Definition of customer needs, wants, products, demand and market identified for Organisation
Discuss about the Market Analysis of Toyota Motor Corporation.
This report chose the automobile market. In this regard, this report begins with a brief description about the company and the market in which it operates. Here, the report also specifies the exact customer needs in the market. Then, the report narrows down to the description on orientation of the company towards the market. In the next section, the report discusses in detail the competitive issues facing the firm. In this part, it discloses the nature and the level of competition alongside the detailed account of competitive strategy profiles as well as regulations. Before closing with a conclusion, the report discusses the STP framework of the company in the automobile market where it belongs.
Sharif Ullah and Tamaki (2011) explicates that customer needs means desire for a particular product tailored towards optimising customers’ satisfaction. Here, the customer needs include the need to move from one area to the other or mobility of goods from one region to another. In some cases customer wants and demands are used in place of customer needs. Product on the other hand is a tool always sought by customers to satisfy their wants. Therefore, the desire for mobility is also want in this report. On the other hand, wants refers desire for something (Chowdhury, 2014) whereas demand is the amount of goods that customers want to satisfy their wants. In this report, the demand is the number of Toyota vehicles that the customers need to buy within a particular period. Here, the products are Toyota brand vehicles. The market refers to the platform characterised by many sellers and buyers and where exchange of possession of goods and services occurs. In this connection, this report focuses on the International automobile market.
The firm was founded in 1937 through the initiative of Kiichiro Toyoda. Kiichiro Toyoda launched the company as a side shoot after gaining experience from his father’s firm. Its head offices are situated in Japan and have operations spread widely across the world. The firm specialises in designing as well as constructing an array of products that allow subcompacts to luxury as well as sport cars alongside SUVs. The firm manufactures the whole of its vehicles with one of the following features; combustions, hybrid engines just to list a few. Furthermore, the firm manufactures a number of automotive parts which are often needed by vehicle owners as spare parts and at times sold to the public(Chowdhury, 2014). The most common models for Toyota include Camry, Corolla, as well as Land Cruiser. Apart from the afore listed brands, Toyota also produces luxury lexus line along with the Tundra truck. By 2009, the firm had 71,116 located in different areas across the world. As earlier pointed out(Toyota, 2016). Toyota operates in automobiles market. According to Statista (2016), the firm’s share in the UK car market from Jan 2014 to Jun 2016 has been revolving around 2.73% as well as 4.17%. This implied that it constantly regulated a significant section of the United Kingdom car market. In 2015, the firm was among the top 10 sellers of cars. The figure 1 below represents the fluctuation of Toyota market share within the above period.
Overview of the Toyota Motors Corporation and its market
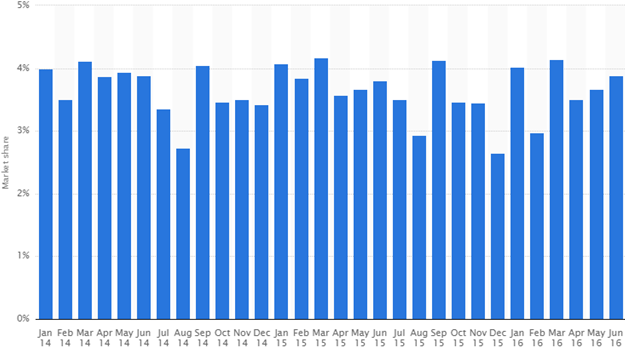
Figure 1: Changes in the Toyota market share between Jan 2015-Jun 2016
Source: Statista (2016)
In the UK market, the company faces stiff competition from its rivals. Its rivals include Alfa Romeo which in 2015 had a market share of 0.19%. Another major competitor is Audi which dominated 6.42% of the UK car market. Also, Toyota faces competition from BMW, Citroen, Ford, Fiat just to mention a few (Autocar, 2016).
Toyota has manifested the use of some market orientation notably product and selling concept. Product and selling concept entails direct involvement in the manufacturing activities of the product that the company sells in the market. In this case, Toyota engages in production of different car brands tailored towards meeting the needs of its customers as pointed out by Liker & Ogden (2011). This market orientation has resulted to the use of differentiation, innovation and branding strategies (Hollensen, 2015).
The firm’s corporate objective is to uphold its position in the automobile sector as the best company in the market and ensure persistent growth. In turn, this growth gives rise to increased profits and dividends advanced to shareholders. However, these goals cannot be achieved in absence of an effective marketing strategy (Kotler, Keller, Manceau & Hémonnet-Goujot, 2015). The firm’s marketing strategy is designed through factoring in its goals in entirety, policies to be applied as well as guidelines (Kotler, 2009; Kotler, Burton, Deans, Brown & Armstrong, 2015). The rationale for this is that, to come up with a comprehensive business model.
In general, the firm’s market strategies include enhanced innovation, deep market penetration, provision of slightly differentiated products and product development. Such marketing strategies help firms especially in increasing their operations across the world as maintained by Best (2012). It is a requirement that the marketing strategies have to concur with firm’s corporate goals. On this note, Toyota Motor company incorporates advanced technology in production activities, pursue measures that mitigate costs and engage in employee training to increase their productivity. Importantly, Toyota lays a lot of trust in innovation, differentiation as well as the underlying market strategies in addressing the pressing needs of consumers. As it stands, consumers are conversant with issues dealing with the environment and a firm that violates environmental conservation practices hardly lures consumers. As earlier noted, the market in which the firm operates is full of other firms that offer similar products to the consumers with slight differentiation depending on customers’ needs.
Orientation of the company towards the market place
The company has managed to engage in diversified operations through employing marketing tactic of branding a suitable car that matches with the area. For instance, the firm initiated a flexible fuel automobile in Brazilian market. On this note, this car is designed to go for 100% using bio-ethanol fuel. In addition, Toyota began producing a hybrid electric car called Prius in the majority of the markets in United States, Japan as well as the European Union(Andrews, Simon, Tian & Zhao, 2011). It was noted that Brazilian consumers preferred fuel saving cars as opposed to the USA, Japan as well as the European Union in the contemporary automobile sector.
Nature and level of competition
At any point in time, firms face competition in the market except for monopoly firms. In this context, it was established that Toyota faces stiff competition from other firms notably Audi, Ford, just to mention a few. Internationalisation of trade provides an easier way for the rest of auto companies to wedge a strong competition in the most established markets like the US as well as China. In most cases, the risks in the automobile sector are associated with the economy. Nevertheless, at the time, aggressive competition, increasing environmental awareness, increasing fuel prices along with entrance of other companies in the automobile sectors have been identified as the major competitive issues curtailing the growth of Toyota (Thompson, 2015). In brief, aggressive competition is a threat to the survival of Toyota company in the sense that stiff competition instigates the management to increase its operational costs due to excessive advertising campaigns and huge investment in research and development. Increased operational costs, cuts down the profit margin and in the worst case scenario may lead to consistent losses thus jeopardising the survival of the firm.
Competitive strategy profiles
Brown, Bessant and Lamming (2013) acknowledge that Toyota Motors employs an array of strategies to promote its competitive advantage in the market. These competitive strategies include cost leadership, differentiation as well as focus strategy. Toyota being a large company denotes that it enjoys economies of scale. Here, the firm mitigates its cost by optimising its technology, reducing the cost of materials as the materials are purchased in bulk among others. In turn, the effect of low cost strategy is manifested in relatively low prices of Toyota Motors products.
Secondly, Toyota Motors uses differentiation strategy. The differentiation strategy is achieved through innovation that results in producing products that meet exact customers’ needs. This is manifested through producing cars that are slightly differentiated (Corolla car model targeting women and youngsters). Lastly focus strategy use has also been manifested by Toyota Motors practices. This involves segmenting a particular market and develops particular products to only serve such segments. A good manifestation is segmentation based on demographic factors such as age leading to selling corolla cars to areas that most women and young people visit.
Competitive Issues facing firm
Toyota Motors uses regulations or a variety of principles to inform its decision making that is critical to improving its competitive advantage. According to Ko, Wang and Kuo (2011), the company observes fourteen key regulations documented as the Toyata way. To start with, the firm ensures that its decisions focus on long-run firm sustainability. Secondly, Toyota observes the regulation involving continuous process flow which facilitates timely identification of mishaps in the company for necessary corrective action. Also, the company observes the regulation involving the application of pull systems which evades overproduction. In addition, the regulation involving sustainability of culture that entails zero tolerance to poor quality on the ground is observed among other regulations. Overall, all these regulations have one goal in mind, that is, to increase Toyota’s competitive advantage.
Market segmentation
According to Loveridge and Mok (2012) marketing segmentation refers to the division of markets into different section. This division can be on the basis of geographic, psychographic characteristics, demographic and behavioural features. Here, geographic segmentation means separating the market based on different locations. Psychographic segmentation means dividing the market based on customers lifestyles and attitudes among others. Demographic segmentation means dividing the market based on population, age structure and gender among others. Lastly, behavioural segmentation involves dividing the market depending on customers’ consumption as well as shopping traits among others.
Toyota can optimise its sales by doing market segmentation on the premise of demography. The ancient type of Corolla’s purchaser is adults who in most cases were females. Based on the past sales data, it was noted that 51% of the people who fancy Corolla were women. Also, the majority of Corolla customers are at least 35years. In fact, the Corolla buyers were known to be younger than 35years were just 28.8 %( Toyota Cars, 2016). Besides the age and preferences, there also other ways in which Toyota can segment its market. So far, the firm has launched three distinct versions that have varying prices as well as features. In order to divide the market in a unique manner, Toyota need to firstly begin with demand based segmentation. In this context, the firm can establish the demands of distinct customers. For instance, if gender based, the firm need to point out what women admire in compact cars without also disregarding what adults admire in a car (Liker, 2014). In addition, segmentation can be conducted based on various income groups. As a consequence, this will not only help the firm in having more knowledge of the market as well as customers demands but also modifying presentation of the ancient model to reflect a newest outlook. However, to maximize profitability, Toyota need to address the following segmentation issue; Toyota has only focused much on demographic segmentation, however, Toyota should focus on geographical segmentation to address the constantly deteriorating volume of sales in those particular regions as noted by Ahmed (2013).
Once the firm has segmented its market alongside knowing the present opportunities, the firm as well as its management should categorise the segments in which it aims at efficiently. Here, Toyota can utilise a variety of patterns such as one-segment specialisation, discriminatory specialisation, product specialisation as well as market specialisation. Also, Toyota can apply complete market coverage. In regard to the previous corolla trends coupled with demand-based segmentation, it is clear that the firm can fit corolla in its appropriate or target market using discriminatory, product or market specialisation (Rowland, 2015). In this connection, women and old segment of the population have special demand for Corolla. Therefore, the firm can apply selective or discriminatory specialisation to capture this market. In choosing a particular target market, it is possible for the firm to position its brand with the changing preferences of its previous customers. Nevertheless, the target market for Toyota is very narrow, therefore the management need to address this issue by targeting a variety of markets. For example, production of car models that young people fancy.
To effectively lure customers to purchase corolla brand, it is key that the firm needs to use an efficient differentiation as well as positioning strategy. In this respect, the firm still needs to utilise its previous model but this time round presenting it in the market in a different way. This difference can be in terms of increased number of features with a slight difference to those being produced by its competitors in the market. In most cases, females fancy an array of colours. In response to this taste, the firm can effectively position itself by producing cars with different colours. In doing this, the firm will be able to lure a greater section of female consumers in comparison to its rivals (Ahmed, 2013).
Furthermore, positioning involves the aspect of the firm providing a product design and creating a brand image which enables the company to serve a specific customer need in the market (Ahmed, 2013). A good product position enables firms to be consumer-oriented. In Toyota, the positioning revolves around corolla brand. Here, positioning can be accomplished by firstly knowing the constructs that it purposes to disseminate to a particular market. Based on the pervious discussions, it is indicated that Toyota should address the positioning issue by effectively position its corolla brand as top quality as well as fuel saving cars that has distinct colours. In doing this, the firm is able to obtain a unique position in the market.
Conclusion
Referring to the report, it has been established that Toyota is among the top companies in the international automobile sector. In the automobile international market, Toyota has oriented itself in the market depending on the customers’ needs. In the report, it has been noted that meeting the exact demands of customers is the cornerstone of the success of a company. In this connection, Toyota has a market orientation that produces the products that have large consumer use. To effectively achieve this, the report suggested that Toyota should segment its market. Focus on activities that target the particular market and create a market position through creation of a good brand image. However, competition is normal in every market. In the report, Toyota faces stiff competition from its rivals like Audi and Ford Motors among others. To overcome the completion, the company should apply more aggressive marketing strategies in comparison to its rivals.
References
Ahmed, R. (2013). Business Perspective Brand Tracking of Toyota Corolla Case Study for Pakistan. International Journal of Asian Social Science,3(4), 930-938.
Andrews, A. P., Simon, J., Tian, F., & Zhao, J. (2011). The Toyota crisis: an economic, operational and strategic analysis of the massive recall.Management Research Review, 34(10), 1064-1077.
Autocar (2016). The UK car market winners and losers of 2015 | Autocar. Retrieved 3 August 2016, from https://www.autocar.co.uk/car-news/industry/uk-car-market-winners-and-losers-2015
Best, R. (2012). Market-based management. New York: Pearson Higher Ed.
Chowdhury, S. D. (2014).Strategic roads that diverge or converge: GM and Toyota in the battle for the top. Business Horizons, 57(1), 127-136.
Hollensen, S. (2015). Marketing management: A relationship approach. New York: Pearson Education.
Kotler, P. (2009). Marketing management: A south Asian perspective. Delhi: Pearson Education India.
Kotler, P., Burton, S., Deans, K., Brown, L., & Armstrong, G. (2015).Marketing. New York: Pearson Higher Education AU.
Kotler, P., Keller, K. L., Manceau, D., & Hémonnet-Goujot, A. (2015).Marketing management (Vol. 14). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Liker, J. K. (2014). Toyota and Kiichiro Toyoda. Handbook of East Asian Entrepreneurship, 204.
Liker, J. K., & Ogden, T. (2011). Toyota under fire. Boston: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Loveridge, R., & Mok, A. L. (2012). Theories of labour market segmentation: a critique. New York: Springer Science & Business Media.
Rowland, C. (2015). Toyota’s Marketing Mix (4Ps) Analysis - Panmore Institute. Panmore Institute. Retrieved 3 August 2016, from https://panmore.com/toyota-marketing-mix-4ps-analysis
Sharif Ullah, A. M. M., & Tamaki, J. I. (2011). Analysis of Kanoâ€Âmodelâ€Âbased customer needs for product development. Systems Engineering,14(2), 154-172.
Statista(2016). Toyota UK market share 2014-2016 | Statistic. Retrieved 3 August 2016, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/300465/toyota-car-market-share-in-the-united-kingdom/
Thompson, A. (2015). Toyota External Analysis: Opportunities & Threats - Panmore Institute. Panmore Institute. Retrieved 3 August 2016, from https://panmore.com/toyota-external-analysis-opportunities-threats
Toyota Cars (2016). 2010 Toyota Corolla Consumer Reviews. Cars.com. Retrieved 3 August 2016, from https://www.cars.com/toyota/corolla/2010/consumer-reviews/
Toyota(2016). TOYOTA IN THE WORLD 2010. Retrieved 3 August 2016, from https://www.toyota-global.com/pages/contents/company/profile/in_the_world/pdf/databook_en_2010.pdf
Brown, S., Bessant, J. R., & Lamming, R. (2013). Strategic operations management. London: Routledge.
Ko, C. H., Wang, W. C. & Kuo, J. D. (2011). Improving formwork engineering using the Toyota Way. Journal of Engineering, Project, and Production Management, 1(1), 13
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2017). Market Analysis Of Toyota Motor Corporation. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/market-analysis-of-toyota-motor-corporation.
"Market Analysis Of Toyota Motor Corporation." My Assignment Help, 2017, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/market-analysis-of-toyota-motor-corporation.
My Assignment Help (2017) Market Analysis Of Toyota Motor Corporation [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/market-analysis-of-toyota-motor-corporation
[Accessed 09 June 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Market Analysis Of Toyota Motor Corporation' (My Assignment Help, 2017) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/market-analysis-of-toyota-motor-corporation> accessed 09 June 2025.
My Assignment Help. Market Analysis Of Toyota Motor Corporation [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2017 [cited 09 June 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/market-analysis-of-toyota-motor-corporation.
