Rationale for the selected country
Describe about the International Business for Market Culture Perceptions.
Market culture describes the ideas, perceptions and social values that a community has towards different situations. In the present extremely competitive business environment, understanding the culture of the market is extremely important. In-depth knowledge regarding the culture of the market can help businesses to utilize effective strategies so that it can able to achieve sustainable growth in the market. Many studies have highlighted the fact that understanding the culture of an economy requires proper analysis of several factors. Present global business environment has increases the significance of understanding the market culture of an economy in order to create positive impact on the revenue level. In this report, the focus will be on the market culture of Taiwan. The report will try to include an in-depth analysis of the existing market culture of the Taiwan economy. The report will also focus on the identification of the best possible strategies that can create maximum positive impact on the Taiwan’s market culture.
As per the article by Harrell (2014), Taiwan is regarded as 15 largest importer in the world. Generally, all the rules and regulations of Taiwan are developed in such a way so that it can able to help businesses to enter into the market effectively. Over the years, Taiwan has able to develop in a rapid rate due effective utilization foreign businesses. However, Taiwan business culture is unfamiliar to most of the western organizations. For that reason, majority of the foreign organizations tries to utilize cross-cultural training to provide knowledge to the employees in order to conduct business effectively in the Taiwan market. However, it has been identified that majority of the organizations has able to grow their businesses in the Taiwan market due to high acceptability among the people.
As per the article by Gelfand et al. (2013) organizations will have to focus on many factors in order to develop effective strategies in the foreign market. Specifically, countries like Taiwan have their own set of perspectives that organizations will have to consider in order to implement effective strategies in the market. As highlighted by Liu (2016) organizations will have to consider several components of Taiwan’s market culture for the effective utilization of the implemented business strategies. The components are as follows:
Values and attitudes:
It has been identified that values and attitudes are completely different in different economies. In fact, majority of the time values and attitudes varies within a country as well. Therefore, many organizations face difficulties in expanding their businesses in different countries. Now, Taiwan is developed in capitalist economy. As a result, values and attitudes of Taiwan’s people is complete different compared to any other European economy. Thus, organizations business strategies will have to be developed in such way so that it can able to create maximum impact on the development of the business perspectives.
Cultural analysis of Taiwan
Education:
As per the article by Fujita et al. (2013), Taiwan is presently utilizing digital educational system. The educational structure of Taiwan is developed in such a way so that it can able to motivate student to opt for higher education. It has been assessed that educational structure of Taiwan has able to create positive impact on the economical development of the country. It has been also assessed that educational structure of Taiwan is inducing people to handle multiple tasks at given time. Therefore, it has created massive impact on the knowledge level of the country.
Taiwan’s social culture is focused has been developed in such a way so that it can able to provide equal opportunities to all the people in the economy. Furthermore, Taiwan social structure is developed in such a way so that it can able to provide all the women in the economy equal opportunity to grow up in their professional career. As mentioned by Linehan (2013) Taiwan’s Culture is a mix of “Taiwanese aborigines cultures” and “Confucianist Han Chinese cultures”. Taiwan represents a perfect mix of modern and traditional understandings. For that reason, it has allowed businesses to implement strategies in an appropriate way.
Religion:
As mentioned by Chang (2015), Taiwan represents a greatly tolerant society that is highly diversified in terms of religious faith. Primarily, the country has three prime religions namely Taoism, Buddhism and Confucianism. However, it does provide opportunities for other religions like Hinduism, Christianity and Islam to have equal amount of opportunities to grow up in the economy. Thus, it highlighted the fact that business strategies will have to be developed in such a way so that it cannot able to hurt any religion feelings.
Manners and Customs:
As mentioned by Chang (2012) understanding the manners and customs are very important to conduct businesses in the foreign country effectively. Taiwan also has specific manners that businesses have to consider in order to conduct their businesses effectively. For instance, people in Taiwan generally maintain polite manners in order to conduct their businesses effectively. Thus, it is very important for the businesses to maintain proper manners and customs so that it can able to create maximum impact on the business development perspectives.
Personal communication:
Many studies have highlighted the significance of personal communication in order to develop business in the foreign country effectively. Now, Taiwan’s official language is Mandarin Chinese. However, the country also utilizes Holo and Japanese languages as well. Thus, business strategies also have to consider the effective utilization of languages so that it can able to communicate with the people in an appropriate manner.
Difference between Taiwan’s market cultures with Singapore
Physical environment:
Taiwan is a separated Island but it is included in the Asian continent. Taiwan whether is more of a tropical climate. Many studies have identified that around population of Taiwan is around 25 million. Furthermore, the average life span of Taiwan’s people is around 80 years. Taiwan’s government makes a conscious effort to maintain low pollution level so that people can able to lead a healthy life. Therefore, it has also induced businesses to utilize healthy atmosphere of Taiwan in order to grow their businesses properly.
Aesthetics:
As per the article by Lee et al. (2015) aesthetics help organizations to identify the best possible way to conduct businesses in a foreign country. As mentioned earlier, every economy has their own set of values and believes. Therefore, proper maintenance of aesthetics helps business to develop its reach in the international market. For instance, Taiwan is more focused in developing technology-based organizations. Therefore, businesses will have to utilize advance technology in their business processes to gain popularity in the market.

Figure 1: Taiwan’s components of culture
(Source: Berry, 2016)
As mentioned by Warner (2014) Taiwan and Singapore is very similar regarding the market culture perspectives. Firstly, both the economy is geographically very small. As a result, both Singapore and Taiwan has to face constant pressure from their larger neighbor. However, both the country has able to grow in a rapid rate due effective utilization of market culture. Now, Singapore represents a multiethnic society that includes Malay, Chinese, Eurasian and Indian communities. Therefore, Singapore represents a well-versed culture that has helped foreign business to conduct businesses in an effective manner. Singapore has also faced lot of issues regarding the maintenance of Indonesian refugees. As majority of the Indonesian people lives below the poverty line, it also has affected the growth rate of the Singaporean economy. On the other hand, Taiwan’s major threat comes from Mainland China. Taiwan has developed several strategies so that it cannot able to affect the business development perspectives of the economy. However, Lee et al. (2015) highlighted the fact that Taiwan and Singapore has many similarities in the implemented regulations regarding effective utilization of trade and commerce. As mentioned earlier, Taiwan is among the prime countries in the world that heavily depends on the imports of products. Now, Singapore also imports everything from food products to luxury products. Thus, both are representing export-oriented economy. Furthermore, both Taiwan and Singapore have realized that their neighbors have attempted to reduce demand for the services and products by developing rival infrastructure. Therefore, both the economy is seeking for new markets so that it can able to maintain its growth rate. However, Singapore and Taiwan has differences in the perspectives regarding racism. Singapore has to implement many rules and regulations to maintain their proper culture in the economy. On the other hand, Taiwan does not have faced any major issues regarding racism. Therefore, it has helped businesses from all parts of the world to capture the Taiwan market effectively.
Hofstede cultural dimension is probably the most common measurement of culture. It includes five dimensions that help to evaluate all possible aspects of culture. Taiwan’s Hofstede cultural analysis is as follows:
Power distance:
Power distance evaluate the extent to which less powerful people in economy accepts the inequality in power. It also describes a particular economy’s attitude towards the inequality. Taiwan scores relatively higher marks of 58 in this dimension (Chen et al., 2014). Thus, it indicates that Taiwan is a hierarchical society. It also reflects that people in Taiwan accept the hierarchical order in which every individual has their own place and it does not require any further justification. Now, hierarchy in businesses reflects that Taiwan is more focused towards the centralized management where subordinates expect to be guided by the management regarding their way of managing responsibilities.
Individualism-collectivism:
This dimension describes the relationship between people with the groups in which they belong. Thus, it also reflects the degree of interdependence that a community maintains among all its members. Now, Taiwan represents a collectivistic society that has very lower grade on the individualism. It highlighted the fact that all the people in the community heavily depends on each other. In fact, people perceive their business groups as an extension of family. Thus, it reflects stronger relationship among each other. Therefore, businesses also have to develop atmosphere where every individual can able to maintain strong relationship with each other. Otherwise, it will create negative impact on the business development perspectives.
Masculinity-femininity:
Masculinity describes the dominance of competitive values in a community like performance driven, assertiveness and success. On the other hand, feminine value describes that dominant value in the society is to have care for others. Taiwan score relatively lesser grades of 45 in masculinity (Fung, 2013). Thus, it reflects that Taiwan is slightly a feminine society. It reflects that organizations will have to develop a caring atmosphere in Taiwan in order to conduct businesses effectively. It also indicates that businesses also will have to consider the well-being of all the employees in order to sustain its position in the market.
Uncertainty avoidance:
This dimension describes the development of rules and structure to reduce the ambiguity in an organization. Thus, it reflects the extent to which people feel threatened by the unknown or ambiguous situations. Taiwan score of 69 describes that it has greater possibility for avoiding any uncertainty (Hua & Nathan, 2016). It also represents the people perceive time is money and have inner urge to work as hard they can. Thus, businesses will have to provide proper atmosphere in order to get best out of the Taiwan’s people.
Long-term orientation:
It reflects that how society has able to maintain connection with its own past while dealing with the present and future challenges. In this dimension, Taiwan score of 93 highlights that the society is highly focused in maintaining their tradition in future. However, it also reflects that Taiwan also accept the present changes that is required to develop the financial condition of the economy.
Indulgence:
This dimension describes the degree to which people try to control their impulses and desires. Taiwan has scored 49 that reflect that the economy does not have any dominant preference. Thus, it highlights that people of Taiwan does not focus too much on controlling their desires.
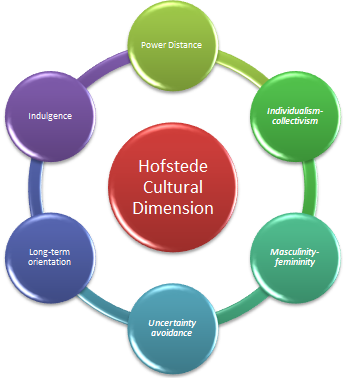
Figure 2: Hofstede cultural dimension
(Source: Sun et al., 2013)
Conclusion:
The above discussion highlights the fact that Taiwan has some unique cultural features that have the potential to create obstacles on the path of foreign business development. Thus, organizations will have to handle all the factors extremely carefully in order to expand business in Taiwan in an appropriate manner. However, the above discussion also highlights that Taiwan is focused to develop businesses so that economy can able to sustain its growth. Therefore, it is up to the businesses to utilize the culture in an effective way.
References:
Berry, C. (2016). The Last Isle: Contemporary Film, Culture, and Trauma in Global Taiwan. Sheng-Mei Ma. Lanham, MA: Rowman and Littlefield, 2015. ix+ 197 pp.£ 80.00. ISBN 978-1-78348-338-9. The China Quarterly, 225, 286-287.
Chang, S. S. Y. (2012). Literary culture in Taiwan: Martial law to market law. Columbia University Press.
Chang, W. C. (2015). Religious attendance and subjective well-being in an eastern-culture country: Empirical evidence from Taiwan. Marburg Journal of Religion, 14(1).
Chen, J. L., Lin, Y. J., Ma, J. P., & Lin, M. T. (2014). An Interpretation Case Study of Cultural Creativity in Design Exhibition of" Taiwan Artisan".International Proceedings of Economics Development and Research, 81, 1.
Fujita, S., Seto, K., Ito, S., Wu, Y., Huang, C. C., & Hasegawa, T. (2013). The characteristics of patient safety culture in Japan, Taiwan and the United States. BMC health services research, 13(1), 1.
Fung, A. Y. (Ed.). (2013). Asian Popular Culture: The Global (Dis) continuity. Routledge.
Gelfand, M. J., Brett, J., Gunia, B. C., Imai, L., Huang, T. J., & Hsu, B. F. (2013). Toward a culture-by-context perspective on negotiation: Negotiating teams in the United States and Taiwan. Journal of Applied Psychology,98(3), 504.
Harrell, S. (2014). Ploughshare village: Culture and context in Taiwan. University of Washington Press.
Hua, S., & Nathan, A. J. (2016). Chinese Political Culture. Routledge.
Kleinman, A., & Lin, T. Y. (Eds.). (2013). Normal and abnormal behavior in Chinese culture (Vol. 2). Springer Science & Business Media.
Lee, Y. C., Wang, C. Y., Weng, S. J., Huang, C. H., Hsieh, W. L., & Wu, H. H. (2015, January). Assessing Patient Safety Culture from Nurses' Viewpoints of a Teaching Hospital in Taiwan. In Proceedings of International Conference on Application of Information and Communication Technology and Statistics in Economy and Education (ICAICTSEE) (p. 37). International Conference on Application of Information and Communication Technology and Statistics and Economy and Education (ICAICTSEE).
Lee, Y. C., Weng, S. J., Stanworth, J. O., Hsieh, L. P., & Wu, H. H. (2015). Identifying Critical Dimensions and Causal Relationships of Patient Safety Culture in Taiwan. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics, 5(5), 995-1000.
Linehan, M. (2013). Book review: The vitality of Taiwan: politics, economics, society and culture. LSE Review of Books.
Liu, J. T. (2016). RESEARCH ON TAIWAN THEME PARKS'EXPERIENCE MARKETING STRATEGY AND REVISIT WILLINGNESS, PURCHASE WILLINGNESS AND RECOMMENDATION WILLINGNESS. International Journal of Organizational Innovation (Online), 9(1), 35.
Sun, P. C., Lin, M. T., Chung, P. H., & Huang, Y. F. (2013). A Cross-Culture Study on Consumer Attitude of Buying Luxury Counterfeits–A Comparison Between Taiwan and Shanghai. In International Conference on Business and Information.
Warner, M. (2014). Culture and management in Asia. Routledge.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2017). International Business For Market Culture Perceptions: An Analysis Of Taiwan's Market Culture. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-market-culture-perceptions.
"International Business For Market Culture Perceptions: An Analysis Of Taiwan's Market Culture." My Assignment Help, 2017, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-market-culture-perceptions.
My Assignment Help (2017) International Business For Market Culture Perceptions: An Analysis Of Taiwan's Market Culture [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-market-culture-perceptions
[Accessed 20 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'International Business For Market Culture Perceptions: An Analysis Of Taiwan's Market Culture' (My Assignment Help, 2017) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-market-culture-perceptions> accessed 20 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. International Business For Market Culture Perceptions: An Analysis Of Taiwan's Market Culture [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2017 [cited 20 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-market-culture-perceptions.
