About Tesco PLC
Question:
Describe about the Tesco PLC.
Tesco PLC is a multinational retailer of British origin dealing in general merchandise and grocery. The company’s headquarter, is situated in Welwyn Garden City, Hertfordshire, England. Tesco is measured as the third largest retailer profit wise in the world and second largest retailer if measured by revenues. With the stores in twelve countries all across Europe and Asia, they are the market leader in the grocery in the UK with the market share of 28.3 %.
Originally starting as a grocery retailer, Tesco expanded its business in the early 1990s and along with grocery they started dealing in books, furniture, toys, clothing, petrol, software, financial services, telecom and internet services, and electronics. The Tesco chain has grown from twelve stores to two thousand and five hundred stores in fifteen years (Anyesha, Hassan and Aboki, 2014).
Tesco has a market capitalization of around 18.2 billion pounds as according to April 2015, and the 28th-largest company in the listing of London Stock Exchange.
Innovation is being the key of success for Tesco. Tesco gives equal focus to its customer as well as on innovation. Tesco aims at making the shopping experience an easy task for its customers. It also aims at improving its services and providing better value for products than just concentrating on pricing only (Barnes, 2011).
To enable this, Tesco pays regular focus in developing the creativity of its workforce and encouraging its staff for coming forward with innovative ideas. As Tesco initiates growth in new territories and be the masters of the domestic market, it sees and applies innovation success through four issues - not being complacent, trying new things, being always prepared towards changes; and being determined that no competitor will be able to achieve more than Tesco for their customer (Brannen, Moore and Mughan, 2013).
Today various assessment tools are available by various researchers who provide analysis of the company, its competitors, position, market, profit, customers, strategies, threats, opportunities, strength, etc. here four different assessment tools will be implied on the Tesco company and an analysis on its working along with recommendation to improve where the company lacks will be mentioned.
Tools like Extended 7s framework, Balance Scorecard, SWOT Analysis, and PESTEL Analysis will help in having the clear picture of Tesco Company’s current position. Every tool has its own approach and will provide the analysis of a different aspect of the company’s organisational structure (Case Study: TESCO PLC: Reporting Corporate Governance Matters in UK Published Accounts, 1995).
The McKinsey 7-S Framework
For ensuring that an organisation is working in harmony and analysing how well an organisation is positioned to achieve its goals and objective. The McKinsey 7-S framework is the best assessment tool to analyse the company’s position. The basic model of 7-S framework includes seven internal aspects of a company that is needed to be aligned for being successful (Clement, 2011).
The McKinsey 7-S framework model can be used for many situations where alignment is required for example:
- For improving the performance of the company
- For examining the likely effects within a company of future changes
- Alignment of processes and departments during an acquisition or merger
- For determining the best way of implementing a proposed strategy (Dudkina, 2015)
Tesco's Expansion and Diversification
Tesco McKinsey 7S model features the link between the seven different elements of the company’s business to increase the total efficiency. In this model, it is clearing indicated that a business has hard and soft elements.

Fig 1:- Tesco McKinsey 7-S Framework
Strategy- Every little Helps is the marketing communication message of Tesco that it pursues along with its cost leadership business strategy. This strategy is being sustained by the supermarket chain due to the excessive exploitation of economies scale and using bargaining power when dealing with suppliers for securing low purchasing costs. Tesco has applied different strategies generally using Balanced Scoreboard method (Fisher, Campbell and Svendsen, 2012).
At present, Tesco is facing a number of complex issues such as scandal of delay in supplier’s payment, profit account scandal, and loss of sales due to bad publicity.
Structure- the organisational structure of Tesco is highly hierarchical and includes many layers from store sales to management to the CEO. To simplify the organisational structure, the roles of deputy store managers were eliminated. The Board of Directors has ten members in total and eleven members of the executive committee of the company. Now the company believes that there is no need of one leader, they should work as a whole from top to down to achieve the successful strategies (Flynn, 2015).
Systems- the supermarket chain of the company basically relies on wide and spread range of systems for approaching a sustainable operation on the daily basis. To get the business back on track after the bad publicity, it faced steps were taken to simplify the organisational systems. The best example of it was the performance evaluation system which was having forty different measures before and they were reduced to only six key performance measures. To achieve its pre determined strategies Tesco used a steering wheel that smartly and simply used to help the employees in the coming future (Garbrah, Binfor and Binfor, 2013).
Soft Elements
Shared Value- The objectives and belief of the company are stated with the help of shared values. The organisation has its belief that by increasing the sophistication of management techniques from being just a simple manufacturing company to a standard value chain.
Staff- Staff means the number of employees a company has throughout its organisation. More than 400,000 employees are recruited all over the world by Tesco (Gottschalk, 2008).
Style- The working style of the company which it takes up help the company to achieve the goals or objectives of the company. Steering wheel style was used by Tesco to achieve its objectives. This wheel has 90-degree arcs, on which the company’s four main areas are considered, and they are employee performance, customers, operations, and customers.
Skill- the capabilities of an organization or its employees to complete a particular task is described as the skills of the company. Tesco administers complete knowledge to its employees so that they could work efficiently and effectively within the organization. It led to skill enhancement of the employees to work as per the standards of Tesco Company.
Innovation and Its Impact on Tesco's Success
The McKinsey 7-S framework has given a clear picture of all the elements, that are needed to align to attain success. Going through all the elements there are a lot of places where a lot of improvement is required if the company wanted to achieve its objectives. Tesco needs to save any amount of money it could to remain the cost leader of the market. The focus of the company should be on the availability, services, and especially on the pricing policy of the company and this should be the new strategic priority of the management (Hanafizadeh and Ravasan, 2011).
When coming to structure, Tesco has a very difficult and highly professional organisational structure, which is not required most of the times. A lot of cost reduction could target if the organisational structure of the company is made a bit easier. A few unnecessary posts could be removed from the hierarchy. The work system followed by the company it quite spread out and thus’ affects and delays the working of the company. A less difficult and renewed system with less number of procedure need to be followed will be beneficial for the company as the workers will work in that time which they use to waste in following unnecessary procedures of the company (Kim and Hallsworth, 2015).
The beliefs and objectives of the company should be clearly defined and easy to follow. The management should simplify its objective to make it understand by the common person working in the company and work hard to attain it. With such a large number of employees, it is necessary for the company to pay attention to their needs, training, and development, so they give back good work performance. The company is paying attention towards all the main areas by using steering wheel style which helps it to focus on all the major factors. Skill factor of the company is also working well. The company prefers to administer the knowledge about every aspect of the company to its employees hence, getting work done from them as according to the company’s standards (Kim and Hallsworth, 2015).
A performance metric known as balanced scorecard is used in strategic management to find and improve different internal functions of the company and their resulting external outcomes. The main work of the balanced scorecard is to make an attempt to measure and then provide a feedback of different internal functions to the company to assist the company in the implementation of strategies and objectives. This assessment tool analyses four separate areas, and they are: - learning and growth, business processes, customers, and finance. The data collected in this tool help in providing quantitative results and used for taking long-term decisions for the company’s future (Kink, 2008).
Fig 2:- The Earlier version of the Balanced Scorecard of Tesco
To grow the UK core
|
Strategic Objective |
Measures |
Target |
|
Improve Sales |
Revenue |
Achieve £ 43bn revenue, in UK market |
|
Obtaining/maintaining profit |
Profit |
>0% increase in profit |
|
Return on capital employed |
ROCE |
14,6% by 2014/15 |
To become the best international retailers online and in stores
|
Strategic Objective |
Measures |
Target |
|
Increase sales in the international market |
Revenue |
In international markets achieve £ 30bn revenue |
|
Obtaining/maintaining profit |
Profit |
5% growth |
To increase retail services in all the markets where the company deals (Tesco Bank)
|
Strategic Objective |
Measures |
Target |
|
Achieve return on investment (ROI) |
ROI |
At least 10% ROI |
|
Increase project revenue |
Revenue, margin |
15% revenue expansion |
To be a renowned creator of remarkably valued brands.
|
Strategic Objective |
Measures |
Target |
|
Growing in basic diluted earnings |
EPS, TSR |
Maintaining of >2% earnings per share. Maintaining of >2% total shareholder return |
Assessment Tools for Tesco's Business Analysis
Tesco has designed its strategy, based on the seven main aspects of the company. It manages their business by using Steering Wheel that helps to appeal all the targeted segments of the market rather than focusing on a particular market segment. Few ideas implemented by Tesco as according to this strategy are as follow:-
More staff means better services- the workers working in the various departments of the company are provided with training and equipments so they can deliver better services to the customer (McKinsey, 2009).
Creating jobs and careers- creating jobs to deliver excellent customer services
The Fruit and Vegetable Team- the additional staff hired by the company can be trained and focus on fresh produce, and making it available for their customers.
Quality and Innovation- refreshing the whole product range of about eight thousand products, to provide innovation in the products
The Big Drop in Prices- Tesco has invested about five hundred million pounds for reducing the prices of everyday products. The goal is to provide product at right price and gaining loyalty of customer and promoting the company (Monreal, McMeekin and Southerton, 2016).
To implement its strategy the managers find out the important internal processes which are necessary to be succeeded by the business is the internal business perspective of the company. Managers are can measure the success of the organization through the metrics which are based on the internal perspective of the company. The focus of this perspective should be on the internal processes that the company needs for achieving its financial and customer objectives. Three principal processes are used to identify the internal business processes and they are operation processes, innovation processes, and post-service processes (Pestle, 2014).

Fig3:- The core of Tesco’s Business Model
By focusing on the given business model of the customer, the wide range of services and products are being provided by the company at reasonable prices whether sold in shops or on online stores. Through customer feedbacks and evaluations the company offers a wide range of offers and improves the quality on a constant basis. Company, suppliers, and customers all get a mutual benefit from the increase in sales as it increases investment and finally lowering the prices of the product and services (Prause, 2014).
When coming to the international scene, Tesco prefers managing its retailing operations through local businesses. It leaves an impact on the local as it offers jobs and services which allow people to get close to the company. Tesco has a team of experts that work with the localities and farmer to improve the standards of the product supplied to the entire chain of the retail stores (Reising, 2006).
The profit of the company grew by 18% even in the difficult economic conditions. Growth shown in the international online sales is around 40%, which means the operating costs are decreased due to the improved supply chain management and inventory management.

Fig 4:- The Sales Growth of Tesco
Innovation- the main focus of the company is to provide an innovative offer to their customers. An innovative technique like self-service checkouts offers their customer a new of shopping. And these innovative techniques have resulted in increased growth of about 40% (Reilly, 2013).
McKinsey 7-S Framework for Analysing Tesco's Business
When it comes to customer services and convenience Tesco believes in innovation. Tesco has a concept called Shopping List that it follows to provide services to its customers. This concept highlights the objectives of the company and makes sure that every employee of the company is also aware of their role in providing customer services. This strategy is working well for the company and proving to be 100%% implementing in the processes.
Staff training is done through a concept called ‘Town Hall’ where the staffs is described about the companies strategies, and if they have any questions, then they can also put it in front of the management. This motivates the staff, and they feel as if working for their own store and reflect progress in growth perspective. Tesco believes that there should not be one leader, but every store has one of its own. It may have worked for the company but it has also created confusion in the mind of employees, regarding the head of to whom they should make an approach (Rietzschel, Slijkhuis and Van Yperen, 2014).
Coming down to the outcome of the balance score card of the company. It is showing that they are using all the perspective properly. Though large amount money is getting invested and they are expecting high return out of it in future, but it is always better to invest in a small amount and see the feedback and then go for a bigger investment. The ‘Steering Wheel’ strategy of Tesco has assisted the company to reach big goals, and that is done by breaking big goals down into smaller, and making it achievable goals. The profit figures are showing a less impressive picture of the company due to the financial crisis and increased investments, but these investments are taken as a long-term investment and expected high returns. There are few criticisms rising regarding the balance scorecard approach of the company, but most of them seem to be related to practical application of the strategy not due to any fundamental flaws (Schafer and Langer, 2005).
SWOT Analysis is an abbreviation used for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to the company. It is a structured planning or assessment tool which is used to evaluate the four elements of the company.
The SWOT Analysis of Tesco company:
Tesco is the third largest retail company dealing in a grocery in the world, with about four thousand plus stores it has a huge market share of about 30.7%. Its strength is its financial position which is going strong over the years. The turnover of Tesco is recorded around 54 billion pounds and shown an increase of 14.9% from the year 2008. Its strategy of providing customer satisfaction at the best prices has helped the company in reviving from the recent financial recession (Spyrou et al., 2014).
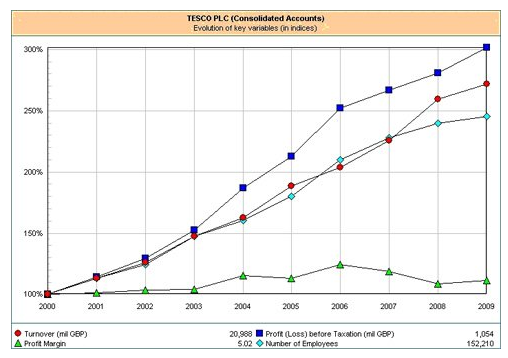
Fig 6: Tesco – Yearly Growth in Key Performance Indicators
The strategy of Tesco which aims at product affordability so that customer gets the product he wants suits his pocket without compromising with the quality. Customer loyalty is strength of Tesco that it gains from various loyalty schemes and offers.
Tesco has shown some weakness in the last year performance wise in comparison to its competitors. A number of sold products were called back by the company which has resulted in damage of brand image and as well as financial loss. In this loss company’s value lines was also included, which is marketed as an alternatives of key brands with high quality but lower price range (Srdjevic, Bajcetic and Srdjevic, 2012).
The concentration of the company’s key operations is within the UK retail sector which acts as a lack of geographical diversification. This is a weakness of the company that is needed to have overcome.
Tesco’s portfolio of commercial network is on the rise. They started with 600 stores in 2009 and out of them more than 400 stores were internationally located. This diversification of the company on global basis can help the company in increasing its scale of economy and also minimising its risk of systematic exposure.
With over 1million customers the popularity of Tesco.com is increasing rapidly this provides an opportunity to the company by reducing the overall cost and attracts new customers which ultimately result in more profit.
Global expansion in developing countries like India will be a great opportunity for the company (Vovchenko, Kochka and Pogorelenko, 2015).
Prediction of the rise in food retail market can act a big opportunity for Tesco as they are already established as a grocery retailers and food is a necessity that will never come to an end.
The global financial crisis has left a bad effect on the UK’s economy which has contracted by 2.4% and estimated to contract further by 4.2%. Tesco is basically set up in the UK market therefore, will be getting a financial setback due to the financial crisis in the country.
Financial recession has affected the customer’s purchasing power, unemployment and decline in income has affected the buying capacity of the customer which is giving an adverse effect on the company’s sales.
The competition in UK grocery market is really fierce. Tesco is actually leading this sector but in the present time facing intense competition and losing its market shares to them (Wood, Wrigley and Coe, 2016).
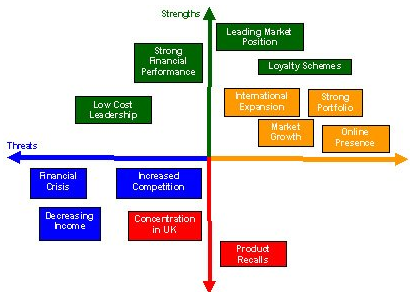
Fig 7: Tesco Abridged SWOT Analysis
The analysis shows that Tesco is a financially strong company but the present financial recession has affected the company badly. And future also it is predicted that market will go down. With the increasing competition it is necessary for the company to work hard and maintain its market share. It is necessary for the company to maintain its customer and as the buying power of customer is decreasing then the company also need to reduce its product prices to make it affordable for its customer.
Investing in the new developing market is definitely a great opportunity for the company which it should to its full strength, as these developing countries are least affected by the financial recession and has huge population who will be the customers for the company (Woods, 2007).
PESTLE analysis is a marketing tool used to assess and track the environment in which the company is operating. The analysis is about the various environments affecting the company and those environmental factors are: -
Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental
Here is the PESTLE analysis of Tesco which identifies the factors impacting the Tesco’s performance:-
Political- china’s removal of all barriers of foreign trades and promoting free flow of it has encouraged companies like Tesco to invest in the developing market. Tesco has joined a joint venture with China and agreed on development of shopping malls in China. This has given the company a great boost in the international market and expected to increase the company’s profit by one quarter (Zalengera et al., 2014).
Government’s promotion of free trading blocks is proving to be a great benefit for the company due to globalisation. There is an immersion of 10 more countries in European Union for the promotion of trade between eastern and western European countries. Now Tesco has got an expanded platform to increase its retail network in EU also.
The main concerning factor for Tesco is the economic factors as they directly impacts the buying behaviour of the customer. UK economy has already declared its economy under recession but the government initiative to reduce the effects of unemployment by reducing the interest rates has minimise the affect of recession for a time being. Now the buying power of customer is back on a steady rise as they get confident of their financial positions. However, still a lot of uncertainty is there in the market regarding the actual financial position of the country. This make customer spend less and try to save more to have a backup for future (Zhang, 2014).
The good point of recession is that people now eat more at home and thus, they purchase grocery items which are the main product of Tesco Retail Company.
The UK population is more of elderly people who eat less than the young and adult generation. The old people are less likely to go to supermarket for shopping their daily needs. However internet is becoming a handling thing for ageing people also but small deliveries are expensive and ineffective to make by the company, therefore it is discouraged.
Consumers are changing their food habit as they are getting more health conscious thus, moving towards the organic food and thus, Tesco also have to change its product range to suit the demand of the customer. Cheque payment and cash at the checkout was introduced by Tesco only (Anyesha, Hassan and Aboki, 2014).
In the present times technology is becoming more handling than going to the supermarket and making the purchases. The operations of retail supermarket are also getting affected by the growing use of internet and people preferring to purchase online grocery. This aspect of shopping through internet is also showing steady growth. 50% of the population is using internet at present which is expected to increase by 70% in the coming future.
Loyalty programs and offers are introduced by Tesco to discourage its customers to switch from them to online shopping.
Tesco is also using App called New Wine App which enables Tesco’s customers to purchase wine through their mobile phone (Barnes, 2011).
Government is promoting environment friendly packaging and products. And there g=has been a substantial rise in the usage of reusable bags fro 71% to 74% and people who prefer not to take plastic bags from retail shops has also risen in recent time from 65% to 68% which has reduced the costing of the company expenses and also leaving a good image of Tesco in the eyes of customers.
Customer is getting aware about carbon footprints so Tesco has also added carbon foot print data on potatoes, dairy products, and orange juice and planning to increase it in breads and other non-food items also (Brannen, Moore and Mughan, 2013).
Tesco has taken steps to create awareness regarding environmental issues. It has started with Greener Living Scheme under which it advices its customers how to reduce food wastage an carbon while cooking meals.
Tesco reward those customers who use reusable bags, recycled phone, and prefers bagless deliveries.
Prediction of increased VAT up to 20% due the financial recession has been done. It will badly affect the non-food segments of Tesco such as clothing, shoes, etc.
National Minimum Wage is planning to increase wage rate up to 15.5 % which add into the operating cost of the company (Case Study: TESCO PLC: Reporting Corporate Governance Matters in UK Published Accounts, 1995).
Conclusion
Tesco is a big grocery retail company running efficiently its business in the current global market. The rescission has made the company rethink about the working and strategies it is implying to run the company. For that various analysis was conducted here to know the exact position of the company, how well the strategies are working, what factors are impacting the working of the company along with it weaknesses, strengths, opportunities, and threats for the company. They are being analysed here and various conclusion were taken out depending upon the analysis taken on the company (Clement, 2011).
The company is running efficiently but it is basically having its major market share in UK and with the decreasing economic condition of the UK economy it is necessary for the company to look for some other options to main its growth, profit and leadership in the market. Tesco is having the strength of being financially secure and being investing in various projects and strategies that will provide high returns in the coming future but with the uncertainty of the present market it is necessary for the company to go for more sustainable approach rather than experimenting with new things (Dudkina, 2015).
Many developing countries have open its doors for foreign companies. This is a great opportunity for Tesco to shift its major market share from UK and earn it from these developing countries. These countries have huge population and still better economic condition as compared to UK economy. This will provide the back up for the company to continue its growth and earn profit. Once the company has a sustainable position then it can again try to experiment with new things (Fisher, Campbell and Svendsen, 2012).
Hence, it is concluded that Tesco need to work on expanding its business in the developing countries rather than just fixing itself at UK where the growing chances has reduced due to the financial crisis the country is facing. It will not only help Tesco to grow but increase it market share also across the globe and improve its image globally against its competitors which is going to be beneficial for the company in long-run (Flynn, 2015).
References
Anyesha, A., Hassan, D. and Aboki, H. (2014). The Conquering Strategies of Oligopoly Firms. A review on entry Strategies of Tesco Company Plc in the UK and beyond. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 16(8), pp.06-15.
Barnes, R. (2011). The great Tesco beauty gamble (the Tesco supermarket chainÂ’s marketing strategy for breaking into the UK beauty services market). Strategic Direction, 27(7).
Brannen, M., Moore, F. and Mughan, T. (2013). Strategic ethnography and reinvigorating Tesco Plc: Leveraging inside/ out bicultural bridging in multicultural teams. Ethnographic Praxis in Industry Conference Proceedings, 2013(1), pp.282-299.
Case Study: TESCO PLC: Reporting Corporate Governance Matters in UK Published Accounts. (1995). Corporate Governance: An International Review, 3(2), pp.100-101.
Clement, M. (2011). Rage against the market: Bristol's Tesco riot. Race & Class, 53(3), pp.81-90.
Dudkina, E. (2015). Effective Organisational Structure of the Corporate Risk Management. V mire nauchnykh otkrytiy, 0(5.8), p.3048.
Fisher, D., Campbell, L. and Svendsen, E. (2012). The organisational structure of urban environmental stewardship. Environmental Politics, 21(1), pp.26-48.
Flynn, D. (2015). Building a Better Model: A Novel Approach for Mapping Organisational and Functional Structure. Procedia Computer Science, 44, pp.194-203.
Garbrah, T., Binfor, F. and Binfor, F. (2013). An Analysis of Internal Environment of a Commercial-oriented Research Organization: Using Mckinsey 7S Framework in a Ghanaian Context. IJARBSS, 3(9).
Gottschalk, P. (2008). Organisational structure as determinant of knowledge management technology in law enforcement. Electronic Government, an International Journal, 5(4), p.364.
Hanafizadeh, P. and Ravasan, A. (2011). A McKinsey 7S Model-Based Framework for ERP Readiness Assessment. International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems, 7(4), pp.23-63.
Kim, W. and Hallsworth, A. (2015). Tesco in Korea: Regulation and Retail Change. Tijdschr Econ Soc Geogr, p.n/a-n/a.
Kim, W. and Hallsworth, A. (2015). Tesco in Korea: Regulation and Retail Change. Tijdschr Econ Soc Geogr, p.n/a-n/a.
Kink, N. (2008). Balanced scorecard. Controlling & Management, 52(4), pp.203-205.
MCKINSEY, M. (2009). Thought by Description. Philosophy and Phenomenological Research, 78(1), pp.83-102.
Monreal, A., McMeekin, A. and Southerton, D. (2016). Beyond acquisition: Exploring energy consumption through the appreciation and appropriation of domestic lighting in the UK.Sustainable Production and Consumption, 7, pp.37-48.
Pestle, W. (2014). Ancestral Appetites: Food in Prehistory. American Anthropologist, 116(1), pp.208-209.
Prause, G. (2014). A Green Corridor Balanced Scorecard. Transport and Telecommunication Journal, 15(4).
Reilly, P. (2013). Every little helps? YouTube, sousveillance and the 'anti-Tesco' riot in Stokes Croft.New Media & Society, 17(5), pp.755-771.
Reising, W. (2006). Balanced Scorecard im öffentlich-rechtlichen Rundfunk. CON, 18(6), pp.299-310.
Rietzschel, E., Slijkhuis, J. and Van Yperen, N. (2014). Task structure, need for structure, and creativity.European Journal of Social Psychology, 44(4), pp.386-399.
Schäfer, H. and Langer, G. (2005). Sustainability Balanced Scorecard. CON, 17(1), pp.5-14.
Spyrou, M., Shanks, K., Cook, M., Pitcher, J. and Lee, R. (2014). An empirical study of electricity and gas demand drivers in large food retail buildings of a national organisation. Energy and Buildings, 68, pp.172-182.
Srdjevic, Z., Bajcetic, R. and Srdjevic, B. (2012). Identifying the Criteria Set for Multicriteria Decision Making Based on SWOT/PESTLE Analysis: A Case Study of Reconstructing A Water Intake Structure. Water Resour Manage, 26(12), pp.3379-3393.
Varia, K. (2005). A balanced approach [balanced scorecard]. Manufacturing Engineer, 84(2), pp.40-43.
Vovchenko, N., Kochka, V. and Pogorelenko, N. (2015). PESTLE ANALYSIS. SBERBANK RUSSIA.Bulletin of the Saint Petersburg State Institute of Technology (Technical University), 54(28), pp.99-101.
Wood, S., Wrigley, N. and Coe, N. (2016). Capital discipline and financial market relations in retail globalization: insights from the case of Tesco plc. J Econ Geogr, p.lbv045.
Woods, M. (2007). Linking risk management to strategic controls: a case study of Tesco plc. IJRAM, 7(8), p.1074.
Zalengera, C., Blanchard, R., Eames, P., Juma, A., Chitawo, M. and Gondwe, K. (2014). Overview of the Malawi energy situation and A PESTLE analysis for sustainable development of renewable energy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 38, pp.335-347.
Zhang, X. (2014). Pneumatic Manipulator Wrist Structure and PLC Control Design. AMR, 912-914, pp.723-726.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2017). Tesco PLC: A Multinational Retailer Of British Origin, Essay.. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-structure.
"Tesco PLC: A Multinational Retailer Of British Origin, Essay.." My Assignment Help, 2017, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-structure.
My Assignment Help (2017) Tesco PLC: A Multinational Retailer Of British Origin, Essay. [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-structure
[Accessed 31 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Tesco PLC: A Multinational Retailer Of British Origin, Essay.' (My Assignment Help, 2017) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-structure> accessed 31 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. Tesco PLC: A Multinational Retailer Of British Origin, Essay. [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2017 [cited 31 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/organisational-structure.
