Australian Agricultural Company
Discuss about the Organization Structure for Australian Agricultural Company.
Beef livestock were brought into Australia in 1788 with the initial flock based on English breeds, specifically the Shorthorn. Through its early progress in cattle breeding, Zebu type livestock from India were introduced. It was followed by introduction of American Brahman breed in 1933 which established Australia as a prominent cattle producer. Several European breeds of cattle were introduced in Australia in the early 1970s. Currently, Australia has become one of the prominent exporters of beef in the world. Some of the major exporting companies of Australian beef industry are Japan, USA, China, Philippines, Taiwan, Korea, Russia, Indonesia and Chile (cattlecouncil.com.au 2016).
The company was established in 1824 as a land development corporation through aid of the British Parliament’s 1,000,000 acres in the Port Stephens locale of New South Wales Colony. In 1831, English Shorthorn breeds were imported to develop company’s flock. In 1850, company’s flock grew despite extreme stock losses, depressions and droughts. Its numbers of sheep grew up to 114,118, number of horses to 1,400 and number of cattle to 8,000. During World War I, the company moved away from wool production due to labor shortage and focused on increasing its cattle instead of sheep. They began to sell their southern states and moved north where they bought Headingly Station in Queensland in 1916, and in 1921 they bought Avon Downs in Northern Territory. The company introduced Santa Gertrudis breed in 1950. It further Introduced Brahman cattle in the company’s new property in Gulf region in the 1980s. Goonoo feedlot was created and developed around Comet River in Central Queensland in the mid 1980s to early 1990s. It had set up Set up a 17,500 capacity feedlot in 1994 and bought another breeding location in Northern Territory which facilitated them in specializing into cattle production for maintaining elevated growth rate. In 2006, they bought Westholme herd with an intention to shift into Wagyu breed to foster the growing success of renowned beef business and in 2014 they established Livingstone Beef, high-tech beef processing factory in Darwin. Currently, Australian Agricultural Company produces quality beef products for domestic consumption and exports (https://aaco.com.au 2016).
|
Chairman |
|
Managing Director & Ceo |
|
Directors |
|
Acting General Manager (Sales & Marketing) |
|
Company Secretary & General Counsel |
|
General Manager (Pastoral) |
|
General Manager (South East Queensland, Wagyu & Feedlots) |
|
Regional Manager (Barkly) |
|
Regional Manager (North Queensland & Victoria River Group) |
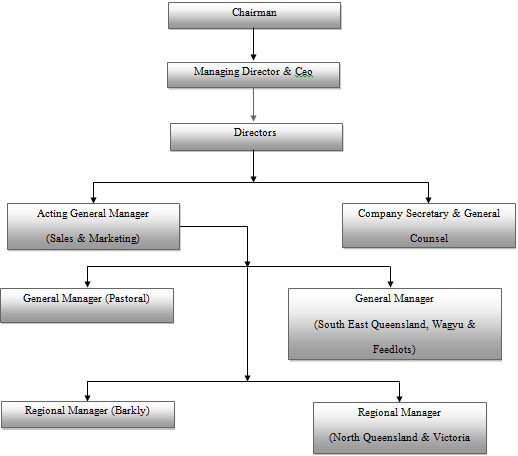
Figure: Organization structure
Source: (https://aaco.com.au 2016)
In today’s world, businesses require structure to survive competition. With a well organized structure, a business has clarity of its objectives and focus and every person employed in the organization are aware about their roles and responsibilities. Organization structure establishes a smooth flow of two way communications between the superiors and the sub-ordinates as the structure specifies the sub-ordinates about their immediate reporting heads. Structure is the basis of referring to a business as an organization. Organizational structure ensures a structured flow of control and delegation of authority, and it allows the organization to work more effectively and efficiently towards its goals (Csaszar 2013).
Importance of Organization Structure
It is a framework that encompasses various precise and understood organizational regulations and strategies planned to summarize the how various job roles and accountabilities are allocated, organized, coordinated and controlled. It also establishes how data flows through various levels within the organization. The organizational structure conveys lot about the nature of the organization and the value sets it has adopted. Hence, when an organization moves into a new business or industry, they always decide on the organization structure they are going to adopt for better results. In some exceptional cases, while the organization may be following a particular structure, the various departments within the organization may be following some other form of structure (Argyres and Zenger 2013).
A successful organization continuously defines the roles and responsibilities and how it matches the organizational requirements. Proper structuring provides an organization with a visible illustration of how it is formed and how it could move forward to achieve the organizational goals (Lunenburg 2012).
Australian Agricultural Company follows a divisional organization structure as their business is spread across various locations. Divisional organization structure is usually adopted by large scale companies that carry out their business spread across various geographic locations. This kind of organization structure consists of numerous teams aligned that are focused on a single product line. This structure offers the business a capability to separate large division of its business into semi-independent teams. These teams are self-administered and concentrated on products of the business (Fairfield 2016).
Divisional structure works well because it allows the team to concentrate on a single product with guidance structure that backs its chief premeditated objectives. Furthermore, it supports the organization towards building everyday customs that contributes to elevated employees’ morale and enhanced knowledge skill set (Alonso Dessein and Matouschek 2015).
The primary reason why the company uses divisional organizational structure is:
It is the most suited form of organizational structure for large scale business as it allows the company to stay focused towards their single product line. Large scale organizations have various business activities that are separated into various small divisions and are needed to be taken care of, for which functional organizational structure is not suitable as it leads to complicated communication and decision making process (Janićijević 2013).
It gives the organization a roadmap for achieving the predetermined organizational objectives as it helps in developing a smooth system for the flow of communication across various levels of the organization and defines the degree of control and delegation of authority.
Type of Organization Structure at Australian Agricultural Company
It gives the business the capability to separate large divisions of business to operate semi-autonomously under its umbrella.
When a business is spread across a vast geographic location, functional structure is not a feasible option for the organization because it gives them limited degree of control whereas divisional structure offers them high degree of control due to semi-autonomous nature of the divisions of the business (Galbraith 2014).
Divisional organization structure contributes to the expansion and growth of the organization as it facilitates development of all the divisions, the outcome of the divisions are evident and also helps in quick decision making (Tran and Tian 2013).
Leadership in an activity which involves establishment of clear vision, sharing the vision with team members so that they would follow voluntarily. Leadership involves providing knowledge, information and techniques through which the predetermined vision can be realized. Leadership helps in enhancing the level of balance and coordination among various team members and stakeholders. A leader is one who walks in times of crisis, and is capable of thinking creatively and act proactively in complex state of affairs (Tannenbaum Weschler and Massarik 2013).
Democratic leadership also known as participative leadership is defined as the leadership style where in a leader shares his decision making capability with other group members by encouraging them to give their valuable inputs. It is based on the principle that each and every member of a team should have an equal opportunity towards contribution of new and creative ideas. However, it should be noted that the authority of choosing an employee for being a part of the decision completely depends upon the leader (Raelin 2012).
We can say that Australian Agricultural Company essentially follows democratic leadership style because:
- It gives equal opportunity to people coming from different background and culture having different skill set, talent towards building a strong a responsible team.
- It promotes comprehensive workplace that welcomes diversity as a part of the work culture.
- It encourages its employees to apply their unique skills, talent, education and understanding to help improve company’s overall performance.
- It has a long history of promotion and development of its employees.
- It promotes the sense of responsibility among its employees by encouraging them towards adopting safer working methods.
- It encourages its employees and management’s involvement in the discussion process from all fronts of business.
- The company’s core values emphasizes on motivating its employees to work closely with the management in every parts of the organization.
- The company encourages team work by working collaboratively to achieve its vision and organizational goals.
- It has created calibration through sharing facts and ideas in an open, transparent and honest manner.
- It sets clear organizational goals and holds each other answerable for the consequences (https://aaco.com.au 2016).
Australian Agricultural Company’s shift from a low worth cattle company to a vertically incorporated and supply chain centric beef producer and marketer in the world is due to the various changes in its strategies that has paid off. The success of the company was largely due to the various strategic transformations that it undertook. Following are the strategies undertaken by the company:
Increasing Sales: Australian Agricultural Company has readjusted their corporate strategy by deciding to increase the value of their cattle by cutting down their live sales and emphasize on processing on their own renowned beef. The company has decided to sell more shortfed and Wagyu beef, and maintaining a steady breeding flock. These evaluations brought about a positive influence on the business. In 2014, beef sales accounted for 59 per cent of the total revenue; in 2015, beef sales accounted for 79 per cent of the total revenue; and in 2016, beef sales accounted for 88 per cent of the revenue (com.au 2016).
Leadership Style at Australian Agricultural Company
Operations: Australian Agricultural Company’s new business strategies have been backed by continuous improvement in its operations. It has invested a substantial amount on strengthening its supply chain network (com.au 2016).
Cattle Breeding and Genetics: The innovation team at Australian Agricultural Company works carefully with bull breeding division to run breeding program of global standards. They use innovative tools to make sure essential qualities are assessed with maximum precision possible under widespread production system (https://aaco.com.au 2016); (Grote Herstatt and Gemünden 2012)
Marketing: There has been a rise in the demand for high quality Wagyu beef brand in the international market. Some of the Asian countries have been witnessing a remarkable growth in the demand for beef. On the basis of the growing demand for the Wagyu beef brand, company seeks to grow its business on a global scale. The countries in which the company sells its high quality beef includes United States of America, Japan, China, Russia, Chile, Philippines, Taiwan, Korea. Further the company seeks to expand its market to various other European, South American and Gulf countries (https://aaco.com.au 2016).
Property Development Planning: The company responsibly chalks out their development plans by taking into consideration the facts such as capacity of the available natural resources. It also follows all the government regulations and complies with all the norms set by the government and cooperates with the investigation of certain technological advancements and unconventional practices (https://aaco.com.au 2016).
Diversification: The company’s decision to diversify their business strategy to shift from its primary production of cattle and focus on upright integration of their beef business incorporating succeeding processing and straight access to export markets specifically in Asia (com.au 2016).
Corporate Social Responsibility: As a part of their corporate social responsibility, the employees participate in community and provincial committees and organizations to improve community relationship and work together with the government undertakings, research groups, and various industry associations that focus on natural reserves management concerns and promote feasible agriculture (https://aaco.com.au 2016).
StructureThe company owns approximately 70 thousand square kilometers of land in Northern Territory and Queensland which is roughly 1 percent of Australia’s landmass and manages a livestock herd of almost 50,000 heads across various properties, feedlots and farms.
Considering the size of the company and its widespread location across Australia under various divisions engaged in breeding, finishing cattle, cultivating grains and food crops to assist cattle production, it can be said that the divisional organizational structure adopted by the company is going well because the structure has helped the company in establishing a clear framework to define the roles and responsibilities of each and every employee and has allowed them to focus on their predetermined objectives through delegation of authority. The above mentioned structure has facilitated in smooth flow of communication and quick decision making due to which it has grown up to become one of the largest beef producer of the world (Cummings and Worley 2014).
Company’s Strategies
In the current era, where there is a rapid transformation in the technology and remarkable demand for each and every product or service, it is very important for any organization whether large or small scale to adapt to the rapid technological transformations to match the growing demands of the customers. Australian Agricultural Company has also adapted to the constant changes within the industry by developing and applying new set of strategies to gain a competitive advantage over its competitors and increase its market share. It has invested substantial amount of capital into enhancement of genetics of its cattle breed. Livingstone Beef processing facility located nearby Darwin is high tech facility that has a capacity of processing 1000 heads of cattle per day mainly aimed at producing beef for exports. It has integrated all its divisions closely to enhance its supply chain management (https://aaco.com.au 2016).
Conclusion
Australian Agricultural Company is one of the finest beef producing company of Australia mainly focused at exporting its high quality Wagyu beef brand and other beef brands to some major beef consuming countries namely USA, Japan, China, Chile, Korea, Russia, Philippines, Taiwan and many other countries.
The company has adopted divisional organizational structure as it facilitates a better and smooth flow of communication among various levels of the organization and well-defined roles and responsibilities of each employee. It follows a democratic leadership style where it encourages its employees to be a part of the discussion in the decision making process. To sustain the growing competition and to meet customer’s demand it has made certain strategic changes by adopting new technologies in production system, advanced cattle breeding and genetics techniques, closely integrating all its functions and divisions to enhance its supply chain capabilities.
References
Alonso, R., Dessein, W. and Matouschek, N., 2015. Organizing to adapt and compete. American Economic Journal: Microeconomics, 7(2), pp.158-187.
Argyres, N. and Zenger, T.R., 2013. 12. Dynamics of organizational structure. Handbook of Economic Organization: Integrating Economic and Organization Theory, p.210.
aspecthuntley.com.au. (2016). asxdata/20160610/pdf/01748186.pdf. [online] Available at: https://www.aspecthuntley.com.au/asxdata/20160610/pdf/01748186.pdf [Accessed 17 Sep. 2016].
businessnewsaus.com.au. (2016). articles/aaco-profit-charges-ahead-with-supply-chain-strategy. [online] Available at: https://www.businessnewsaus.com.au/articles/aaco-profit-charges-ahead-with-supply-chain-strategy.html [Accessed 17 Sep. 2016].
cattlecouncil.com.au. (2016). assets/Beef%20Fast%20Facts%202013_EMAIL.PDF. [online] Available at: https://www.cattlecouncil.com.au/assets/Beef%20Fast%20Facts%202013_EMAIL.PDF [Accessed 17 Sep. 2016].
Csaszar, F.A., 2013. An efficient frontier in organization design: Organizational structure as a determinant of exploration and exploitation.Organization Science, 24(4), pp.1083-1101.
Cummings, T.G. and Worley, C.G., 2014. Organization development and change. Cengage learning.
Fairfield, K.D., 2016. Understanding Functional and Divisional Organizational Structure A Classroom Exercise. Management Teaching Review, p.2379298116661843.
Galbraith, J.R., 2014. Designing organizations: strategy, structure, and process at the business unit and enterprise levels. John Wiley & Sons.
Grote, M., Herstatt, C. and Gemünden, H.G., 2012. Crossâ€ÂDivisional Innovation in the Large Corporation: Thoughts and Evidence on Its Value and the Role of the Early Stages of Innovation. Creativity and Innovation Management, 21(4), pp.361-375.
https://aaco.com.au/. (2016). about-us/our-history/. [online] Available at: https://aaco.com.au/about-us/our-history/ [Accessed 17 Sep. 2016].
https://aaco.com.au/. (2016). people-careers/working-with-aaco. [online] Available at: https://aaco.com.au/people-careers/working-with-aaco/ [Accessed 17 Sep. 2016].
Janićijević, N., 2013. The mutual impact of organizational culture and structure. Ekonomski Anali/Economic Annals, 58(198), pp.35-60.
Lunenburg, F.C., 2012. Organizational structure: Mintzberg’s framework.International journal of scholarly, academic, intellectual diversity, 14(1), pp.1-8.
Raelin, J.A., 2012. Dialogue and deliberation as expressions of democratic leadership in participatory organizational change. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 25(1), pp.7-23.
Tannenbaum, R., Weschler, I. and Massarik, F., 2013. Leadership and organization. Routledge.
theaustralian.com.au. (2016). business/business-spectator/aaco-to-diversify-strategy/news-story. [online] Available at: https://aaco.com.au/. (2016) [Accessed 17 Sep. 2016].
Tran, Q. and Tian, Y., 2013. Organizational structure: Influencing factors and impact on a firm.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2018). The Essay On Organization Structure Of Australian Agricultural Company Is Concise.. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organization-structure-australian-agricultural-company.
"The Essay On Organization Structure Of Australian Agricultural Company Is Concise.." My Assignment Help, 2018, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organization-structure-australian-agricultural-company.
My Assignment Help (2018) The Essay On Organization Structure Of Australian Agricultural Company Is Concise. [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organization-structure-australian-agricultural-company
[Accessed 30 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'The Essay On Organization Structure Of Australian Agricultural Company Is Concise.' (My Assignment Help, 2018) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organization-structure-australian-agricultural-company> accessed 30 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. The Essay On Organization Structure Of Australian Agricultural Company Is Concise. [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2018 [cited 30 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organization-structure-australian-agricultural-company.
