Objective of the Study
Question:
Describe about the Correlation between Activity Based Costing with the Financial Performance of in Case of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises (SME) in United Kingdom?
The study investigates the correlation between activity based costing and the improvement of the financial performance of the firm. The impact of activity based costing on the financial performance of the firm has been studied in small and medium sized manufacturing organizations. Activity based costing can increase the production process efficiency, cost advantage and proficiency of product planning and improvement of the financial performance. The effectiveness of ABC includes the fitness of the cost drivers, accuracy of cost calculation, credibility of cost information and cost reporting usefulness. The results show that ABC effectiveness is significantly and positively correlated with the improvement of the return on investment. It is also positively correlated with the other strategic initiatives of the organization.
1.1. Introduction
Activity based costing has been adopted for strategic decision making of the organization for improving the profit performance of the organization. According to Kaplan (1990), ABC information is used widely by the organizations in UK for the assessment of the continuous improvement of the organization and to monitor the process performance of the organization (Evaluating and Improving Costing in Organizations, 2009). ABC is a widely accepted cost management system of the organization (Askarany, n.d.). Although there is significant diversity of opinion regarding the efficacy of the cost management system, it is widely used cost management system (Schiffauerova & Thomson, 2006). In order to overcome the over generalizations of the traditional system of costing and excessive simplified allocation of costs and lack of visibility for the indirect costs, organizations have adopted the activity based costing system (Unland, 1997). The activity based costing system is based on cost model that trace the expense of the organization (both direct and indirect) that has been made to the products , services and customers (Porter & Kehoe, 1993) ; (Kinney & Raiborn, 2009).
There has been rapid change of the environment around the companies. In the present era of global competition, evolving technological environment consumers are demanding products at lower prices with superior quality (Lewis, 2005). This has resulted in aggressive pricing of the products. The increase in level of global competition have been complemented by the shortening the life cycle of the products (Horngren, Oliver & Harrison Jr., 2015). The changes have influenced the managers to seek new strategies and re organize new techniques or innovations and adoption of a more complex cost management system in order to continuously improve the performance of the organization along with growth in the profitability (Rojas, 2015); (Cooper and Kaplan, 2015). The sophisticated cost management system increases the competitive advantage of the organization in terms of cost, quality and management of the performance of the firm (Cooper & S. Kaplan, 2015). The traditional cost management system provides inadequate information for today’s global and technological environment (Garrison, Noreen and Brewer, 2007). In order to achieve the goal, the organizations has adopted the advanced process of cost management techniques like activity based costing for the improvement of the process and financial performance of the organization (Management Accounting Research, 2000). It improves the competitiveness of the organization and results in sustainable development (Kaplan & Anderson, n.d.). The core idea behind activity based costing is production of products and services that generates activities which consumes resources (Kfknowledgebank.kaplan.co.uk, 2015) .
Effectiveness of Activity Based Costing
1.3.1. Aims of the Research
The aim of the research is to identify whether the increasing use of ABC is directly associated with the improvement of the financial performance of the organization. The relation between the use of ABC and improvement of the financial performance of the organization is not considered in regard to the firm or industry specific environmental conditions.
The objectives of the research will give the research right direction. The objectives of the research are given below –
1. To identify whether there is positive association between the extent of the use of ABC and relative improvement in the financial performance of the organization.
2. To identify the impact of specific enabling factors in association between the extent of use of ABC and the relative improvement of the financial performance of the organization.
3. To identify whether the relative improvement in the financial performance of the organization is associated with the level of success of the ABC.
1. Is there any positive association between the extent of use of ABC and the relative improvement of the financial performance of the organization?2. What is the impact of the specific enabling factors on the use of ABC and the relative improvement of the financial performance of the organization?
3. What is relation between the improvements of the financial performance with the level of success of ABC?
The traditional system of costing use over generalizations as the cost allocations in the traditional system of costing is over simplified in nature and there is lack of visibility for the indirect costs. Thus it is essential for the organizations to adopt activity based costing techniques. The activity based costing is based on the cost model which traces the expense of the organization directly and indirectly that has been allocation to products, services and channels. The impact of activity based costing on the financial performance of the organization has been studied in small and medium sized organizations.
The correlation of activity based costing with the financial performance of the organization has gained importance. In the increasingly competitive environment of business, the organizations have to improve their competitiveness by enhancing the accuracy of their cost information. The accurate cost information reflects the cost of the products and services. Thus it is important to analyze the correlation between activity based costing and the financial performance of the organization in the changing business scenario.
In the present study the impact of activity based costing on the small and medium sized manufacturing organizations has been studied. In the global market place the manufacturing firms are facing increasing competition (Anderson & Young, 1999). There is burden on the companies to manufacture high quality products that is successful in the new changing environment (Malmi, 1999). In this changing scenario, the traditional system of costing has lost relevance in the manufacturing environment as there has been significant rise in overhead and reduction in direct labor. The traditional costing system has a distorting effect on the cost of the products and lead to poor strategic decision making. One of the innovative methods that has been designed to deal with the deficiencies in the traditional system of costing; the activity based costing has found significance (Gunasekaran & Sarhadi, 1998).
Activity Based Costing in Manufacturing Environment
The current research is divided into six chapters that together analyze the research. This will help the researcher to arrive at a desired conclusion. The standard structure of the research has been followed by the researcher to meet the requirements of the research to ensure the transparency and reliability of the study. This will ensure an easy interpretation of the research. The chapters are described below –
The first chapter provides a brief introduction of the research. The objectives of the research have been determined by the researcher. The background and rationale of the research has been provided. The research questions are determined to support the objectives of the research that will drive the research to the right direction.
The second chapter is the literature review chapter. The theories of the topic and the implementation of the theories have been discussed in this chapter. Suitable ideas and principles of the research topic have been discussed. The theories are mentioned and evaluated to determine the gap between the theoretical evidences and the implementation of the theories in real life.
The third chapter is the research methodology chapter. The hypothesis of the research has been discussed in this chapter. The author has selected appropriate methods to answer the questions of the research.
The fourth chapter focuses on hypothesis testing. The positive association of activity based costing on the improvement of the return on investment has been tested.
The fifth chapter has explained the findings of the testing. The researcher has analyzed the results obtained to arrive at a suitable conclusion.
Globalization has increased the importance of use of modern techniques of cost management. The traditional cost management system does not provide accurate information of the cost of the organization. In this context activity based costing has found importance. The correlation of activity based costing with the financial performance of the organization has been studied in small and medium sized manufacturing organizations in UK.
Activity based costing has received great deal of attention as a cost management innovation. According to Cooper (1990) , activity based costing is necessary to trace the overhead costs to the cost objects and thus it is essential to account for the batch and product level costs. It has been argued by many researchers that activity based costing is effective in specific environmental conditions like in case of a complex manufacturing organization and environments with specialty product costs (Ittner, Lanen & Larcker, 2002). It is also applicable in diverse business environments (CLlarke, Hill & Stevens, 1999). Although the association of activity based costing is seen mostly with the manufacturing organizations, they can be applied in all organizations. The theories of diffusion of innovation, transaction cost economics and information technology has suggested that organization adopt innovation such as ABC to obtain benefits directly or indirectly that affect the financial performance of the organization (Malmi, 1997). Activity based costing has been used by organizations for strategic decision making of the organization (Anderson and Young, 1999). The success of an organization depends on application of appropriate strategic options. Drake et al. (1999), found that innovative activity based costing can produce either a higher or lower level of profit when the workers of the organization use activity based costing (Cagwin & Bouwman, 2002).
Traditional System of Costing vs Activity Based Costing
Activity based costing improves the effectiveness of the financial performance of the organization (Neely, Gregory & Platts, 1995). The four components of the effectiveness of activity based costing are cost driver fitness, accuracy of cost calculation , credibility of cost information and usefulness of cost reporting which result in increase in the revenue and profitability of the organization (Ittner & Larcker, 2001). It results in efficiency of the production process, cost advantage and product planning that leads to superior performance of the organization (Cagwin & Bouwman, 2000).
ABC is a more accurate form of costing that is used to price the products and services than the traditional costing system (Dekker & Van Goor, 2000). Activity based costing helps the manager to analyze the various factors that lead to cost and how it is managed (Gosselin, 1997). ABC provides timely, accurate and quality cost information which is essential for the continuous improvement of the process performance of the organization (BaykasoÄŸlu & KaplanoÄŸlu, 2008).
The four components of the ABC effectiveness include cost driver fitness, cost calculation accuracy, cost information credibility and cost reporting usefulness.
Cost driver fitness refers to the various factors that is assigned to activity based costing to correlate the various activities for easy measurement and convenience for actual practice. The objective of ABC is to provide accurate information of the various costs of the organization by using the various cost drivers to assign activity costs to the products and services (Rajan et al., 2014). The costs drivers have cause and effect relationship between the amount of indirect costs that has been attributed to the products and services and the consumption of resource by the products and services via the various activities that have been performed (Reyhanoglu, n.d.). The cost driver fitness is useful for the managers for the preparation of budget and measurement of performance of the organization as the activity based budgets are essential for the preparation of objectives of each activity that assess the future need of the resources of the organization (THANH HOA, 2010).
Cost calculation accuracy refers to the ability of the organizations to allocate the indirect costs of the products and services on the various activities performed that used multiple cost drivers. The costs are calculated by ABC by linking the expenditure to the various activities. Multiple cost drivers used for cost calculation reduce the risk of distortion and provide accuracy in calculation of cost (Kaplan & Anderson, 2007).
The managers can identify the potential problems as well as the opportunities in the organization using the cost information that will help them in taking more informed decisions (EmblemsvaÌŠg, 2003). The ABC cost information creditability enables the managers to oversee the activities and process of the business by giving a cross functional and integrate view of the organization. This will support the strategic and operation decisions of the organization in various ways like product lines, segments of the market, customer relationship and improvement of the process. The accurate and reliable information provided by ABC assists in strategic decision making in terms of the product mix, pricing and improvement of the process and evaluation of the business performance (Goddard & Ooi, 1998).
ABC cost reporting is used for understanding, evaluating and improving the job performance for better decision making and gain competitive advantage over the competitors. The cost reporting of ABC is used to promote and enhance the understanding of the various activities performed and contribute to the improvement of the performance of the organization (Sohal & Chung, 1998). Cost reporting is used to monitor the activities of the organization such as planning, scheduling of the work activities, assigning the tasks and clarification of the objectives and priorities of the organization (Mitchell, 1994).
The effectiveness of activity based costing is based on the cost driver fitness, cost calculation accuracy, cost information credibility and cost reporting usefulness. Cost driver fitness and cost calculation accuracy helps to analyze the various costs of the organization and the identify the costs that are accurate. In addition to this cost driver fitness and cost information credibility will analyze the various costs, labor time, utilization of raw material, production time and reduce the wastage of the raw material and identification of the value added and non value added activities. The efficiency of the production process can be improved by using the cost reports of each activity, material used in the production process and analysis of the activities (Anderson, Hesford & Young, 2002).
Activity based costing can be used to analyze the procurement cost of raw materials , manufacturing cost and maintenance cost and costs related to packaging and transportation (Asif, Joost de Bruijn, Douglas & Fisscher, 2009). Cost analysis of every activity results in reduction of the cost at each stage. In the competitive working environment in a turbulent economy it is important to have a superior cost control system with coherent performance measurement (Kirche, Kadipasaoglu & Khumawala *, 2005).
Activity based costing results in improving the financial performance of the organization in terms of increase in the revenue, profit and market position (Clancy, 2007). ABC can get cost information credibility to take management operating decision. ABC is used in corporate cost control and customer profitability (Kennedy & Affleckâ€ÂGraves, 2001). Activity based costing assist the managers in better decision making that provides support to the pricing strategies (Tangen, 2004).
The complexity of the manufacturing organizations has increased. The management of the manufacturing organizations today is possible with relevant , accurate information that is readily available. The cost information is essential to operationalise the functional strategies and make informed decisions on the product mix and cost of the products. In the manufacturing organizations, the activity based has emerged as an alternative to the conventional system of costing. It is seen that activity based costing is more beneficial when it is implemented in advanced manufacturing practices. ABC helps in the identification and measurement of the cost drivers associated with the value added and non value added manufacturing activities which makes it easier for the adoption of cost control and allocation of the resources that is essential for the implementation of manufacturing process (Herath, Wickramasinghe & Indrani, 2010). The manufacturing process in the organization has changed to a large extent. In the world class manufacturing environments there has been significant change in the accounting system, compensation and incentive structure and performance measurement (Tornberg, Jämsen & Paranko, 2002). The traditional manufacturing process use the performance measures that is used to track the unit manufacturing cost related to the equipment utilization, ratios if direct and indirect labor volume , number of set ups and number of orders. On the other hand the activity based costing tracks the actual cost and quality, reduction of the cycle time, calculation of the delivery time and delivery rate and percentage of actual production. Activity based costing provides accurate identification and measurement of the new types of performance measures that is an important component for the success of the manufacturing companies (Banker, Bardhan & Chen, 2008). It allows the manager to identify the redundant sources. ABC can support the implementation of TQM and other programs for improving the quality of the manufacturing process. ABC assist managers to take better decisions related to allocation of resources. According to Cooper and Kaplan (1991, 1999), ABC will ensure discipline in the process that is necessary to gather and trace the costs of the various activities. It is used to measure the relevant output measures (Kallunki & Silvola, n.d.). Apart from implementation of the activity based costing system in the organization, there are other process improvement practice that takes place in the organization such as the total quality management technique and techniques for continuous improvement of the process of the organization (Banker, Bardhan and Chen, 2008).
2.10. Activity based costing results in cost and performance management
According to Kaplan and Cooper (1998), activity based costing can be viewed as a cost management and performance management model that contribute significantly to the operational improvement and formulation of strategies of the organization. According to Gosselin (1997), specific characteristics and the structure of the organization leads to the adoption and implementation of ABC by the firms and the firms whose organization structure does not require ABC, they do not implement ABC.
ABC may be able to add value but it is also correlated with the other variables that derive the true value. The control systems have indirect effect rather than direct effect on the performance of the organization (Brown, Booth & Giacobbe, 2004).
Although there is little evidence that there is direct link between the change in the ABC system and increase in the value of the share holder or the profitability of the organization. It has been concluded by Gordon and Silver (1999) that adoption of ABC has been questioned seriously as the positive impact of ABC on the financial performance of the organization cannot be established clearly. Thus many firms may be reluctant to change to an ABC system as it requires considerable investment. The Gosselin’s (1997) paradox explains the casual link between the introduction of activity based costing and the performance of the organization. The studies of activity based costing on the performance of the firm are referred to as event studies. Gordon and Silvester (1999) have used the event study approach in order to examine the impact of activity based costing on the firm value. The performance of ten firms published in the article of Business week on May 30, 1988 was studied. These firms had implemented ABC. There was no significant difference in the financial performance of the organization on implementing ABC. Thus it was concluded by Gordon and Silvester (1999), that ABC does not affect the value of the firms. But it was argued by Cooper and Kaplan (1992) , that ultimate aim of ABC is to maximize the profit of the organization. If implementation of the ABC system is supported by the other techniques then it will result in increase in sales and there will be reduction in the expenses of the firm (Kennedy and Graves, 2001).
Researchers have noted that the ABC system and other strategic business initiatives complement each other and enhance the performance of the business. ABC system provides better information of the process; it is beneficial if the other process is employed concurrently. Many organizations have found that ABC fits with the cost of quality framework. In many cases it has been noticed that implementation o ABC in the organization has not been successful. In such organizations, success of ABC implementation depends on the technical factors and exogenous factors. It has been suggested by Reeve (1996) that an integrated ABC system requires a sophisticated system of information technology and real time activity driver information. The ABC modules are developed using the SAP, Oracle and PeopleSoft. ABC system can substantially reduce the distortions in the product costs. The better cost information results in better decision making process. Other factors that affect the decision usefulness of the cost information includes the usage of cost data by the firm in the pricing decisions, reduction of cost and strategic focus and average profit margin of the organization. ABC is considered as one of the new business initiatives by the organization that includes TQM ( Total quality management ) , JIT ( Just in time ) , FMS ( Flexible manufacturing system) and BPR ( Business Process Re-engineering. The researchers have gained limited success while linking these initiatives with the improved financial performance of the organization (SHIL and PRAMANIK, 2012).
According to Robin Cooper and Robert S. Kaplan (1991) , Activity based costing has the potential to solve the traditional problems of costing. It has major advantages over the traditional costing system. However it has been stated by Ittner ET ( 2002) , that ABC has indirect effect on the financial efficiency of the organization. The traditional system of costing are allocated to the costs on the basis of the direct and indirect cost classification (Kennedy and Graves, 2001). For example raw materials can be said to be directly associated with the products and it is based on the number of working hours. But in case of activity based costing, the costs are computed on the basis of various activities. In activity based costing there are various cost drivers that help the business to get better information of the variable cost and the cost management system is improved. The major difference between traditional system of costing and activity based costing is that ABC focuses on all the costs. It includes the indirect cost as well as the direct costs. But traditional system of costing focuses on the costs that in required for the production of goods and services.
1. Introduction
The exploration approach alludes to the methodology of directing the examination by centering the issue explanation said in the first part (Bamberger, 2000). It is very important to design the research strategy efficiently for achieving the research objectives. The proper strategies have been chosen on the premise of the exploration points and destinations that the conclusions can be acquired to match the research objectives. In this paper, the researcher as focused on addressing the validity of the relationship between activities based costing and financial performance of SMEs. The research methodology helps in designing a pathway for conducting the research so that the findings can be linked with the research objectives. It must be noted that each component of the research methodology is significantly important for conducting the study in a right direction (Crouch & Pearce, 2012).
According to Bamberger (2000), research framework is the outline of the entire approach to give a fundamental and orderly structure of the way to drive the examination towards right direction. The research study has been conducting in order to assess the correlation between the activity based costing and the financial performance of the SMEs in United Kingdom. In this case, the researcher has adopted positivism philosophy, deductive approach along with a descriptive research design. This study will collect both secondary and primary data for achieving the research objectives successfully (Cameron, 2009).
Research onion can be described as a systematic structure along with a method for undertaking the research with the aid of various important phases where each and every element have been designed in a particular way. The researcher needs to go through each layer starting from the outer most layer of the research onion and therefore reaching to a final conclusion. This has helped in framing the research strategies in a systematic manner.
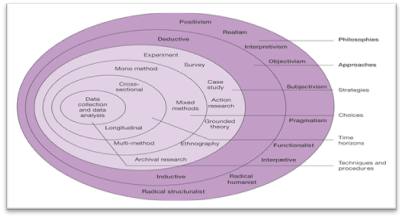
(Source: (Saunders, Lewis & Thornhill, 2003))
The first layer of the research onion is research philosophy. It implies that the researcher must choose an appropriate research philosophy as the other steps are significantly associated with this step. In order to assess the correlation between adoption of activity based costing technique and the financial performance of the firm of the SMEs in United Kingdom, the researcher needs to focus on choosing an appropriate philosophy (Adams, 2007). It has been found that positivism philosophy will be suitable for conducting the study as it will help in undertaking the study of correlation between these two parameters and describe how activity based costing is responsible for influencing the financial performance of the chosen company.
Second layer of the research onion is research approach. There are two common research approaches used by academic researchers: inductive and deductive research. Inductive approach includes observation, gathering data and analysis of the data with the aid of effective tools and ultimately development of the relevant theories (Bamberger, 2000). In contrast, deductive approach is associated with the selection of appropriate theories, hypothesis testing, and analysis of data and implementation of the relevant theories in order to validate the theoretical frameworks. In this research study, deductive research approach for this study. In the literature review section, relevant theories have been already discussed. These theoretical evidences will be validated through collection of the secondary data and data analysis (Daniel Kipo, 2013).
Research design helps in designing a pathway for interpretation of the gathered data. The results of the data analysis are entirely based on the purpose as well objectives of the research study. It is very important to a suitable research design which will help in guiding the entire study on the right track. There three common research designs which are generally accepted by the researchers such as exploratory, descriptive and explanatory. It has been found that the exploratory study significantly helps in enlightening the background information of the recognized problem statement of the research study. On the other had Crouch & Pearce (2012), has described explanatory design as a research design which helps in identification of the chosen problem (Giddings & Grant, 2006). Descriptive design of a research extensively emphasizes on relating the major objectives of the research study with the findings obtained from analysis of gathered data. In this research study, descriptive research design is found to be appropriate. Hence, in order to identify the correlation between the activity based costing and the performance of the SMEs (Schifferdecker & Reed, 2009).
Data collection is the method of gathering relevant data and information to analyze any research. In this research, secondary data is used for analyzing. Secondary data has been collected from various sources to analyze the research performed by the analyzer. The secondary data is collected from various, books, magazines, journals and papers. All the resources used in this paper are reliable and properly referenced. The secondary data refers to the past research studies and research papers along with the theoretical frameworks. Relevant information has been collected for the SMEs in order to establish the correlation between activity based costing and improvement in financial performance (Johnson & Christensen, 2000).Gathered secondary data needs to be analyzed in order to reach firm conclusion and achieving the objectives of the research paper. In this paper, the study has considered only secondary data. Majorly, research studies conducted for analyzing the role of activity based costing in enhancing the financial performance of the business firms have been considered in this paper. Hence, meta-analysis of the gathered data can be conducted for reaching conclusion regarding the correlation between activities based costing and financial performance of an SME (Hair, 2007).
Ethical consideration is an important aspect of research study. This study will gather wide range of primary data from the respondents. It is ensured by the researcher that the collected data will only be used for the academic purpose. Additionally, the personal information of the respondents will be kept confidential (Crouch & Pearce, 2012).
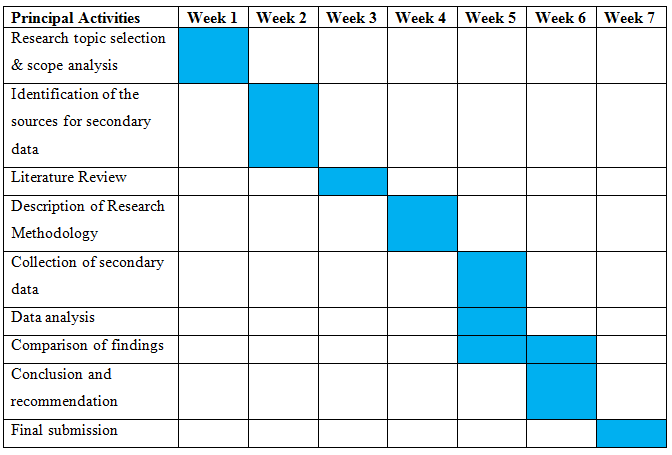
(Gantt Chart)
Several research studies have demonstrated that activity based costing helps in obtaining competitive advantage and thus the financial performance is improved. However, some research studies have depicted a contradictory idea and stated that not always activity based costing will provide the same benefits to the organization (Ravindran, 2009). It has been found that a positive correlation exist between the adoption of activity based costing technique and enhancement in the financial performance of the organization (Kaden, Linda & Prince, 2012).
Management practices and techniques have been changing over time and the organizations are shifting from managing the business vertically to managing horizontally. Studies have demonstrated that activity based costing significantly contributes in providing relevant information regarding operations and cost which helps in reflecting the horizontal view. Activity based costing furnishes correct cost information which is used by the management for initiating improvements. It has been observed that activity based costing produces huge amount of data which is critical for managing the performance of the organization (Herath, Wickramasinghe & Indrani, 2010).
Activity Based Costing and Supply Chain Management
Studies have been conducted to identify the role of activity based costing in enhancing the overall supply chain management of the organization. Effective supply chain management helps in reducing the cost of operations and ultimately contributes in enhancing the financial performance of the organization (Cagwin & Bouwman, 2002). However, it has been found that different studies have demonstrated that organizational performance can be measured by considering different point of views. According to (Gunasekaran, McNeil & Singh, 2000), activity based costing can help in improving the overall performance by becoming more efficient as well as more effective (Cokins, Capusneanu & Barbu, 2011). The major reason behind enhanced effectiveness is ABC helps in providing a clear picture regarding the use of resources, creation of value for the customers and the money being gained or lost. ABC costing helps in identification of the value added activities and helps in elimination of redundant or non-value added activities (Adioti & Valverde, 2013).
Efficient Cost Allocation
In order to judge the effectiveness of Activity costing in improvement of financial performance various research projects has been conducted. The researches shows that Activity cost techniques allocate individual costs to all products and services and determines the cost drivers for each individual products (Skoda, 2009). Thus, the main activity of ABC is to cost activities and not products. Thus the allocation of the costs to the activities and thereby determination of cost drivers gives the organizations the opportunities to successfully reduce the cost drivers and avoid the activities which are highly cost bearing in order to secure a sound financial performance (Cagwin & Bouwman, 2002).
Unlike the traditional costing system, the ABC system captures the direct costs, which helps in allocation of specific cost to the activity that triggers the cots rather than assigning the cost to the whole product. Moreover, ABC costing fixes selling price of the multiple products based on the overhead allocation and cost driver allocation (Wang, 2010). Further it is commented in the researches that activity based costing improves the company’s financial performance because it allows the visibility of value-added activities and non-value added activities in the financial reports of the organizations. After the determination of the value added activities, the organization will become aware of the costs that are compulsory for the company to bear since these the costs for these activities will be paid by the customers (Duh, Lin, Wang & Huang, 2009). Some of the value-added activities are namely product designing, manufacturing, product delivery etc. However, the organization also has the ability to reduce the non-value added activities like production time lags, product redesigning and remanufacturing in order to effectively reduce the financial costs (Oseifuah, 2013).
Credibility of Cost Information
Credibility of the cost information helps the management of an organization in identification of the potential issues as well as the opportunities. Eventually, the business organization makes well informed and rational decision (Ittner, Lanen & Larcker, 2002). Credibility of the cost information provided by ABC helps in enabling the managers to supervise the business activities and procedures along with supporting strategic as well as operational decision in distinct areas such as market segment, product line, process improvement etc. ABC helps in providing accurate, relevant and reliable information relating to cost which needed for making suitable strategic decision in terms of pricing, sourcing, product mix, evaluation of the business procedure etc (Cokins, Capusneanu & Barbu, 2011).
ABC in Private and Public Sector
Researches show that private sector organizations generally adopt ABC costing because cost in private sector determines the profit rates. The use of ABC analysis in the Private sectors helps in allocation of cost drivers to the diverse activities undertaken by the private sector organizations. However, there is no necessity of Activity based costing in case of public sector organizations because these organizations produce similar type of activities and hence the overhead costs are similar. Thus, it has been suggested that ABC can be helpful in enhancing the financial position if the overheads of the organization are not limited to manufacturing overhead only rather it stretches to other overheads like administrative and selling expenses (Eriksen, Urrutia & Cunningham, 2011). As per the reports of Economic Times around 20 to 50% of the manufacturing companies, 15 to 25% of the financial services companies, 6 to 12% of the communications companies and 12 to 18% of the private and public sector companies have enhanced their financial performance with the introduction of ABC costing (Horngren et al. 2011).
Alternative Techniques for Enhancing Financial Performance
Although activity based costing provides accurate financial information however, the process is complicated and cost consuming. Thus, the financial performance of an organization is affected since the organization has to bear high costs for effective installations of the activity costing methods within the business activities (Hardan & Shatnawi, 2013). Theoretical evidences suggests that the use of approaches like Just-in-Time, Total Quality management and Activity based costing can make significant enhancements of the financial performance of a particular organization (Back, Maxwell & Isidore, 2000; Feridun, Korhan & Ozakca, 2005).
ABC in Manufacturing Industry
Researches in the manufacturing industries revealed that the use of ABC costing helped the manufacturing companies to identify the unprofitable products, discontinue the particular product line, and discontinue the customers who were found to be unprofitable. As per the reports of Mintel, the manufacturing companies have been able to able to save around $ 1.8 million with respect to quality costs, wastage material costs and reactive maintenance costs. The industries were able to reduce the non-value added services like transportation of materials, loss of inventory and freight costs from 22% to 17%. These savings contributed significantly in increasing the after-tax income of the companies making the companies liquid (Cagwin & Bouwman, 2002).
Elimination of Unnecessary Cost
Moreover, by identifying the value added services the companies effectively discontinued with the non-profitable product lines and introduced similar products as the p4rofitable product lines. The academic researches of different industries shows that the discontinuity of unprofitable product line, unprofitable customers and reduction of non-value added costs increases the gross profit percentage of the organizations availing ABC techniques (Ittner, Lanen & Larcker, 2002). The stock returns like return on equity and return on assets are the major indicators of financial performance of any organization. The increment in the Gross profit percentage indirectly increases the profitability and liquidity ratios thereby indicating the financial performance of the company has improved (Jelsy & Vetrivel, 2012).
Thus apart from the complexity of ABC technique and the high implementation costs, the costing system is appropriate for all large scale manufacturing companies because there is a direct co relation between the use of ABC and the rate of enhancement of financial performance. However in order to compensate for the financial loss incurred due to installation of the ABC technique, it is suggested that organizations having sufficient financial soundness and high profitability should employ the ABC system. This system does not generate profitable returns rather it enhances the profitability of the organizations (Karolefski, 2004).
Past research studies have focused on the fact that some particular conditions of the environment such as complexity as well as competition will have significant impact on the potential benefits of the utilization of activity based costing techniques. The existing theoretical evidences have stated that in an appropriate enabling condition, the enhanced costing information provided by the activity based costing assists in a better decision making procedure which ultimately results in the improved financial performance (Johnson & Christensen, 2000). Hence, it can be stated that correlation between the utilization of activity based costing and the relative enhancement in the financial performance of the organization is significantly influenced by particular enabling factors. From the past study, the following table can be developed which indicates the impact of each enabling factor in enhancing the financial performance of the organization through activity based costing (Lin, 2012).
|
Enabling Factors |
Direction of Impact |
|
Importance of Cost |
Positive |
|
Use of Sophisticated Technology |
Positive (Adioti & Valverde, 2013) |
|
Complexity of the business unit |
Positive |
|
Level of the intra-company transactions |
Negative |
|
Unutilized capability |
Negative |
|
Competition |
Positive |
Apart from the above enabling factors, significant factors are identified that are responsible for influencing the relationship between financial performance and activity based costing.
Size and Product Diversity of Business: Different studies have found that size and product diversity of a business positively influence the effectiveness of activity based costing which contributes in elevating the financial performance (Lin, 2012). According to Elhamma (2012), a positive correlation exists between the size of the organization and effectiveness of activity based costing. It has been found that greater product mix significantly helps in yielding higher operating income while ABC is implemented (Askarany, Brierley & Yazdifar, 2012). However, the cost of implementing ABC is not considered in this study. In case of smaller organization, it is very important to consider the cost and benefit of implementing activity based costing (Hutchinson, 2010). Additionally, the advantage of activity based costing is found to be significant in case of the manufacturing units (Fei & Isa, 2010).
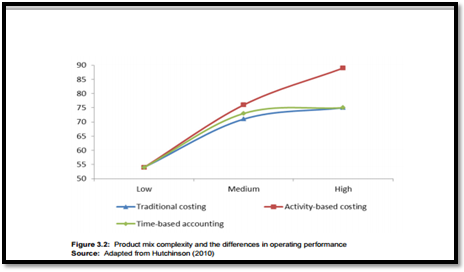
(Source: Hutchinson, 2010)
Fixed Overhead Structure: Research studies have found that the impact of ABC can be clearly understood in case of the companies with greater fixed overhead cost (Jänkälä & Silvola, 2012).
Organizational Culture and Strategy: Organizational culture and the strategy significantly influence the adoption as well as control of activity based costing which creates an impact on the effectiveness of the activity based costing. If an organization adopts cost leadership strategy, activity based costing will be appropriate strategy for diminishing cost (Ittner & Larcker, 2001). On the other hand, it has been found that the companies that have adopted differentiation strategy can also find ABC helpful. Research studies have demonstrated that companies focusing on the differentiation strategy have achieved significant benefit from activity based costing due to the enhanced complexity as well as uncertainty arising from continuous innovation. Thus, the company achieves competitive advantage and the market share of the company enhances along with improved financial performance (Elhamma & Fei, 2013).
Attitude of People towards ABC: Attitude of the people has a major role to play in implementing the activity based costing in an organization. It has been found that attitude of the people is favorable as they consider this costing technique to be a success. However, sometimes the project leader and the users may express different views regarding activity based costing. This issue can be easily resolved by providing proper training which will help in eradicating the resistance against activity based costing in an organization which will eventually lead to better financial performance (Fei & Isa, 2010).
Level of ABC Usage: The overall performance of an organization gets influenced by the usage of activity based costing. Various research studies have identified different aspects that contribute in achieving competitiveness in the open market and enhancing the overall performance of the organization (Tornberg, Jämsen & Paranko, 2002). First of all, ABC is an effective mechanism in case of product costing and the level of overhead allocation has a significant association with the accuracy of thee activity based costing. ABC significantly contributes in the decision making process for capital investment that is associated with the new product lines. Moreover, elimination of the non-value adding steps help in reducing the cost and the company can combat with the pricing strategy of the competitors. Thus, it can be stated that the level of ABC usage has a positive influence on the correlation between the financial performance and implementation of activity based costing (Duh, Lin, Wang & Huang, 2009).
Analyzing the wide range of secondary literature, it has been found that scholars have proposed various theories and provided evidences regarding the success of the activity based costing. According to the past research studies when the management is asked to express their views regarding their personal opinion regarding the success of the activity based costing technique; they have exhibited high level of satisfaction regarding the practice. Additionally, they were asked to revert regarding the level of satisfaction of the existing costing system within the organization (Abdul Majid & Sulaiman, 2008). It has been observed that the researchers have implicitly assumed that the improvement of the financial performance of the organization is significantly associated with the success of the activity based costing system (Ittner & Larcker, 2001). However, the most of the studies do not demonstrate significant evidence relating the success of the activity based costing system with the improvement of the financial performance of the organization. It can be inferred that the organization has not been able to contribute in enhancing the financial performance as the activity based costing has been implemented successfully (Khadash & Nassar, 2010). The benefits of the activity based costing can be realized once it has been successfully implemented as well as monitored (Krajnc, Logožar & Korošec, 2012). Otherwise, it will not be helpful in producing reliable cost information for assisting the decision making process. Moreover, it may fail in identifying the non value adding steps and procedures for elimination of unnecessary cost which eventually improves the financial performance of the firm. Hence, it can be stated that the relative enhancement of the financial performance has a positive association with the level of success of activity based costing in the SMEs (Tornberg, Jämsen & Paranko, 2002). In the research studies some specific measures are considered for estimating the success of the study. These measures include perceived success of the management, satisfaction of the company regarding the costing system and the belief that activity based costing system has been found to be worth implementing (Duh, Lin, Wang & Huang, 2009).
Analysis of the gathered data has demonstrated that activity based costing significantly contributes in different functions of the business which ultimately leads to improvement in the financial performance of the organization. This section has established that activity based costing significantly contributes in the improvement of the financial position. Moreover, this section has identified the important enabling factors which have a significant impact on the correlation between ABC and financial performance of the company (Herath, Wickramasinghe & Indrani, 2010). Complexity, size, fixed overhead, use of information technology, usage, organizational strategy, culture and attitude of the people has significant potential to influence the correlation between the financial performance and activity based costing. Additionally, this section has established a positive correlation between financial performance and success of activity based costing in the business firms (Ittner & Larcker, 2001).
Chapter 6: Conclusion
This study has provided significant evidence in support of the fact that a positive correlation between activity based costing and financial performance of a business firm. Activity based costing helps in reducing cost and enhances efficiency of the business activities that helps in improving the profitability of the firm. It has been identified that various factors must be considered as those have significant impact on the association between the two components. The enabling conditions include complexity of the firm, use of technology, competition, size of the business, organizational culture and strategy, attitude of people towards activity based costing etc. Moreover, this study has found that success of the activity based costing is positively associated with the improvement in the financial performance of an organization.
6.2.1. Objective 1
Secondary data has provided extensive support regarding the positive correlation between the activity based costing and financial performance of a business firm. It is evident that the management practice and techniques have undergone several changes and the business firms need to adopt new practice for sustaining in the new environment. This study has found that activity based costing is responsible for allocating the individual cost to the entire product as well as services which determine the cost driver for each product. Thus the organization gets an opportunity to decline the cost drivers of the business activities in order to ensure better financial performance. In case of the SMEs of United Kingdom, controlling cost is crucial for organizational success. Hence activity based costing is an efficient methodology that can be adopted by SMEs. Activity based costing significantly helps in providing relevant, accurate and reliable cost information which is used for making strategic decision. In order to make right decision, accurate cost information is essential which is produced with the aid of activity based costing. Thus activity based costing contributes in enhancing the financial performance of the business firm. Moreover, activity based costing helps in identification of the unnecessary cost and activities which can be removed for enhancing the efficiency of the process as well as cost will be reduced. As ABC provides a clear picture regarding the resource utilization, creation of value for the customers and income or loss, overall supply chain management of the organization is improved. In this manner, activity based costing helps in enhancing the financial performance of the business firm. The first objective of this study is to find out whether a positive correlation exists between the ABC and financial performance. Hence, it can be concluded that a positive correlation between ABC and financial performance is evident from the past studies.
6.2.2. Objective 2
The second objective of this study is to identify the enabling factors that have significant impact on the correlation between these two components. First of all, past research studies have demonstrated that there is some specific condition that influences the utilization and outcome of the activity based costing technique. It has been found that competition in the market and complexity of the business unit positively influences the association between ABC and financial performance. On the other hand it has been found that use of improved and sophisticated technology helps in enhancing the overall business process and consequently it has a positive impact on the relationship between ABC and the financial performance of the firm. On the other hand, it has been found that the intra company transaction and unutilized capacity are the two factors which have negative impact on the correlation between these two components. Additionally, the size and product diversity significantly helps in improving the performance of the firm as larger organization and greater product mix helps in increasing the net operating income. Research studies have exhibited that the companies having large fixed overhead structure can clearly recognize the benefits of implementing activity based costing. Hence, in case of SMEs the impact of implementing activity based costing may not be very prominent as the fixed overhead is lower. Organizational culture and strategy have significant contribution in thee association between ABC and financial performance. ABC costing has been found to be deliver good results in case of both cost leadership strategy and differentiation strategy. Moreover this study has established that level of ABC usage and attitude of people have significant positive influence on the association between ABC and financial performance.
6.2.3. Objective 3
Third objective of this research paper is to establish a correlation between the financial performance and the success of activity based costing. The research studies have clearly implied that most of the organization has a demonstrated high level of satisfaction after implementation of activity based costing system. On the other hand, significant number of studies has exhibited different scenario. Despite of implementing activity based costing; some organizations have not encountered improvement in the financial performance. Hence, it can be stated that there is a positive correlation between improvement in the financial performance and the success of the activity based costing. It is recommended that the organizations must focus on adoption of effective strategy for implementing as well as monitoring activity based costing.
The research study has been able to recognize an overall positive synergistic impact from the simultaneous utilization of the initiatives. However, this study has not addressed which specific initiatives will provide the impact. Hence, further studies can be conducted for addressing the following questions:
- Which combinations of business initiatives will be helpful in providing a positive impact when it is simultaneously used with activity based costing?
- Is there any particular order of implementation of the business initiatives in order to maximize the advantages?
Reference
Abdul Majid, J., & Sulaiman, M. (2008). Implementation of activity based costing in Malaysia. Asian Review Of Accounting, 16(1), 39-55. doi:10.1108/13217340810872463
Adams, J. (2007). Research methods for graduate business and social science students. New Delhi: SAGE Publications.
Adioti, A., & Valverde, R. (2013). Time-Driven Activity Based Costing for the Improvement of IT Service Operations. IJBM, 9(1). doi:10.5539/ijbm.v9n1p109
Anderson, S., & Young, S. (1999). The impact of contextual and process factors on the evaluation of activity-based costing systems. Accounting, Organizations And Society, 24(7), 525-559. doi:10.1016/s0361-3682(99)00018-5
Anderson, S., & Young, S. (1999). The impact of contextual and process factors on the evaluation of activity-based costing systems. Accounting, Organizations And Society, 24(7), 525-559. doi:10.1016/s0361-3682(99)00018-5
Anderson, S., Hesford, J., & Young, S. (2002). Factors influencing the performance of activity based costing teams: a field study of ABC model development time in the automobile industry. Accounting, Organizations And Society, 27(3), 195-211. doi:10.1016/s0361-3682(01)00057-5
Asif, M., Joost de Bruijn, E., Douglas, A., & Fisscher, O. (2009). Why quality management programs fail. Int J Qual & Reliability Mgmt, 26(8), 778-794. doi:10.1108/02656710910984165
Askarany, D. Interaction between Target Costing and Activity-Based Costing: Is Target Costing a True Costing Technique?. SSRN Journal. doi:10.2139/ssrn.1888824
Askarany, D., Brierley, J., & Yazdifar, H. (2012). The effect of innovation characteristics on activity-based costing adoption. International Journal Of Managerial And Financial Accounting, 4(3), 291. doi:10.1504/ijmfa.2012.047854
Back, W., Maxwell, D., & Isidore, L. (2000). Activity-Based Costing as a Tool for Process Improvement Evaluations. J. Manage. Eng., 16(2), 48-58. doi:10.1061/(asce)0742-597x(2000)16:2(48)
Bamberger, M. (2000). Integrating quantitative and qualitative research in development projects. Washington, D.C.: World Bank.
Banker, R., Bardhan, I., & Chen, T. (2008). The role of manufacturing practices in mediating the impact of activity-based costing on plant performance. Accounting, Organizations And Society, 33(1), 1-19. doi:10.1016/j.aos.2006.12.001
Banker, R., Bardhan, I., & Chen, T. (2008). The role of manufacturing practices in mediating the impact of activity-based costing on plant performance. Accounting, Organizations And Society, 33(1), 1-19. doi:10.1016/j.aos.2006.12.001
BaykasoÄŸlu, A., & KaplanoÄŸlu, V. (2008). Application of activity-based costing to a land transportation company: A case study. International Journal Of Production Economics, 116(2), 308-324. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2008.08.049
Brown, D., Booth, P., & Giacobbe, F. (2004). Technological and organizational influences on the adoption of activity-based costing in Australia. Accounting And Finance, 44(3), 329-356. doi:10.1111/j.1467-629x.2004.00118.x
Bryman, A., & Bell, E. (2003). Business research methods. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cagwin, D., & Bouwman, M. (2000). The Association Between Activity-Based Costing And Improvement In Financial Performance (1st ed., pp. 1-10). Retrieved from https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.198.8499&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Cagwin, D., & Bouwman, M. (2002). The association between activity-based costing and improvement in financial performance. Management Accounting Research, 13(1), 1-39. doi:10.1006/mare.2001.0175
Cagwin, D., & Bouwman, M. (2002). The association between activity-based costing and improvement in financial performance. Management Accounting Research, 13(1), 1-39. doi:10.1006/mare.2001.0175
Cameron, R. (2009). A sequential mixed model research design: Design, analytical and display issues.International Journal Of Multiple Research Approaches, 3(2), 140-152. doi:10.5172/mra.3.2.140
Clancy, C. (2007). The Performance of Performance Measurement. Health Services Research, 42(5), 1797-1801. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2007.00785.x
CLlarke, P., Hill, N., & Stevens, K. (1999). ACTIVITY-BASED COSTING IN IRELAND: BARRIERS TO, AND OPPORTUNITIES FOR, CHANGE. Critical Perspectives On Accounting, 10(4), 443-468. doi:10.1006/cpac.1997.0197
Cokins, G., Capusneanu, S., & Barbu, C. (2011). Decisions Based on Synthesis Documents Information of the ABC (Activity-Based Costing) Method. Ijafr, 1(1). doi:10.5296/ijafr.v1i1.905
Cooper, R., & Kaplan, R. (2015). Profit Priorities from Activity Based Costing. dzhphillips.com. Retrieved 9 February 2015, from https://dzhphillips.com/knowledge/documents/Markets/Manufacturing-Processing-Wholesale-Distribution/Manufacturing/Profit-Priorities-from-Activity-Based-Costing.pdf
Cooper, R., & S. Kaplan, R. (2015). Measure Costs Right - Make the Right Decisions. dzhphillips.com. Retrieved 9 February 2015, from https://dzhphillips.com/knowledge/documents/Markets/Manufacturing-Processing-Wholesale-Distribution/Distributors/Measure-Costs-Right-Make-the-Right-Decisions.pdf
Crouch, C., & Pearce, J. (2012). Doing research in design. Oxford: Berg.
Daniel Kipo, D. (2013). Mixed Research Methods: Reflections on Social Public Policy. ASS, 9(17). doi:10.5539/ass.v9n17p259
Dekker, H., & Van Goor, A. (2000). Supply Chain Management and Management Accounting: A Case Study of Activity-Based Costing. International Journal Of Logistics Research And Applications, 3(1), 41-52. doi:10.1080/13675560050006664
Duh, R., Lin, T., Wang, W., & Huang, C. (2009). The design and implementation of activityâ€Âbased costing. International Journal Of Accounting & Information Management, 17(1), 27-52. doi:10.1108/18347640910967726
Elhamma, A. & Fei, Z.Y. 2013. The relationship between activity based costing, business strategy and performance in Moroccan enterprises. Accounting and Management Information Systems, 12(1):22–38.
Elhamma, A. & Fei, Z.Y. 2013. The relationship between activity based costing, business strategy and performance in Moroccan enterprises. Accounting and Management Information Systems, 12(1):22–38.
Elhamma, A. 2012. The relationship between firm size, activity based costing and performance: an application on Moroccan enterprises. Journal of Accounting, Business and Management, 19(1):90–102.
EmblemsvaÌŠg, J. (2003). Life-cycle costing. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley.
Eriksen, S., Urrutia, I., & Cunningham, G. (2011). Design of an activity based costing system for a public hospital: a case study. International Journal Of Managerial And Financial Accounting, 3(1), 1. doi:10.1504/ijmfa.2011.038361
Evaluating and Improving Costing in Organizations. (2009) (1st ed., pp. 5-40). Retrieved from https://www.ifac.org/sites/default/files/publications/files/IGPG-Evaluating-and-Improving-Costing-July-2009.pdf
Fei, Z., & Isa, C. (2010). Factors Influencing Activity-Based Costing Success: A Research Framework.International Journal Of Trade, Economics And Finance, 1(2), 144-150. doi:10.7763/ijtef.2010.v1.26
Feridun, M., Korhan, O., & Ozakca, A. (2005). Impact Of Total Quality Management (TQM), Activity Based Costing (ABC), and Just-In-Time (JIT) on corporate financial performance: an empirical analysis on the Turkish textile industry. IFE Psychologia, 13(2). doi:10.4314/ifep.v13i2.23674
Garrison, R., Noreen, E., & Brewer, P. (2007). Managerial accounting. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Giddings, L., & Grant, B. (2006). Mixed methods research for the novice researcher. Contemporary Nurse, 23(1), 3-11. doi:10.5172/conu.2006.23.1.3
Goddard, A., & Ooi, K. (1998). Activity-Based Costing and Central Overhead Cost Allocation in Universities: A Case Study. Public Money & Management, 18(3), 31-38. doi:10.1111/1467-9302.00124
Gosselin, M. (1997). The effect of strategy and organizational structure on the adoption and implementation of activity-based costing. Accounting, Organizations And Society, 22(2), 105-122. doi:10.1016/s0361-3682(96)00031-1
Gunasekaran, A., & Sarhadi, M. (1998). Implementation of activity-based costing in manufacturing. International Journal Of Production Economics, 56-57, 231-242. doi:10.1016/s0925-5273(97)00139-4
Gunasekaran, A., McNeil, R., & Singh, D. (2000). Activity-based management in a small company: A case study. Production Planning & Control, 11(4), 391-399. doi:10.1080/095372800232126
Hair, J. (2007). Research methods for business. Chichester, West Sussex, England: John Wiley & Sons.
Herath, S., Wickramasinghe, D., & Indrani, M. (2010). A teaching case on implementing an activity-based costing system in a service firm: Lakhiru Insurance Company. International Journal Of Managerial And Financial Accounting, 2(2), 177. doi:10.1504/ijmfa.2010.033290
Horngren, C., Oliver, M., & Harrison Jr., W. (2015). Accounting: (9th Edition) Front Cover (pp. 1-200).
Hutchinson, R. 2010. Quantifying the impact of cost accounting system design on manufacturing performance: a simulation approach. Advances in Management Accounting, 18 (81) –109.
Ittner, C., & Larcker, D. (2001). Assessing empirical research in managerial accounting: a value-based management perspective. Journal Of Accounting And Economics, 32(1-3), 349-410. doi:10.1016/s0165-4101(01)00026-x
Ittner, C., Lanen, W., & Larcker, D. (2002). The Association Between Activity-Based Costing and Manufacturing Performance. Journal Of Accounting Research, 40(3), 711-726. doi:10.1111/1475-679x.00068
Ittner, C., Lanen, W., & Larcker, D. (2002). The Association Between Activity-Based Costing and Manufacturing Performance. Journal Of Accounting Research, 40(3), 711-726. doi:10.1111/1475-679x.00068
Jänkälä, S., & Silvola, H. (2012). Lagging Effects of the Use of Activity-Based Costing on the Financial Performance of Small Firms*. Journal Of Small Business Management, 50(3), 498-523. doi:10.1111/j.1540-627x.2012.00364.x
Johnson, B., & Christensen, L. (2000). Educational research. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Kaden, R., Linda, G., & Prince, M. (2012). Leading edge marketing research. Thousand Oaks, Calif.: SAGE Publications.
Kallunki, J., & Silvola, H. The Effect of Organizational Life Cycle Stage on the Use of Activity-Based Costing. SSRN Journal. doi:10.2139/ssrn.890527
Kaplan, R., & Anderson, S. (2007). Time-driven activity-based costing. Boston: Harvard Business School Press.
Kaplan, R., & Anderson, S. Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing. SSRN Journal. doi:10.2139/ssrn.485443
Kennedy, T., & Affleckâ€ÂÂGraves, J. (2001). The Impact of Activityâ€ÂÂBased Costing Techniques on Firm Performance. Journal Of Management Accounting Research, 13(1), 19-45. doi:10.2308/jmar.2001.13.1.19
Kennedy, T., & Graves, J. (2001). The Impact of Activity Based costing on Firm Performance (1st ed., pp. 15-35). Retrieved from https://coin.wne.uw.edu.pl/pmodzelewski/The%20impact%20of%20activity%20based%20costing%20techniques%20on%20firm%20performance.pdf
Kfknowledgebank.kaplan.co.uk,. (2015). Activity Based Costing (ABC). Retrieved 9 February 2015, from https://kfknowledgebank.kaplan.co.uk/KFKB/Wiki%20Pages/Activity%20Based%20Costing%20(ABC).aspx
Khadash, H., & Nassar, M. (2010). The implementation of activity-based costing and the financial performance of the Jordanian industrial shareholding companies. AAJFA, 2(2), 135. doi:10.1504/aajfa.2010.037282
Kinney, M., & Raiborn, C. (2009). Cost accounting. Mason, OH, USA: Thomson/South-Western.
Kirche, E., Kadipasaoglu, S., & Khumawala *, B. (2005). Maximizing supply chain profits with effective order management: integration of activity-based costing and theory of constraints with mixed-integer modelling. International Journal Of Production Research, 43(7), 1297-1311. doi:10.1080/00207540412331299648
Krajnc, J., Logožar, K., & Korošec, B. (2012). Activity-based Management of Logistic Costs in a Manufacturing Company: A Case of Increased Visibility of Logistics Costs in a Slovenian Paper Manufacturing Company. PROMET, 24(1). doi:10.7307/ptt.v24i1.265
Lewis, R. (2005). Activity-based Models for Cost Management Systems (pp. 16-80).
Lin, W. (2012). Financial performance and customer service: An examination using activity-based costing of 38 international airlines. Journal Of Air Transport Management, 19, 13-15. doi:10.1016/j.jairtraman.2011.12.002
Lopiano, K., Young, L., & Gotway, C. (2010). A comparison of errors in variables methods for use in regression models with spatially misaligned data. Statistical Methods In Medical Research, 20(1), 29-47. doi:10.1177/0962280210370266
Malmi, T. (1997). Towards explaining activity-based costing failure: accounting and control in a decentralized organization. Management Accounting Research, 8(4), 459-480. doi:10.1006/mare.1997.0057
Malmi, T. (1999). Activity-based costing diffusion across organizations: an exploratory empirical analysis of Finnish firms. Accounting, Organizations And Society, 24(8), 649-672. doi:10.1016/s0361-3682(99)00011-2
Management Accounting Research. (2000). Management Accounting Research, 11(1), 167. doi:10.1006/mare.2000.0123
Mitchell, F. (1994). A commentary on the applications of activity-based costing. Management Accounting Research, 5(3-4), 261-277. doi:10.1006/mare.1994.1016
Neely, A., Gregory, M., & Platts, K. (1995). Performance measurement system design. Int Jrnl Of Op & Prod Mnagemnt, 15(4), 80-116. doi:10.1108/01443579510083622
Porter, T., & Kehoe, J. (1993). Using activity-based costing and value analysis to take the pain out of downsizing at a naval shipyard. Natl. Prod. Rev., 13(1), 115-125. doi:10.1002/npr.4040130113
Rajan, M., Datar, S., Wynder, M., Tan, R., & Maguire, W. (2014). Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (pp. 200-300).
Ravindran, A. (2009). Operations research methodologies. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Reyhanoglu, M. Activity-Based Costing System Advantages and Disadvantages. SSRN Journal. doi:10.2139/ssrn.644561
Rojas, E. (2015). The Disadvantages & Advantages of Activity-Based Costing. Small Business - Chron.com. Retrieved 9 February 2015, from https://smallbusiness.chron.com/disadvantages-advantages-activitybased-costing-45096.html
Saunders, M., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2003). Research methods for business students. Harlow, England: Prentice Hall.
Schiffauerova, A., & Thomson, V. (2006). A review of research on cost of quality models and best practices. Int J Qual & Reliability Mgmt, 23(6), 647-669. doi:10.1108/02656710610672470
Schifferdecker, K., & Reed, V. (2009). Using mixed methods research in medical education: basic guidelines for researchers. Medical Education, 43(7), 637-644. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2923.2009.03386.x
SHIL, N., & PRAMANIK, A. (2012). APPLICATION OF ACTIVITY BASED COSTING IN MANUFACTURING COMPANIES IN BANGLADESH: A SURVEY BASED STUDY (1st ed., pp. 170-176). Retrieved from https://www.ewubd.edu/~nikhil/Publications/Activity%20Based%20Costing.pdf
Sohal, A., & Chung, W. (1998). Activity based costing in manufacturing: two case studies on implementation. Integrated Mfg Systems, 9(3), 137-147. doi:10.1108/09576069810210312
Tangen, S. (2004). Performance measurement: from philosophy to practice. Int J Productivity & Perf Mgmt, 53(8), 726-737. doi:10.1108/17410400410569134
THANH HOA, N. (2010) (1st ed., pp. 1-40). Retrieved from https://dl.is.vnu.edu.vn/bitstream/123456789/140/1/Nguyen%20Thanh%20Hoa.pdf
Tornberg, K., Jämsen, M., & Paranko, J. (2002). Activity-based costing and process modeling for cost-conscious product design: A case study in a manufacturing company. International Journal Of Production Economics, 79(1), 75-82. doi:10.1016/s0925-5273(00)00179-1
Unland, J. (1997). Cost and quality. [Frederick, Md.]: [Aspen].
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2016). The Impact Of Activity Based Costing On Manufacturing Organizations' Financial Performance (essay).. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/research-study-on-the-correlation-between-activity-based-costing.
"The Impact Of Activity Based Costing On Manufacturing Organizations' Financial Performance (essay).." My Assignment Help, 2016, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/research-study-on-the-correlation-between-activity-based-costing.
My Assignment Help (2016) The Impact Of Activity Based Costing On Manufacturing Organizations' Financial Performance (essay). [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/research-study-on-the-correlation-between-activity-based-costing
[Accessed 25 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'The Impact Of Activity Based Costing On Manufacturing Organizations' Financial Performance (essay).' (My Assignment Help, 2016) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/research-study-on-the-correlation-between-activity-based-costing> accessed 25 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. The Impact Of Activity Based Costing On Manufacturing Organizations' Financial Performance (essay). [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2016 [cited 25 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/research-study-on-the-correlation-between-activity-based-costing.
