About Bharat Forge Limited
Question:
Describe about the Strategies of Bharat Forge Limited (BFL)?
Bharat Forge Limited (BFL) incorporated in year 19th June, 1961 in Mumbai is the global leader in manufacturing and metal forming and Flagship Company of Kalyani Group that values $ 2.4 billion. Based in Pune the Indian Multinational is a technology driven global leader in metal forming (Bharat Forge, 2015). The company serves various sectors that include oil and gas, automotive, locomotive, construction and mining, power, marine and aerospace. BFL with its biggest repository of metallurgical knowledge in the region offers its marquee customers that are geographically dispersed a full service supply capability in fields of engineering, product design, testing, manufacturing and validation. BFL is recognised as the world’s largest forging company that has its manufacturing facilities in India, France, Sweden and Germany (Bharat Forge, 2015). The company not only serve with automotive sector but also the non-automotive sector with its critical and safety components that deliver high performance. BFL is the world’s largest exporter and manufacturer of automotive components and unmatched expertise in manufacturing of chassis components.
Having achieved a remarkable success in automotive industry BFL is now looking ahead to redefine its presence in other business verticals like power, oil and gas, construction, aerospace and general engineering (Mukerjee, 2009). BFL’s huge metallurgical knowledge, manufacturing powers and design and engineering capability will serve as strong pillars to create a unique market position in these sectors. They look forward to transforming themselves from a global supplier of auto components to an engineering company that offer diverse services in different sectors. BFL has defined a clear vision of building a strong economical backbone for the country, strengthening capabilities of the nation and developing a larger global imprint not only for their company but for the whole country (Bharat Forge, 2015). BFL defines its core objectives as being committed while listening and responding to their customer, business partners and associates needs and treating their individual values with respect and integrity. BFL ensures to remain committed to their entrepreneurial spirit that is the key driving force behind an increase in shareholder value and unmatched growth.
BFL enjoys a large global market share with its customer base including almost virtually every automotive OEM and Tier 1 supplier globally (Mukerjee, 2009). World’s renowned automobile leaders like Toyota, Daimler, BMW, Chrysler, General Motors, Audi, Volkswagen, Volvo, Renault, Ford, Honda, Scania, Caterpillar-Perkins, Arvin Meritor, Iveco, Cummins, Detroit Diesel, Dana Corporation and several other market players source their most complicated forging requirements like front axle beams, machined crankshafts and steering knuckles from BFL (The Economics Times, 2012). The company’s unmatched capabilities to produce complex forgings of both aluminium and steel are its unique feature and serves as a competitive advantage against competitors. In its domestic market BFL is the largest manufacturer of crankshafts and producing 5,000,000 crankshaft forgings annually, enabling it to secure a rank of second largest producer of crankshafts in international market (Mukerjee, 2009). Effective leadership, competitive business strategies and a customer-oriented organisational culture and structure are the key reasons behind their global success.
Diverse Customer Base
Diversification: Diversification is the new growth strategy of BFL wherein they are looking ahead to expand in other business sectors in which they already have existing presence (Bharat Forge, 2014). The prime objective of diversification strategy is to enter non-automotive component business that will help them take advantage of opportunities offered by these sectors and de-risk the revenue model of the company (NDTV Profit, 2015). The company is formulating strategies to expand in sectors like railways, aerospace, oil and gas, power, construction and engineering. They are the first Indian company that is involved in the manufacturing of crankshafts for locomotive engines. They have a number of international clients however for the first time is eyeing to win a $100 million contract with Indian railways who has always imported its crankshafts. BFL recently has been working very closely with the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) and Diesel Locomotive Works to design crankshafts for domestic locomotive (Bharat Forge, 2014). As railway is a fast growing sector BFL is focusing all its strategies to tap the opportunities presented by the sector and are all concentrating on developing new products that meet customer requirements. They hope to achieve around 10 time growth within five years through their diversification strategies. BFL plans to diversify in 5-6 new sectors in coming five years and establish new verticals each of which will value $100 million.
Acquisition: BFL’s acquisition strategies helped them become the first company in Indian automotive component industry that adapted inorganic growth to expand globally (NDTV Profit, 2015). Their effective acquisition strategies helped BFL in accessing new geographical customers, enhance their technological capabilities and expand their product range. BFL in year 2004 acquired two companies based in Germany called Carl Dan Peddinghaus (CDP) and CDP Aluminiumtechnik that help them enhance their forging manufacturing capabilities (NDTV Profit, 2015). In year 2005 acquisition of Federal Forge presently known as Bharat Forge America Inc. helped them create a manufacturing presence in America which is its largest market (NDTV Profit, 2015). BFL is focusing on rapid global expansion while de-risking its business. BFL has already achieved market de-risking by increasing its global presence and its acquisition strategy will help in achieving product de-risking.
De-Risking: BFL aims at de-rising as a business strategy as it focuses on developing a new business model with diversified product profile as it moves to the non-automotive segment. Their long-term goal is to develop a business that is not dependent on a specific product, geography, industry segment or customer (NDTV Profit, 2015). The key objective of this strategy is to create inherent resilience so that the company can remain profitable irrespective of the pressure created by various macro economical cycles. BFL focuses to make future investments based on an asset light strategy (The Hindu, 2014). The company’s existing capacity seems to been enough in achieving desired goals in nest 2-3 years however in order to achieve long-term goals it is formulating strategies to enhance its capacities and create new capabilities. In order to secure a large market share in the new target market their strategies will emphasize on product development, developing a strong organisational framework, undergo product approval process and then start planning for a new facility based on outcomes. This strategy will not only help them achieve sustainable growth but will also generate comparatively high returns.
Diversification Strategy
Innovation: BFL has always been recognised as one of the most innovative organisations and their future strategies also focuses on innovation in product development being their path to achieve exponential growth (The Hindu, 2014). They have the required capabilities to manufacture innovative products and develop indigenous technologies. Their future growth strategy focuses on making huge investments on R&D in near future to deliver more value through their products and provide most innovative solutions to their customers. BFL considers its people as its most precious asset and the driving force behind innovation (NDTV Profit, 2015). It is planning to make investments to provide more learning and development opportunities to their employees by offering education programmes from the graduate level to the doctoral level (NDTV Profit, 2015). They aim to develop a highly competitive and skilled talent pool that will be responsible for handling company’s research and innovation needs.
Thus, diversification, acquisition, de-risking of revenue model and innovation are the four business strategies that will enable BFL achieve their vision and desired performance objectives.
Culture of an organisation refers to the shared beliefs and values that help framing the behaviour pattern of its employees (Hellriegel & John W. Slocum, 2011). Organisational culture helps ensuring that organisations will be able to achieve their desired goals and performance objectives by acclimatising employees and keeping them in-line. It determines the type of relationship that exists between organisation’s employees and its beliefs, values, principles, stories and norms (Fox, 2007). Organisational culture helps determining the quality of products and services offered by greatly influencing its overall performance effectiveness. Organisational culture also serves as a competitive advantage that rivals can never imitate.
Organisational cultures are of six types namely; Power culture wherein control is the key term and all decisions are made by top management, it is characterised by quick decision making however owing to low employee engagement and motivation it result in high employee turnover (Hellriegel & John W. Slocum, 2011). Role Culture wherein individuals are assigned specific roles, it helps ensuring all tasks are well allocated however employees are de-motivated because of limited development opportunities available to them. Task Culture wherein individuals are considered equivalent to machines and are judged on productivity not performance, in this case employees are comparative motivated as they are engaged however there is competition within the teams that create pressure on team members (Fox, 2007). Person Culture wherein high focus is given on employee training and development, it leads to high motivation but high investment is needed to conduct training programs. Entrepreneurial Culture wherein innovation and change are the key terms, it provides ample opportunities to employees who are highly motivated however it is associated with high risk (Hellriegel & John W. Slocum, 2011). Bureaucratic Culture wherein rules and procedures are key terms, changes and risks are avoided which increases longevity however it limits employee creative and does not favour innovation.
An analysis of different types of organisational culture reveals that Bharat Forge Limited (BFL) has developed an organisational culture that is a mix of person and entrepreneurial culture. They consider their people as their primary asset and always ensure that these assets are upgraded through various training and development programmes. Their organisational culture serves as a competitive advantage for them wherein in their values make them unique from other competitors. Spirit of innovation forms the heart of their organisation’s DNA and plays a vital role in delivering high value to their customers through complete focus on value addition and technology (Bharat Forge, 2015). Innovation and a risk taking attitude characterises their entrepreneurial culture that help them on their chosen path of diversification and manufacturing products that are of high quality and drivers change and sustainability (Bharat Forge, 2015). BFL under their effective leadership has developed a knowledge sharing culture wherein individuals are encouraged to openly share their views and actively participate in decision making.
Acquisition Strategy
BFL is a highly people-oriented organisation that treats its employees as their greatest assets and makes all attempts to nurture and develop them on a continuous basis which in turn help them retain their position as the world’s largest forging company. In year 2009, BFL was honoured with the National Award for “Best HR practices2009”. BFL greatly encourages diversity of workforce wherein they have developed a highly multi-cultural workforce across their facilities at multiple continents. They are recognised as a people company where people factor is designated highest priority. They have created a culture wherein people can realise their full potential and deliver their best performance while enjoying their work.
Organisational structure is the structural framework that determine hierarchical pattern within an organisation (Hellriegel & John W. Slocum, 2011). It defines the way tasks are allocated, coordinated and supervised within an organisation enabling it to achieve desired goals and performance objectives. There are three types of organisational structure however organisations can make variations to their structure as demanded by the situation.
Functional Structure: Based on the skills and specialisations of employees that are grouped into specific functional areas (Fox, 2007). This type of structure is greatly helpful in cases where cost-minimisation is a concern because their management and control is easy which in turn help improving efficiency. However lack of effective communication in this structure can lead to its failure making it difficult to achieve desired goals.
Divisional Structure: This structure enables large organisations segregate large sections of their business into semi-autonomous groups (Hellriegel & John W. Slocum, 2011). All these groups are treated as separate entity and have no control over functioning of other divisions. It comprises of various parallel teams that focus on single service line or product. This structure allows team to focus on single service or product with a leadership structure that assists in its main strategic objectives. However as it involves company’s own divisions competition with each other it gives rise to various conflicts like office politics, unfair allocation of resources etc.
Matrix Structure: This structure enable organisations define their reporting relationships in the form of a matrix or grid instead of a traditional hierarchy (Hellriegel & John W. Slocum, 2011). Thus, an employee need to operate under a dual reporting relationship generally both functional and product manager. The best advantage of this structure is efficient information exchange and high employee motivation. However it leads to high internal complexity and internal conflicts that are difficult to maintain.
An analysis of various organisational structures reveals that BFL displays characteristics of a functional structure wherein all employees are groups in specific functional areas based on their skills and specialisations (NDTV Profit, 2015). BFL have divided the employees into separate units based on roles and responsibilities as shown in figure below. They have different departments for different functions like marketing, engineering, sales, HR and finance (The Economics Times, 2012). Functional organisational structure enable BFL achieve high level of specialisation because each department is managed by a leader that had complete knowledge and expertise in that specific field. This structure is easy to manage and control because leaders can easily evaluate performances and plan improvements when required. This structure provided ample growth opportunities to employees which start their careers at entry-level position and grow to leadership positions by developing specialised knowledge (Hellriegel & John W. Slocum, 2011). This structure helps enhancing efficiency and productivity owing to the expertise gained by employees in their functional area. As the career paths in this structure are clearly defined employees are highly motivated to acquire new skills and expertise in their functional area that will help them achieve desired career goals. Highly motivated and skilled employees tend to perform better and display high productivity.
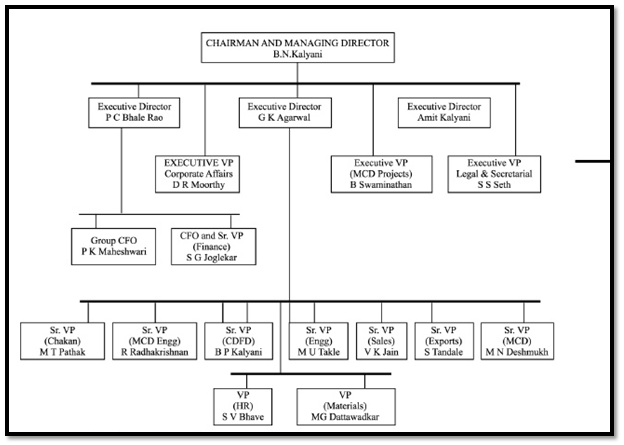
Fig.1. Source: The Economics Times (2012)
However, like all other organisational structure this structure also has some associated disadvantages like it fails to deliver desired results in absence of effective communication (Hellriegel & John W. Slocum, 2011). BFL has kept less hierarchical levels in their organisational structure keeping it somewhat flat in order to encourage open communication and knowledge sharing.
Conclusion
Organisational culture and structure are highly interrelated and greatly influence organisation’s overall performance efficiency and productivity. An entrepreneurial culture and functional organisational structure with less hierarchies has enabled BFL emerge as the world’s largest forging company that is recognised worldwide for its innovative products and solutions that help their clients handle most complex problems. Innovation is at the heart of BFL which is driving force behind all their strategies and support them in achieving desired goals and objectives. With an aim to diversify in other business sectors BFL under its effective leadership has developed a unique culture and structure that itself serve as a competitive advantage that cannot be imitated by rivals.
References
Bharat Forge, (2014) Bharat Forge hopes to bag orders worth a minimum of $100m from Indian Railways. [Online]
Available at: https://bharatforge.com/german/images/PDFs/news-events/PR_2013_1.pdf
[Accessed 2015].
Bharat Forge, (2015) Bharat Forge: About Us. [Online]
Available at: https://bharatforge.com/company/about-us.html
[Accessed 2015].
Bharat Forge, (2015) Spirit of Innovation. [Online]
Available at: Bharat Forge to bank on asset light strategy
[Accessed 2015].
Fox, W., (2007) Managing Organisational Behaviour. Cape Town: Juta and Company Ltd.
Hellriegel, D. & John W. Slocum, J., (2011) Organisational Behaviour. New York: Cengage Learning.
Mukerjee, (2009) Industrial Marketing. New Delhi: Excel Books India.
NDTV Profit, (2015) Bharat Forge Ltd.. [Online]
Available at: https://profit.ndtv.com/stock/bharat-forge-ltd_bharatforg/reports-chairman-speech
[Accessed 2015].
The Economics Times, (2012) Company History - Bharat Forge Ltd. [Online]
Available at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/bharat-forge-ltd/infocompanyhistory/companyid-13958.cms
[Accessed 2015].
The Hindu, (2014) Bharat Forge to bank on asset light strategy. [Online]
Available at: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/bharat-forge-to-bank-on-asset-light-strategy/article6313667.ece
[Accessed 2015].
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2016). Bharat Forge Limited - Global Leader In Metal Forming And Manufacturing. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-strategies-bharat-forge-limited-bfl.
"Bharat Forge Limited - Global Leader In Metal Forming And Manufacturing." My Assignment Help, 2016, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-strategies-bharat-forge-limited-bfl.
My Assignment Help (2016) Bharat Forge Limited - Global Leader In Metal Forming And Manufacturing [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-strategies-bharat-forge-limited-bfl
[Accessed 23 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Bharat Forge Limited - Global Leader In Metal Forming And Manufacturing' (My Assignment Help, 2016) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-strategies-bharat-forge-limited-bfl> accessed 23 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. Bharat Forge Limited - Global Leader In Metal Forming And Manufacturing [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2016 [cited 23 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-strategies-bharat-forge-limited-bfl.
