The YMCA of London, Ontario
Question:
Case study on “The YMCA of London, Ontario”.
The case “The YMCA of London, Ontario” focuses on the need to engage in long-term planning while developing community relations. The Young Men’s Christian Association (YMCA) was founded in the year 1844 in London and is one of the oldest and largest movements for youth in the world (Ymca.int, 2016). It is a not-for-profit community dedicated to meet the human and health service needs of men, women and children. Shaun Elliott, chief executive officer in 2005 reflected on the YMCA of London or the London Y or the association. The CEO has changed the scenario of the company by converting deficit into surplus. The turnaround of the association has been accomplished using internal cost cutting and growth through program expansion. According to the case study, the association had grown to 46,500 individuals by the end of 2005 and Elliott aimed for 102,000 as next level of growth by 2010. The CEO knew that to reach this target, he needs to increase the focus and spend more time on longer term strategic initiatives and community relations.
YMCA Canada serves people of all ages; abilities and backgrounds in helping them attain a healthy lifestyle and encourage them to make the community a better place. The YMCA of London was found in 1856 as an opportunity for personal growth in spirit, mind and body for people of all beliefs, backgrounds and abilities. The values of YMCA are honesty, caring, respect and responsibility. The organizational structure comprises of CEO who was accountable to a volunteer board of directors, several general managers and one general manager reporting to the CEO. The board also had three senior directors and one director (Lmhc.ca, 2016). The three core service areas are health, fitness and recreation; childcare services and camping and outdoor education. The three service areas have very different business models that create challenges for organizational focus and resource allocation (Lmhc.ca, 2016).
The three business models for health, fitness and recreation; childcare services and camping and outdoor education face significant challenges. The CEO, Elliott is concerned and believes that the time had come for the service area leaders to identify and create growth opportunities. There is a need to increase focus on strategic issues for longer-term development and address the internal and external issues raised in the case.
The main aim of any organization is to earn profits. YMCA being a not-for-profit association is to utilize its surplus revenues for achieving goals rather than distributing it as profit or dividends. The multi-service approach was challenging for Elliott and a few symptoms indicated that the association was not achieving its mission or goals (Lee & Lawrence, 2013). The symptoms were both operational and behavioural:
Operational symptoms- The Health, Fitness and Recreation or HFR services ran at a loss as the revenue generated was less. Wage scales in the association was low than in many other industries. The CEO managed most of the HFR facilities and there were no other coordinating mechanisms. These symptoms are clear signals to hindrance caused in YMCA.
Challenges Faced by the Organization
Behavioural symptoms- The retention rates were expected to decrease in the HFR. There were inconsistencies observed in the program quality, member service, facility maintenance, staff management and house-keeping between branches at the HFR. The staff satisfaction surveys consistently identified wages as an issue.
The main issue identified in the case study is that the senior management is lacking strategic leadership to make strategic plans. As stated in the case study, the numbers of senior managers have not increased in the last four years.
Strategic leadership is important in the organizations as the management express a strategic vision for the organization. Leadership is an important function of the management as it involves motivating, persuading and doing necessary things to achieve the vision.
- Communication
Communication is one of the critical components to leadership success. To grow as a leader and manager, one must be an effective and transparent communicator (Myatt, 2013). According to the case study, communication requires constant attention in the association as there are three different areas. Every program in the camping and outdoor communication produces its own sales and promotion materials and parent communications. However, many programs and facilities are not clearly identified by YMCA such as Children’s Safety Village or Camp Queen Elizabeth. There is a need to send adequate messages to strengthen London Y as a brand.
- Organizational Culture
Leadership affects organizational culture as culture is created by the action and behaviour of the leaders (Azanza, Moriano, & Molero, 2013). According to the case study, YMCA has a culture of involving their members by encouraging them. The allocation of resources and rewards also affect the organizational culture. Elliott experienced issues with resource allocation and communication while creating focus on strategic leadership. While the association was planning to expand, the resources are not sufficient to meet or support the expansion. Despite the company making efforts to reward good performance through reasonable compensation and rewards, there is dissatisfaction among employees concerning wages.
- Consistency
Consistency in leadership is critical as it is the difference between failure and success. Consistency establishes reputation as it helps measuring the bridge between failure and success (Burke, 2013). In the given case study, the CEO managed most of the HFR facilities in which each unit is run separately by its general manager. The tasks such as hiring, uniform purchasing, training, program development and sales and promotion are done by general managers. These responsibilities resulted in inconsistencies in program quality, member service, facility maintenance, staff management and house-keeping between branches at the HFR. There is a need to increase consistency for enhancing efficiency in the association.
The root cause of the problem is identified as strategic leadership in the organization. As Elliott made efforts to reduce cost and enhance growth, is turned around the financial structure of the company by changing deficit into profits. The organization has several general managers and one general manager reporting to the CEO. There is a need for more general managers reporting to the CEO. Even the directors are three in number. YMCA London took the responsibility of fundraising and developing programs. The association has a strong record of investing and securing grants. The foundation was expected to conduct annual campaigns, capital campaigns and enhance planned giving (Osman & Noordin, 2015).
Root Cause of the Problem
The general managers and manager were responsible for camping and outdoor education and community services. The senior directors were responsible for finance, development, communications and human resources. The association has not seen an increase in senior managers in the last four years. As the new targets are established by Elliott, he must have hired or conducted internal promotions for increasing the number of senior managers and directors. The compensation decisions would be based on the performance of senior directors against their plans. For expansion of the programs and services, the organization required greater investment. The senior management expected that there are expansion opportunities existing in a few rural communities and counties. The program only allowed expansion as much as staffing and funding allowed (Osman & Noordin, 2015).
YMCA could have appointed more senior managers for controlling the large number of employees in every service area with multiple departments. The elite group became out of touch with staff and various locations. Since the employees were dissatisfied with wages, the motivational factor to work in a better manner was reduced. The managers had to conduct multiple tasks themselves such as hiring, training, staff development and many more activities all by themselves. The association could have hired more staff or human resources for conducting these activities (Haynie, Mossholder, & Harris, 2013).

Figure 1: Cause and Effect Relationship in YMCA
Source: Created by Author
|
Positive Effects |
Negative Effects |
|
Growth in participation level of employees |
Unsatisfactory wages for staff in childcare services |
|
Increase in YMCA’s revenue |
Loss of contact with employees |
|
Expansion of new branches |
Expected decline in retention |
|
Increase in number of programs |
Insufficient senior management to control the growth of the organization |
Table 1: Positive and Negative Effects of Factors Causing Root Problem
The root problem of the association from the given case study is identified as lack of strategic leadership. The organization needs to employ efficient leadership strategies discussed as follows:
- Appointing Qualified CEO
The association can consider appointing a qualified CEO or many other CEO’s for handling the different functions. The chief executive officer or the CEO is responsible for developing and executing an organization’s long term strategy and increasing shareholder value. The CEOs could be appointed for operations, marketing, finance and mentoring (Parand, Dopson, & Vincent, 2013). The duties of the additional CEO’s could include:
- Ensuring company is organized and well staffed to attain desired objective.
- Ensuring effective internal controls and management information
- Communicating effectively with the employees and other relevant stakeholders (Graham, Harvey, & Puri, 2013).
- Conduct Strategic and Operational Meetings
YMCA can conduct strategic and operational meetings. Meetings help in recognizing executive time as resource. It also helps in increasing meaningful collaboration. The meetings shall help in:
- Providing key stakeholders with the current state, opportunities and priorities of the organization.
- Identify obstacles and impediments and ways to reconcile situations.
- Discuss a list of possible goals for the upcoming quarter or year.
- Aligning goals with the current state of market and business environment.
- Engage everyone and take opinion from people to meet the goals (Kosmin & Roberts, 2013).
- Add a Senior Management Layer
YMCA can consider adding a new layer of senior management team as they are considering expansion of services and programs. Adding a new senior management layer shall help in changing the management structure. The current structure at YMCA is more of flat organizational structure where there are few or no levels of management (Pettigrew, 2014). The hierarchical employees shall be ranked at various levels in the organization. It shall help in:
- Minimizing the skill gap
- Motivating employees
- Better department loyalty
|
Alternatives |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Appointing Qualified CEO |
The benefits of appointing qualified CEOs are to make more creative decisions. The CEOs shall also help in making stronger decisions. As the CRO keeps abreast of all material understandings, the CEO shall ensure that the processes and systems are in place while the management is adequately informed (Rule & Tskhay, 2014). |
The size of the association and the programs undertaken may not be met by simply appointing one CEO. As there are multiple business models, it may require appointing multiple CEOs for every function or department such as operations, finance, marketing and mentoring. It would also increase the cost as the CEO needs to be paid for the employment (Ou, Waldman, & Peterson, 2015). |
|
Conduct strategic and operational meetings |
The meetings are a great way of information sharing. The business meetings can help in knowing the problems faced by employees. Meetings also encourage and motivate the staff by discussing the perfect environment for work. Feedback can be provided both by the superiors and subordinates to discuss the strategies and operations in the organization (Liu & Maitlis, 2013). |
The disadvantage of business meetings for strategic and operational purpose is that it is time-consuming. Meetings may also increase expenditure. Another potential disadvantage of a business meeting is a lack of a leader to run the show, so to speak. This may result in a deviation from the agenda, or a lack of one altogether, which in turn makes the meeting run much longer than it should (Allen et al., 2014) |
|
Add a senior management layer |
The additional in senior management layer shall help in addressing the root problem as identified in the organization. It shall help in increasing efficiency of the organization. The level of motivation shall be high (Pettigrew, 2014). |
The process can be costly and there may exist rivalry between different departments. The increased bureaucracy may hinder the organization’s speed to change. The cost shall also increase as the salaries would increase organizational cost (Pettigrew, 2014). |
Table 2: Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternatives
From the above range of solutions, the best alternative solution is identified as adding a layer of hierarchy or senior management in the organization. YMCA can consider adapting to multi-divisional organizational structure based on geographic locations or services. The main problem identified from the case study is lack of strategic leadership. The multi-divisional structure shall help in reinforcing organizational culture and supporting the strategic direction. Elliott makes efforts in expansion of programs and services. With the implementation of multi-divisional structure, the diversification and growth can be facilitated. The operating decisions can be decentralized because currently the operational processes are centralized (Schuler & Jackson, 2014).
Importance of Strategic Leadership, Communication, and Consistency
Strategic decision-making is the responsibility of the top management. The new layer of management shall help the employees in communicating and presenting reports regularly. The new senior layer can assess the reports and make strategic changes as required. The short-term goals for six months are to fill up the critical positions required in the organization. YMCA can appoint Senior Director of Development, General Manager for HFR and Development and Executive Administrator (Pettigrew, 2014). The decision effects can be represented in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Effects of Decision-Making
As discussed in the previous sections, a new layer of management needs to be created at YMCA. As shown in Figure 3, a new layer of management is created with a higher hierarchy than the managers and under CEO. The CEO can appoint a new set of senior management so that the managers report to the heads or directors. The new manager, director and administrator shall look after the sub-units based on geographic locations or processes. The case study reveals that the department for finance, human resources, development and communication needs to be enhanced. Therefore, the new management structure can be implemented by affecting the overall processes (Fan, Wong, & Zhang, 2012).
The communication processes and reporting must be revised. Currently, one manager was directly reporting to the CEO while the other was making their own decisions. The new structure and process may be implemented by revising the communication flow. Upward and downward communication plans must be followed so that the message is transmitted from the top layer to the bottom layer. The structure must be applied in different geographical regions of London at YMCA. The strategic planning and control responsibilities must be maintained at every region. This organizational structure allows the adaptation of each division and its functional departments, such as sales, finance and marketing, to the local market's idiosyncrasies. To enhance the division's responsiveness, decision-making lies at the division level. In addition, with a focus on the local market, each division can develop and produce goods and services that appeal to its market and that the division produces and transports using local resources (Morgan, 2013).
Not only the processes shall change, but the organizations shall implement changes in attitudes and values of the employees. Firstly, the scope of change shall be identified by recognizing stakeholders and the potential benefits. Secondly, the vision must be created by engaging leadership. The communication must be made for the need to change. Thirdly, commitment must be driven by engaging the workforce in planning cost, benefits and wages for the new layer of management. Fourthly, new tools and technologies as required by the senior management shall be implemented. Lastly, the progress must be measured and corrective actions shall be taken as required (Senge et al., 2011).
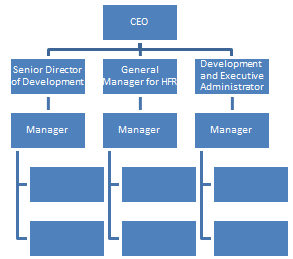
Figure 3: Multi-divisional Structure
Source: Created by Author
The YMCA team has committed itself to build healthy communities. The management structure has changed in the years. It is observed that the recommendation based on the case study and the strategy applied by the organization is similar. YMCA has added senior management level for changing the communication patterns and reporting processes. In this manner, the senior management can focus more on strategic direction and longer term plans for the organization. While the operational level staffs or general managers look after the operations of the organization (Ymcagta.org, 2016).
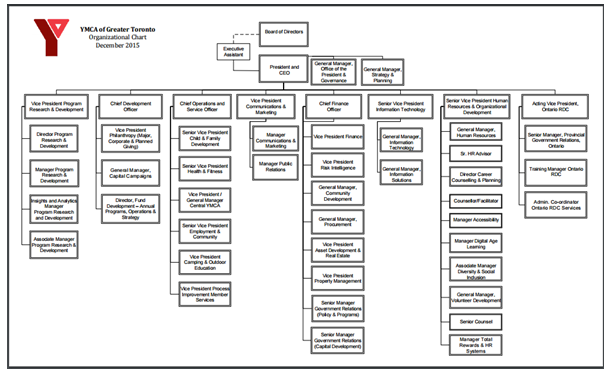
Figure 4: Current Organizational Chart
Source: (Ymcagta.org, 2016)
Conclusion
Conclusively, the YMCA has addressed the areas of concern by determining what is best for London Y. The different business models and strategy are taken into account for meeting the overall aims and objectives of the organization. The main issue identified in the case study is that the senior management is lacking strategic leadership to make strategic plans. As stated in the case study, the numbers of senior managers have not increased in the last four years. There is a need to increase focus on strategic issues for longer-term development and address the internal and external issues raised in the case. The tasks such as hiring, uniform purchasing, training, program development and sales and promotion are done by general managers. YMCA London took the responsibility of fundraising and developing programs. As the new targets are established by Elliott, he must have hired or conducted internal promotions for increasing the number of senior managers and directors. YMCA can consider adding a new layer of senior management team as they are considering expansion of services and programs. The additional in senior management layer shall help in addressing the root problem as identified in the organization.
References
Allen, J., Beck, T., Scott, C., & Rogelberg, S. (2014). Understanding workplace meetings.
Azanza, G., Moriano, J., & Molero, F. (2013). Authentic leadership and organizational culture as drivers of employees’ job satisfaction.
Burke, W. (2013). Organization change. Thousand Oaks, Calif.: Sage Publications.
Fan, J., Wong, T., & Zhang, T. (2012). Institutions and Organizational Structure:
Graham, J., Harvey, C., & Puri, M. (2013). Managerial attitudes and corporate actions.
Haynie, J., Mossholder, K., & Harris, S. (2013). Justice and Job Engagement:
Kosmin, L. & Roberts, C. (2013). Company meetings and resolutions. New York: Wiley.
Lee, R. & Lawrence, P. (2013). Organizational Behaviour. Hoboken: Taylor and Francis.
Liu, F. & Maitlis, S. (2013). Emotional Dynamics and Strategizing Processes: A Study of Strategic Conversations in Top Team Meetings.
Lmhc.ca,. (2016). LMHC | Tenants. Lmhc.ca. Retrieved 14 June 2016,p
Morgan, G. (2013). Riding the waves of change. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Myatt, M. (2013). Why Your Organization Suffers From Leadership Dysfunction.
Osman, I. & Noordin, F. (2015). The Impact of Organisational Justice, Organisational Trust and Teamwork on Talent Retention:
Ou, A., Waldman, D., & Peterson, S. (2015). Do Humble CEOs Matter? An Examination of CEO Humility and Firm Outcomes.
Parand, A., Dopson, S., & Vincent, C. (2013). The role of chief executive officers in a quality improvement initiative:
Pettigrew, A. (2014). The politics of organizational decision-making. London: Harper & Row Publishers, Inc.
Schuler, R. & Jackson, S. (2014). Strategic human resource management. Malden, MA: Blackwell.
Senge, P., Kleiner, A., Roberts, C., Ross, R., Roth, G., & Smith, B. (2011). The Dance of Change. London: Nicholas Brealey Pub.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2017). Long-term Planning For Community Relations: A Case Study Of YMCA Of London, Ontario. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/principles-of-management.
"Long-term Planning For Community Relations: A Case Study Of YMCA Of London, Ontario." My Assignment Help, 2017, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/principles-of-management.
My Assignment Help (2017) Long-term Planning For Community Relations: A Case Study Of YMCA Of London, Ontario [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/principles-of-management
[Accessed 18 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Long-term Planning For Community Relations: A Case Study Of YMCA Of London, Ontario' (My Assignment Help, 2017) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/principles-of-management> accessed 18 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. Long-term Planning For Community Relations: A Case Study Of YMCA Of London, Ontario [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2017 [cited 18 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/principles-of-management.
