Supplier Selection Criteria at Rolls-Royce Ltd
Question:
Write a report about the purchasing management.
The study shows the conceptualization of the various techniques used in purchasing management. The discussions of the report involves the process of selection of the suppliers and relative sourcing of the suppliers such as single, multiple, local and overseas sources. The study further shows the details of the purchasing costs involved in the project and implementation of information and communication technologies (ICT) for the purpose of managing activities related to purchasing operations. The study shows the justification of the order cycle of the customers and supplier selection criteria
The organization selected for the purpose of study is “Rolls-Royce Limited”. The company is known for its elite class of British car models. The company later on started with the manufacturing of aero plane engines. The main operating areas of the company lies in civil defense, power systems and areas related to nuclear resources. Due to presence of wide variety of segments of the company, suppliers need to cope up with the variety of requirements of the company. The supply chain division of Rolls-Royce buys various commodities such as combustion and casings, compressors, turbines, corporate service and facilities management. The supplier of the company is based on the most potential individuals who engage themselves in fair trade policies along with transparent selection of the manufacturing parts. The company also engages in issuing notice to the suppliers regarding fair trade policies related to prevention of counterfeit parts into its products. The marine supply chain of the company is based on offshore supply service. Rolls-Royce is known for manufacturing one of a kind engine used in its Olympus and Concorde models. The primal competitor of the company is General Electric which is leading the market due to the cost effectiveness, efficiency and speed in their car models. Some of the other competitors of the company include UTC aerospace, Honeywell and Pratt Whitney. The goals and vision of the company is to provide the most advanced technological solutions in air as well as sea (The Rolls-Royce Story. 2016).
According to Chai & Ngai (2013), a company selects the suppliers based on the following criteria:
- Identification Process: This stage involves the preparing the list of potential suppliers.
- Performance assessment: The next stage followed by identification of the suppliers is based on the comparison of the available suppliers and selection of the potential supplier based on the information gathered.
- Approving the suppliers: This factor identifies the suppliers which are appropriate to take the orders. The sourcing of the eligible suppliers of the company is based on the nature of commodity which is being ordered as per requirement.
- Surveillance: The real time surveillance of the activities of the suppliers ensures improvement in the performance level. The rating system top select the suppliers is based on scorecard.
An example of vendor scorecard and criteria for selection of the suppliers has been shown below as follows:
|
Scorecard Dimension |
Explanation |
Weight |
A 100% |
B 75% |
C 50% |
D 25% |
F 0% |
Vendor Scores |
|
Costs/Pricing |
30% |
18% |
||||||
|
Terms of payment |
Vendor ranked based on terms of payment |
15% |
B |
|||||
|
Pricing of products |
Comparing the pricing based on alternatives |
10% |
>3.5% Less Than Average |
Average +/- 1.5% |
>3.5% More than Average |
>6% More Than Average |
>11% More Than Average |
C |
|
Pricing Metric |
Cost/Pricing |
5% |
D |
|||||
|
Supply Chain |
30% |
17% |
||||||
|
Weighted Average Lead Time |
Duration from point of acceptance |
15% |
D |
|||||
|
Response time of email for purchasing |
Time to respond to the emails |
3% |
A |
|||||
|
Communication Quality - Purchasing |
Quality communication through mail |
3% |
Clear Communication |
Moderate understanding of the responses |
Response difficult to understand |
A |
||
|
Flexibility |
Accommodation of additional business request |
3% |
Ease of handling Special requests |
Moderate handling of special requests |
Special request not accepted |
C |
||
|
Late Orders |
Late purchase orders |
6% |
0 |
1+ |
A |
|||
|
Quality |
20% |
10% |
||||||
|
QC Issues |
Definition of QC Issues Metric |
10% |
A |
|||||
|
Quality Metric 2 |
Definition of Quality Metric 2 |
10% |
F |
|||||
|
Product Development |
20% |
17% |
||||||
|
PD Metric 1 |
PD Explanation 1 |
10% |
A |
|||||
|
PD Metric 2 |
PD Explanation 2 |
5% |
B |
|||||
|
PD Metric 3 |
PD Explanation 3 |
5% |
B |
|||||
|
Total |
100% |
62% |
The high risks are associated with the unique requirements of the products, irregular availability of the same are essential. The technology level of the supplier acts as a bottleneck to the company. The risk of storage of materials is also a matter of concern.
According to Heese (2015), based on the variety of products of the company in several departments it will be most appropriate to select multiple sourcing of the suppliers. This form of sourcing is considered to be less risky and assures a continuous flow of the supply of required materials. This particular form of practice will ensure that multiple suppliers are dealt efficiently thereby avoiding the dependence on a single customer. Multiple sourcing also offers greater flexibility in terms of volume ordered for supply. As Rolls-Royce requires the products to be prepared for different segments, this form of sourcing ensures availability of core raw materials for the unique requirements. The new entrants in the supply market are given an opportunity with this particular form of sourcing (Dotoli & Falagario 2012).
Sourcing Strategies and Purchasing Costs
The Kraljic matrix is a useful tool for making purchasing decision based on strategic positioning. The purchasing portfolio based on the Kraljic matrix is shown below as follows:
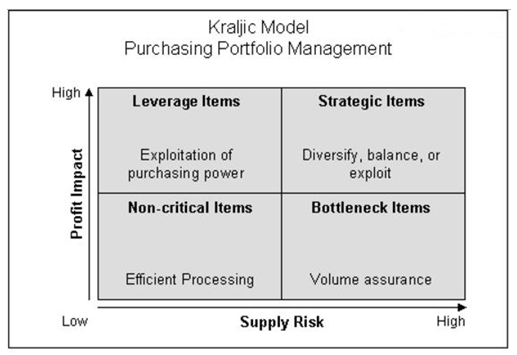
Source: B.V. (2016)
The purchasing goals of Rolls-Royce are based on the best industry practice. The purchasing operations are worked together in global teams. The purchasing team ensures that the values are not compromising on the quality aspect. In order to effectively deliver the values, the company spends billions for the service and quality aspect. Rolls-Royce puts an augmented focus on the economic forces abiding the market before placing purchasing orders. The strategies are aimed to focus on a lean supply chain solution with significantly reducing the waste and adaptation of the most advanced technologies to stay cost competitive throughout the supply chain process (Purchasing, 2016).
The process of communication at various levels of the purchasing decisions is driven by the Internet communication technology (ICT). The importance of ICT is due to three main factors. The first being it allows the companies to exchange important information with the trading partners in a foster and easier way than the traditional means of media. The second most important aspect of ICT has been seen in the cost-effectiveness of electronically enabled communication techniques such as facts and electronic data interchange. The aforementioned technology also allows the company to customize the availability of information that is relevant to the specific trading partners. This allows the trading partners to obtain the most relevant knowledge on the computer systems (Prajogo & Olhager 2012).
The Internet communication model to facilitate the purchasing performance has been shown below as follows:

Figure 2: Internet Communication Model
(Source: Bascand, 2013)
According to Wisner & Leong (2015), the use of Internet communications technology for the purpose of effective supply-chain management in Rolls-Royce the participants involved in the purchasing decision can effectively communicate about the orders. It is considered as more convenient, cheaper and the trading partners can shared the real-time information without mentioning about specific time, date and type of information shared between them. The use of Internet communications technology in Rolls-Royce important integrated the various supply chain activities through enterprise resource planning, customer relationship manager and supply relationship model (Sharif et al., 2013).
As discussed by Prajogo & Olhager (2012), the enterprise resource planning refers to the amalgamation of the various departments of the supply chain such as procurement of raw materials, purchasing, planning and vendor sourcing. With ICT the aforementioned activities becomes not only easier to implement but also monitor the same. Hence managing of resources, operations, logistics and customers requires immediate access to data and information that only information technology can offer. Supply-chain of Rolls-Royce needs to meet the challenges of the present and future. Some of the important aspects of supply-chain decisions influence the sustainability, consumer safety, and supply chain security, legal and ethical behaviors. These are not only expected or demanded by consumers and the government worldwide, these are the factors which can only be effectively managed, monitored and realized through effective use of Internet communication technology. Even at the lowest levels of Rolls-Royce the individual supply-chain managers are tested for measuring performance, improving supply chain visibility and managing relationships with the vendors are dependent on the information technology. Therefore it is crucial for the company to maintain a healthy relationship with the information technology department of Rolls-Royce for making the supply-chain more responsive globally. The most important aspect of the Internet communication technology is related to the fact that ensures the company to make the fastest purchasing decisions (Fitzsimmons & Fitzsimmons 2013).
Information and Communication Technologies in Purchasing Operations
Total cost ownership
Cost analysis of the company is done with various cost management tools. Total cost ownership (TCO) is one such concept which can identify the several costs related issues. This allows the company to know about the requirements of the cost involved in the supply chain activities. This approach of costing not only considers the purchasing price but it also includes cost related inbound transportation, follow-up, administrative expenses and expediting. it also takes into consideration cost related to inspection and testing of the raw materials before it arrives for assembling. Several other factors such as downtime, storage, warranty, customer returns and service cost is also estimated in this particular approach. The main objective of the total cost of ownership is not only to compare the prices but it also determines areas to minimize the cost and lowering the cost of each cost element as much as possible (Monczka et al., 2015).
According to this model the total cost of ownership is only a part associated procuring a service. The major focus of this approach is to identify those costs, which directly affect the decision-making process in the supply-chain activities. Hence, this particular model is applicable to highlight the cost reduction opportunities and improve the evaluation and selection criteria of the suppliers (Al-Alawi & Bradley, 2013).
This particular costing system is most appropriate for meeting the costing requirements of the diversified segments existing in Rolls-Royce. The traditional approach of cost accounting ideally considers only the direct costs, which are associated to the actual expenditures. Activity-based costing method identifies the cost drivers for the various indirect costs and tries to translate them into direct costs. The main challenge of this approach lies in identification of the various indirect costs and putting them into cost activity pool of the cost drivers. The manufacturing costs of the company are segregated costs, which respond to the changes in unit level activities i.e. changes based on the quantity produced. It also comprises of the batch level activities which are directly related to total number of batches of the units produced. Lastly the manufacturing overhead takes into account the product level activities, which proved to be beneficial for all the units of the equipments (Schulze & Ewering, 2012).
The models of activity-based costing based on the transformation process of the various indirect costs are shown below as follows:
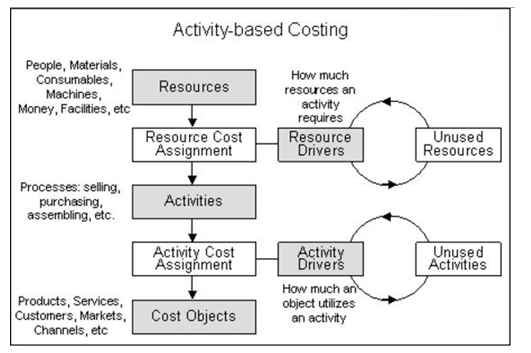
Figure 3: Activity Based Costing
(Source: Activity Based Costing Knowledge & Beyond, 2016)
Activity-based costing can be beneficial for facilitating a better marketing mix, accurate prediction of costs, tracks the requirement based on the changes in quantity produced, changes in cost due to organizational structure and identifying the cost activities of the different work processes. This particular method of costing is often useful to know the reason behind poor financial performance of an organization (Mansor et al. 2012).
Conclusion
The purchasing activity discussed in this report has a critical role for achieving a sustainable future for Rolls-Royce limited. The ease of procurement and selection of suppliers will ensure that the organization is able to achieve the best manufacturing process in the car making industry. Due to the variety in the services and strategic considerations multiple sourcing is best suited to meet the procurement goals. From the various findings of this can be stated that the sourcing criteria of the company gives a major focus on the quality of the parts used in its manufacturing process. Internet communication and technology can further enhance the decision-making process the purchasing operations. The advent of advanced technologies such as RFID tags and GPS tracking system ensures a real-time communication with the suppliers and electronically monitor the enterprise resources. The cost analysis section of the report considers two major costing tools. The total cost of ownership approach is not only useful track the opportunities for cost reduction but also aids the selection criteria of the suppliers. The activity-based costing ensures the appropriate translation of the indirect expenses of the various supply chain costs thereby providing a fair cost analysis.
Reference list
Activity Based Costing | Knowledge & Beyond. (2016). Knowledge & Beyond. Retrieved 11 June 2016,
Al-Alawi, B. M., & Bradley, T. H. (2013). Total cost of ownership, payback, and consumer preference modeling of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Applied Energy, 103, 488-506.
Bascand, G. (2013). Household use of information and communication technology: 2012.
B.V. (2016). Kraljic Model - Knowledge Center. 12manage.com. Retrieved 11 June 2016,
Chai, J., Liu, J. N., & Ngai, E. W. (2013). Application of decision-making techniques in supplier selection: A systematic review of literature. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(10), 3872-3885.
Dotoli, M., & Falagario, M. (2012). A hierarchical model for optimal supplier selection in multiple sourcing contexts. International Journal of Production Research, 50(11), 2953-2967.
Fitzsimmons, J., & Fitzsimmons, M. (2013). Service management: Operations, strategy, information technology. McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
Heese, H. S. (2015). Single versus multiple sourcing and the evolution of bargaining positions. Omega, 54, 125-133.
Mansor, N. N. A., Tayles, M., & Pike, R. (2012). Information Usefulness and Usage in Business Decision-Making: An Activity-Based Costing (ABC) Perspective. International Journal of Management, 29(1), 19.
Monczka, R., Handfield, R., Giunipero, L., & Patterson, J. (2015). Purchasing and supply chain management. Cengage Learning.
Prajogo, D., & Olhager, J. (2012). Supply chain integration and performance: The effects of long-term relationships, information technology and sharing, and logistics integration. International Journal of Production Economics, 135(1), 514-522.
Prajogo, D., & Olhager, J. (2012). Supply chain integration and performance: The effects of long-term relationships, information technology and sharing, and logistics integration. International Journal of Production Economics, 135(1), 514-522.
Purchasing. (2016). Rolls-royce.com. Retrieved 10 June 2016,
Schulze, M., Seuring, S., & Ewering, C. (2012). Applying activity-based costing in a supply chain environment. International Journal of Production Economics, 135(2), 716-725.
Sharif, A. M., Alshawi, S., Kamal, M. M., Eldabi, T., & Mazhar, A. (2013). Exploring the role of supplier relationship management for sustainable operations: an OR perspective. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 65(6), 963-978.
The Rolls-Royce Story. (2016). Rolls-roycemotorcars.com. Retrieved 10 June 2016,
Wisner, J., Tan, K. C., & Leong, G. (2015). Principles of supply chain management: a balanced approach. Cengage Learning.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2017). Purchasing Management Techniques: A Study Of Rolls-Royce Ltd. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/purchasing-management.
"Purchasing Management Techniques: A Study Of Rolls-Royce Ltd." My Assignment Help, 2017, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/purchasing-management.
My Assignment Help (2017) Purchasing Management Techniques: A Study Of Rolls-Royce Ltd [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/purchasing-management
[Accessed 07 June 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Purchasing Management Techniques: A Study Of Rolls-Royce Ltd' (My Assignment Help, 2017) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/purchasing-management> accessed 07 June 2025.
My Assignment Help. Purchasing Management Techniques: A Study Of Rolls-Royce Ltd [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2017 [cited 07 June 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/purchasing-management.
