.

Figure: Bowman's Strategy Clock
(Source: Anon, 2016)
Hybrid - Virgin Atlantic is a part of hybrid as hybrid mainly deals with interesting companies. The companies offer products at a lower cost; however, the products are of higher professed value as compared to its customers. They offer great value as well as cargo products to their customers. Virgin Atlantic is very passionate about their customer service and provides the travelers with a choice of meal. The company also ensures that the travelers are provided with pre-requested meal (Shakhshir 2014). For example, Virgin Atlantic provides all the premium services at a reasonable cost so that they meet up to the expectation of the customers.
Differentiation - Virgin Atlantic is also a part of differentiation as they provide the passengers with high-perceived value. In this case, the company will either increase the price or maintain themselves through higher marginal profit. Virgin Atlantic itself is a brand that helps the company to follow differentiation strategies. The airline is known for higher customer service and premium prices (Eyvrigh 2016).
Focused Differentiation – The focused differentiation mainly deals with the high quality services provided by Virgin Atlantic. The services that it provides are of high-perceived value. The travelers will be attracted towards the services depending on the perceived value. The spa and the luxury hotel services provided by Virgin Atlantic are of high-perceived value that is enough to charge large premiums. The travelers will pay for this service if they believe that they will be highly satisfied with the service. For example, Virgin Atlantic established a separate premium economy that included a separate check-in area as well as wider seat with more breathing space.
Increased price / Standard Product – Under this position, the companies generally increases the price without any increase in the value of products. When the prices are increased, the company starts earning profit (Carter 2013). For example, with the delivery of G-VRED, Virgin commenced a new design, with the fuselage painted in metallic silver and an amended tail fin, with red and purple features and the Virgin logo.
High Price / Low value – This position for the companies that operates under monopolistic market structure. However, Virgin Atlantic belongs to competitive market structure. The main competitors of Virgin Atlantic are American Airlines Group Inc, British Airways and Air France.
Low value / Standard Price – When a company follows this position, they are bound to lose market share. As a result, Virgin Atlantic will avoid this position so as hold its position in the market (Grigoletto 2016).
Entry and Exit of barriers – As far as aviation industry are concerned; entry and exit barriers are quite high. This is mainly because; Virgin Atlantic will not be able to exit the sector when they wish to as the regulators often persisting that they will fulfill the contractual compulsion towards the stakeholders. Beside this, Virgin Atlantic is also characterized by tight regulation. This indicates that a regulator needs to be content about the safety aspect in addition to the airworthiness and the economic stability of the carriers. Virgin Atlantic faces an external environment, as the entry barriers are formidable. As a result, it becomes difficult for the new entrants to entrench themselves (Anton 2015).
Figure: Porter’s five forces
(Source: Cgma.org, 2016)
Industry Rivalry – The airline industry is drenched with a number of carriers entering the market in search of profits. In the case of Virgin Atlantic, industry rivalry is very high. There is always a race to the bottom as growing carriers compete for a shrinking traveler tart leading to fare battle. Industry rivalry between airlines is leading to more consolidation and lack of profitability is driving airlines towards mega amalgamation. For example, British Airways (BA) had been the only airline from the United Kingdom serving long-haul routes to destinations in North America.
Power of suppliers – In the case of Virgin Atlantic, the suppliers are mainly the sellers who supplies carriers as well as makers of Airbus. The suppliers also include the individuals who make extra parts for the airline. The power of suppliers is low as there are a number of suppliers competing for business. The carriers like Virgin Atlantic will have a distinct advantage because if fuel becomes expensive there will be few buyers (Rothaermel 2016).
Power of buyers – The power of buyers is comparatively higher as airline industry is a buyers’ market. Virgin Atlantic is a low cost carrier. However, many airlines have successfully imitated the business model of Virgin Atlantic. In other words, the airlines are taking away travelers from Virgin Atlantic. The buyers are mainly spoilt for choice as they have a lot of choice to choose from. The choice includes purchasing online tickets and the removal of the mediator layer with the propagation of online booking straight from the airlines (Porter 2012).
Threat of Substitutes – The threat of substitutes is not very high in the case of Virgin Atlantic. This is mainly because the individual in the West mainly prefers to travel by air. Due to the ongoing recession, most of the airlines company shifted to teleconferencing in order to reduce the need to travel by air.
Stakeholders have significant impact on company’s decision-making. Stakeholders are customers, suppliers of raw materials and shareholders. Stakeholders’ management plan includes several aspects such as identification of project, analysis, preparation of action plan etc. The power-interest matrix divides the stakeholders into four groups. There are some stakeholders in the company, who have high power and low interest (De Brucker et al. 2013).

Figure: Power/Interest matrix
(Source: Kerzner 2013)
The firms needs to give priority to this kind of stakeholders and requires o meet their needs. Some stakeholders have high power and high interest on the company. They may be old suppliers or large shareholders, who are engaged with the business closely.
The stakeholders, who have low power in company’s decision-making, need to be informed about new project development. The stakeholders with low interest and low power in business are given minimum effort. They are less important for business. Therefore, the company has to give minimum effort to retain them in business. Stakeholders, who invest in business, need to know about the action plan of the business (Waligo et al. 2013). Expansion of business in new market requires preplanning. New investment requires finance, which is provided by the stakeholders. Hence, they have interest in business.
For example, Virgin Atlantic considers all the key stakeholders to keep them happy. As a result, Virgin Atlantic needs to maintain the same level of success as well as effective strategic management.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that Virgin Atlantic is not a low cost leader and the power of buyers are comparatively higher as airline industry is a buyers’ market. Virgin Atlantic is very obsessive about their customer service and provides the explorers with a choice of meal. It has also been concluded that Virgin Atlantic provides preflight sparkling wine that is known as the upper class dining. The airport lounge is similar to that of lavishness hotel. Virgin Atlantic itself is a brand that helps the company to follow differentiation strategies. It has also been concluded that Virgin Atlantic provides two different class systems to the passengers such as economy class and upper class. Sustainability strategy of this firm includes carbon efficiency and new cleaner fuel to reduce wastage of resources.
References
Abubakar, s.g., 2016. Examining the culture of an organisation, its leadership styles, structure, diversity issues and conflicts: a case study of virgin atlantic, united kingdom. Development, 4(2).
Agarwal, R., Grassl, W. and Pahl, J., 2012. Meta-SWOT: introducing a new strategic planning tool. Journal of Business Strategy, 33(2), pp.12-21.
Agha, S., Alrubaiee, L. and Jamhour, M., 2012. Effect of core competence on competitive advantage and organizational performance. International Journal of Business and management, 7(1), p.192.
Anton, R., 2015. An Integrated Strategy Framework (ISF) for Combining Porter's 5-Forces, Diamond, PESTEL, and SWOT Analysis.
Burns, P.M. and Cowlishaw, C., 2014. Climate change discourses: how UK airlines communicate their case to the public. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 22(5), pp.750-767.
Carter, J., 2013. Marketing Plan Example: Virgin Atlantic Little Red.
Cgma.org. 2016, Porter’s Five Forces of Competitive Position Analysis - CGMA. [online] Available at: https://www.cgma.org/Resources/Tools/essential-tools/Pages/porters-five-forces.aspx?TestCookiesEnabled=redirect [Accessed 17 Aug. 2016].
De Brucker, K., Macharis, C. and Verbeke, A., 2013. Multi-criteria analysis and the resolution of sustainable development dilemmas: A stakeholder management approach. European journal of operational research, 224(1), pp.122-131.
Eyvrigh, G.M., 2016. A REVIEW OF MARKETING STRATEGIES. Kuwait Chapter of the Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, 6(1), p.77.
Grant, R.M., 2016. Contemporary strategy analysis: Text and cases edition. John Wiley & Sons.
Grigoletto, M., 2016. La strategia: da Porter a Bowman. Il caso della Singapore airlines.
Hill, C.W., Jones, G.R. and Schilling, M.A., 2014. Strategic management: theory: an integrated approach. Cengage Learning.
Jurevicius, O. 2013., Conquer the Challenge of Expansion with McKinsey 7s. [online] Strategic Management Insight. Available at: https://www.strategicmanagementinsight.com/tools/mckinsey-7s-model-framework.html [Accessed 17 Aug. 2016].
Kerzner, H.R., 2013. Project management: a systems approach to planning, scheduling, and controlling. John Wiley & Sons.
Lin, C., Tsai, H.L., Wu, Y.J. and Kiang, M., 2012. A fuzzy quantitative VRIO-based framework for evaluating organizational activities. Management Decision, 50(8), pp.1396-1411.
Malbašić, I. and BrÄÂić, R., 2012. Organizational values in managerial communication. Management: Journal of Contemporary Management Issues, 17(2), pp.99-118.
Mitchell, B.C., Fredendall, L.D. and Cantrell, R.S., 2015. Using McKinsey’s 7 S Model to Empirically Examine Organizational Effectiveness among the NBA Teams. International Journal of Management & Human Resources,3(1).
Peng, M.W., 2013. Global strategy. Cengage learning.
Porter, M., 2012. Micheal Porter's 5 forces. University of National Economy. Javalgi, RRG, Martin, CL, and Young, RB (2006). Marketing research, market orientation and customer relationship management: a framework and implications for service providers. Journal of Services Marketing, 20(1), pp.12-23.
Radut, C., 2015. Strategies of change for the hotel industry. Porter, Kotler, Bowmann positions. Knowledge Horizons. Economics, 7(4), p.79.
Rothaermel, F.T., 2015. Strategic management. McGraw-Hill.
Rothaermel, F.T., 2016. Competitive Advantage in Technology Intensive Industries. Technological Innovation: Generating Economic Results (2nd Edition)(Advances in the Study of Entrepreneurship, Innovation &, 26, pp.233-256.
Shakhshir, G., 2014. Positioning Strategies Development. The Annals Of The University Of Oradea, 977, pp.416-437.
Simão, J. and Diaz, P., 2013. An extended VRIO model as a framework for sustainable tourism planning: a review. Tourism as a Tool for Development,4, p.71.
Waligo, V.M., Clarke, J. and Hawkins, R., 2013. Implementing sustainable tourism: A multi-stakeholder involvement management framework. Tourism Management, 36, pp.342-353.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2017). Essay: Strategic Management Analysis Of Virgin Atlantic." (56 Characters). Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/culture-of-an-organisation-strategic-management.
"Essay: Strategic Management Analysis Of Virgin Atlantic." (56 Characters)." My Assignment Help, 2017, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/culture-of-an-organisation-strategic-management.
My Assignment Help (2017) Essay: Strategic Management Analysis Of Virgin Atlantic." (56 Characters) [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/culture-of-an-organisation-strategic-management
[Accessed 22 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Essay: Strategic Management Analysis Of Virgin Atlantic." (56 Characters)' (My Assignment Help, 2017) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/culture-of-an-organisation-strategic-management> accessed 22 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. Essay: Strategic Management Analysis Of Virgin Atlantic." (56 Characters) [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2017 [cited 22 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/culture-of-an-organisation-strategic-management.
