Describe about the Marketing Orientation for Critical Tactics for Implementing.
Companies are developing and planning strategies that let them attain a competitive advantage through their core competencies. In other words companies are selecting their business orientation which is the method to do their business in a more competitive manner. While selecting to be market oriented companies are trying to direct their organizational efforts towards better performances, increased productivity and profitability. (Belz 2009)The report is a description on Boots UK Limited’s business orientation. The methods that has been used to make Boots market oriented and the various benefits that are incurred to the company by adopting market orientation strategy. The various challenges faced by the company in order to implement the strategies.
Boots UK Limited is a pharmacy chain outlets operating in the United Kingdom and Ireland. The company’s range of products include pharmaceuticals, healthcare, beauty and skincare. The company was founded in the year 1849 by John Boot. The company is currently headquartered at Nottingham in the United Kingdom. The company employs over 70,000 employees in the United Kingdom and 1,900 in Ireland. The company has a retail website and also has a loyalty card program called the Boots Advantage Card. (Burt 2011)The company has several outlets in high street, airport terminals and shopping centers. The company The Boots Company Plc merged with Alliance Unichem in 2006 to form Alliance Boots, which was later bought by Kohlberg Kravis Roberts and Stefano Pressina in 2007. From 2012 Walgreens gradually bought stakes in Alliance Boots, hence the Boots became a subsidiary company of Walgreens Boots Alliance. The company’s slogan is “Feel good”.
Boots UK is pharmaceutical health and beauty products company with over 2,500 stores from small local community pharmacy to large health and beauty stores. The brand is committed to provide unique customer and patient care through employees, who are the strength of the business. (Hill, Jones & Schilling n.d.) Boots has devised their operational plan on basis of macro environments like political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors within UK and micro environmental factors like customer, employees, suppliers, shareholders, competitors and so on. The business orientation refers to the several dimensions of business as marketing orientation, product orientation, employee orientation or customer orientation of Boots. (Best 2009)
Through this dimension a business designs their products after conducting market research on customer, in order to meet their needs. There are three components of customer orientation namely market segmentation or customer segmentation, competitive orientation that can be understood by Porter’s 5 forces and interfunctional coordination.
Analysis of Business Orientation of Boots
The customer segmentation can be done by geographical, demographic, psychographic or behavioral variables. Boots undertake segmentation on basis of population, size of geographical area, sex, age, education, income, interest, lifestyle, social status, personality, customer loyalty and so on. Boots primarily caters to upper and upper-middle class income groups of all ages, sex, education, interest in a concentrated geographical areas of UK and Ireland. (Netessine & Tang 2009)

Figure 1: Boots products on basis of segmentation
Source: Author
Porter’s Five Forces is used to study the industry level competition existing by the following analysis:
Entry of competitors: Boots is a large scale company operating in the UK and Ireland where threat from new entrants is significantly low due to high investments required.

Figure 2:Porter's 5 Forces
Source: (Schermerhorn 2010)
Threat of Substitute: The threat from substitute products in cosmetics as well as medicine is considerably high due to UK and Ireland opening up its markets to foreign companies.
Bargaining power of buyers: Due to presence of large number of competitors Boots experiences significant bargaining power from buyers.
Bargaining power of suppliers: The bargaining power of suppliers is considerably less as compared to the sheer size of Boots. (Schermerhorn 2010)
Rivalry among existing players: Tesco is importing medicines of cheaper variant from Russia and China, which is the primary competitor of Boots. Other competitors are Bluemercury, Macy’s, Sephora and so on, with cut throat competition amongst them. (Porter 2008)
In this process the business aims to develop its current product. Either the existing product is developed or the product efficiency is increased.
Ansoff’s matrix depicts four quadrants of product development, market penetration, market development and diversification. The matrix is used by Boots in order to assess product oriented development. In product development the company has developed many cosmetic and beauty care products which has provided a competitive edge. (Haq 2008)In product diversification the company has created variant of the same product in new market segment as in case of toiletry products, the company manufactures unique toilet papers or its Ireland market. The company has been primarily catering to upper and upper-middle class segment hence the company has not penetrated the various other income segments of the market. Boots has also not explored other markets in international sphere hence the company has not attempt market development. (Alon 2013)

Figure 3: Ansoff's Matrix
Source : (Alon 2013)
The process entails introduction of new employees to the techniques, processes, goals and profile of the organization to get accustomed to its culture. The concept of marketing mix product, price, place and promotion has been extended to add people, process and physical evidence.
Marketing Orientation
At Boots people component in the marketing mix includes the management and the employees who are responsible for marketing activities. The organizational culture of Boots is reflected through its employees as these dynamic individuals effectively promote products of Boots to customers and provide services. The HRM team at Boots provides necessary training, mentoring for enhancing skills, knowledge and technical expertise of these employees. The process are the various marketing activities that create overall efficiency and effectiveness for systems. Physical evidence includes the stores and outlets present of Boots that deliver friendly, tidy and healthy experiences. (Belz 2009)
The customer is regarded as the king in this step and the business strategies to service or value add benefits it provides clients. Boots attend and delivers to its customers by applying the marketing mix. This enables the company to provide right sets of products at the right place and right price. Boots store near NHS keeps mostly medicines compared to cosmetic products and its stores on High Street keeps more of cosmetics. Whereas at the airports its stores has constituents from medicines as well as cosmetics.
Customer convenience is another aspect of customer orientation where Boots provides its customers with efficient value chain. Boots operate in three forms of stores, one being Boots’ shops like Boots health and beauty stores, Boots flagship stores and Boots travel stores and most of the stores are located in densely populated areas. It has been estimated that UK’s 90% population stays in 10 minutes drive proximity to Boots stores. (Buttle 2009)
The company has a loyalty card program that is very well accepted and provides customers a sense of value. The company also provides online shopping portals that is connected to its stores and ensure safe, convenient and on-time deliveries.
The above analysis of Boots business orientation reflects that the company is profitable and most of its revenue is generated from a segment of customers. In order that Boots redirects its activities in a more market oriented manner the following recommendations has been formed;
- Boots targets a narrow spectrum of customer from the upper and upper-middle class. In order to be more market oriented the company needs to expand its private label products and open up stores in a wide variety of location that gives access to all.
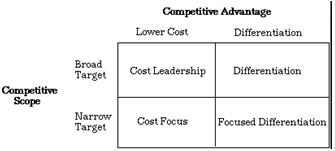
- Boots is analyzed in Porter’s generic strategies to categories its products as cost leaders, focus products or differentiated products. (Akan et al. 2006)The company’s products mostly cater to focus strategy where they cater to a single segment of the consumer. The company needs to focus on creating more cost leader types of products to cater to the broader segment on the market. (Porter 2008)
![Porter's Generic Strategies]()
Figure 4: Porter's Generic Strategies
Source: (Porter 2008)
- The company needs to apply the BCG matrix to identify its products under the heads as those which are star products, products which are cash cows and earn revenue for the company. Products that low revenue earning and those which are totally unviable. This analysis of its various products will entail the company to focus on products that have capability to generate greater revenues.(Lowy 2011)
![BCG Matrix]()
Figure 5: BCG Matrix
Source: (Lowy 2011)
While analyzing the Ansoff’s matrix for the company, findings were that market penetration has been totally ignored. Hence the company has to focus on market expansion to expand its current business.
Boots is competing with Tesco, Body Shop, Sainsbury’s, Asda, Superdrug, M&S, Morrison, Debenhams and so on. The feature that will enable the company to set it apart from others is product development as it has physical as well as insubstantial benefits and helps attain competitive advantage.
Production Orientation
A business that implements and redirects business orientation to market orientation is able to directly assess the benefits that accrue to them. The several benefits that Boots will have implementing market oriented strategies are as follows;
Customer centric approach will help the company cater to customers better enhancing their levels of satisfaction and loyalty.
Boots stores are equipped and refurbished according to demands of customers such that adequate stock are replenished according to needs. This strategy helps addressing customer demands.
The customer loyalty program at Boots is made to increase buyer’s value, which in turn affects frequent shopping and customer loyalty.
The market oriented approach allows Boots to maintain competitive advantage over others. (Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson n.d.)
The marketing oriented strategies if applied efficiently can help the company yield adequate results and considerable market share. There are certain issues that are faced by the company while applying these strategies. Some of the challenges faced are as follows;
The cost for conducting market research and determining ways make business market oriented is hefty. The procedure to determine the technique is highly cost ineffective.
Customers often have to pay higher price for their desired product at Boots. As there is an available stock at Boots every time and customers get their desired product, the products are often priced at above market price tags.
In market orientation product development often varied customers have different choice leading to uncertainties in product development. (Škrinjar 2008)
Conclusion
Marketing is a critical aspect for every organization as its success depends on it. Boots is a leading retailer in UK providing varied products to its customers from health to beauty and skincare. The company is profitable sue to its dynamic marketing team and R&D team that functions hand in hand to develop strategies for efficient and effective policies for the company. The company has capability to becoming the top retailer in UK if it is able to adapt certain changes and innovative techniques to its current state of art processes. The company already enjoys a huge brand loyalty and has a million of satisfied customer base. The company has to constantly surge and keep innovating tactics and forms of marketing in order to emerge as a global player in pharmaceuticals, health and skin care brand. (Diffey 2009)
Akan, O, Allen, R, Helms, M & Spralls III, S 2006, 'Critical tactics for implementing Porter's generic strategies', Journal of Business Strategy, vol 27(1), pp. 43-53.
Allen, R, Helms, M, Takeda, M & White, C 2007, 'Porter's generic strategies: An exploratory study of their use in Japan', Journal of Business Strategies, vol 24, no. 1, p. 69.
Alon, I,JEAVD 2013, Global marketing: contemporary theory, practice, and cases, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Belz, FMAPK 2009, Sustainability marketing: A global perspective, Wiley, Chichester.
Best, RJ 2009, 'Market-based management: strategies for growing customer value and profitability', 2009.
Burt, G 2011, 'owards the integration of system modelling with scenario planning to support strategy: the case of the UK energy industry', Journal of the Operational Research Society, vol 62(5), pp. 830-839.
Buttle, F 2009, Customer relationship management: concepts and technologies, Routledge.
Diffey, B 2009, 'Spectral uniformity: a new index of broad spectrum (UVA) protection.', International journal of cosmetic science, vol 31(1), pp. 63-68.
Haq, F,WHYAJJ 2008, ' Applying Ansoff’s Growth Strategy Matrix to Consumer Segments and Typologies in Spiritual Tourism,’', In refereed paper presented at 8th International Business Research Conference.
Hill, C, Jones, G & Schilling, M, Strategic management theory: an integrated approach, Cengage Learning.
Hitt, M, Ireland, RD & Hoskisson, R, Strategic Management cases: competitiveness and globalization, Cengage Learning.
Lowy, AAHP 2011, The Power of the 2 x 2 matrix: Using 2 x 2 thinking to solve business problems and make better decisions, John Wiley & Sons.
Moon, J,GJP,GSAHC 2011, 'Management control for sustainability strategy', CIMA Research Executive Summary Series, vol 7(12), pp. 1-20.
Morgan, REABP 2008, 'Market Orientation, Generative Learning, Innovation Strategy and Business Performance Interâ€ÂRelationships in Bioscience Firms', Journal of Management Studies, vol 45(8), pp. 1329-1353.
Netessine, S & Tang, CS 2009, Consumer-Driven Demand and Operations Management Models, Spinger, Philadelphia,U.S.A.
Porter, ME 2008, Competitive strategy: Techniques for analyzing industries and competitors, Simon and Schuster.
Porter, ME 2008, On Competetion, Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation, United States of America.
Schermerhorn, J 2010, Exploring Management, 2nd edn, John Wiley and Sons, New Jersey.
Škrinjar, R,B-VVAI-ŠM 2008, 'The impact of business process orientation on financial and non-financial performance.', Business Process Management Journal, vol 14(5), pp. 738-754.
Spee, APAJP 2009, 'Strategy tools as boundary objects. Strategic Organization', vol 7(2), pp. 223-232.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2017). Marketing Orientation For Critical Tactics For Implementing. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/marketing-orientation-critical-tactics-for-implementing.
"Marketing Orientation For Critical Tactics For Implementing." My Assignment Help, 2017, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/marketing-orientation-critical-tactics-for-implementing.
My Assignment Help (2017) Marketing Orientation For Critical Tactics For Implementing [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/marketing-orientation-critical-tactics-for-implementing
[Accessed 23 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Marketing Orientation For Critical Tactics For Implementing' (My Assignment Help, 2017) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/marketing-orientation-critical-tactics-for-implementing> accessed 23 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. Marketing Orientation For Critical Tactics For Implementing [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2017 [cited 23 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/marketing-orientation-critical-tactics-for-implementing.