Types of Heat Treatment
Discuss About The Properties Behavior Of The Parent Material.
Heat treatment is a group of metal working or industrial processes that are used in altering the chemical and physical properties of a material. Manufacturing of products such as glass also uses heat treatments since this process involves too much chilling or heating normally to extreme temperatures in order to achieve an anticipated result such as softening or hardening of materials. The techniques used in heat treatment are case hardening, quenching, tempering, annealing, precipitation strengthening, annealing and normalizing. This process only applies only to process where heating and cooling takes place in order to alter properties (Brooks, 2016, p. 44).
- Annealing
This is the process for softening materials or bringing about the changes in properties needed for example electrical, machinability or mechanical properties or dimensional stability. This process comprises steel heating to or near the critical temperature to enable it suitable for fabrication. Annealing of a material can be done heating the material at a well-known temperature and then let the material to cool slowly to a room temperature in an oven.
- Normalizing
This method is appropriate only for ferrous metals. Here, the heating of metal is done to a higher temperature afterward it is cooled in the air after removing it from the furnace and this is what differentiates it from annealing approach. Normalizing is used in some plate mills in the production of large forgings for example axles and railroads wheels (Grupta, 2008, p. 76).
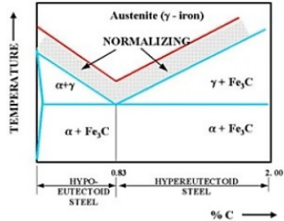
- Hardening or Quenching
Hardening is done to increase the strength and wear properties. Alloy content and carbon are one of the pre-requisites needed for hardening. A metal for example cast iron or steel needs to be heated into the austenitic crystal phase then cooled quickly in case hardening is done by quenching. The cooling may be done using the gas such as nitrogen, forced air, oil, the polymer dissolved in brine or water depending on alloy and other considerations such as distortion and cracking (Goebbels, 2009, p. 12).
- Case hardening
This is the method of roughening the surface of the metal using low carbon steel and infusing elements into the surface of the material leading to the formation a tinny coating of a harder alloy. The machine parts resistance to wear without interfering with tough interior parts is improved by case hardening (Dardyshire, 2010, p. 56).
- Austempering
This type of heat treatment method is applied in ferrous metals mostly ductile iron and steel. A bainite microstructure is produced in steel while acicular ferrite, high carbon, and ferrite structures are produced in cast irons. This method is commonly is used in eliminating or reducing distortion or improving mechanical properties (Schmitz, 2015, p. 32).
- Tempering
Other Treatment Processes
Tempering is done by preheating previously normalized or quenched steel to a temperature beneath the dangerous rang, holding and then cooling to achieve the desired mechanical features. The brittleness of quenched steel is reduced by this method. The hardness of the material is directly affected temperature since lower the hardness of the material is affected the higher temperature.
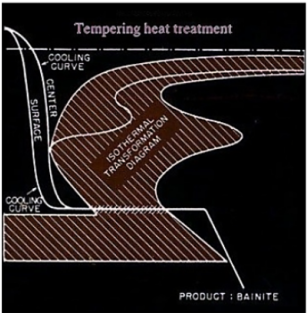
Fig: Showing tempering method
- Surface Hardening
This method involves handling of steel by mechanical means or heating to upsurge the hardness of the outer surface as the core remains reasonably soft. This method is valued because of its little and superior flexibility in manufacturing and the oldest surface hardening method is carburizing whereby steel is placed at high temperature for several hours in a carbonaceous environment. Afterward, the carbon diffuses into steel surface thus rendering it harder. Nit riding is also another method which makes use of heat and nitrogen.
Explain how liquid processing method and mechanical processing affect the structure, behavior, and properties of the parental material
The properties of a certain alloy such as aluminum which has magnesium and silicon as the main alloying elements possess properties such as high corrosion resistance, weldability, high strength and heat treatability which are affected by the casting. The properties of casting are greatly affected by the molding process employed and the properties of molding process used. The mold used in material casting depends on alloy involved, type of casting to be produced and the complexity of shape to be cast. During casting, chilling of molten metal which occurs at the mold wall resulting in the formation of a thin skin at the metal interface which increases around the interface as solidification increases. The parental structure or properties of the material such as high hardness comes as a result of chilling effects of molds while improve strength can be caused by ensuring a slow rate of heat loss in the naturally bonded sand mold (Thelning, 2013, p. 34).
Investigate how the composition of the metal alloy, polymers and polymer matrix influence the properties of the parental material
Parental metals belong to a single category and they exhibit properties of the original metals. An alloy is a mixture of substance made by combining different elements without a chemical reaction. When a second element is added to this single metals, the lattice parameter of the alloy will be different from the parental material thus changing the properties of the material, for example, a metal such as steel which is a mixture of carbon which is hard and brittle and iron which is soft and ductile. When they are mixed them, hardness and ductility are increased (Funatani, 2009, p. 97).
How Liquid Processing and Mechanical Processing Affect Parent Material
Polymer matrix composite comprises of continuous or short fibers joined together by an organic polymer matrix and they are planned to transfer loads between the fibers through the matrix. They are categorized into two that is reinforced plastic and advanced composites. Mechanicals loads applied to the material is supported by the reinforcements while the matrix bond fibers together. The reinforcing fibers may be arranged and oriented in different forms to provide different physical properties such as corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance on the parental material depending on the application (Williams, 2008, p. 312).
Polymers in engineering include synthetic material such as electrons and plastic and natural materials such as rubber. The backbone of every organic material is a chain of carbons and the molecules have the ability to form chains. The properties of the parental material will be affected when for example material like polyethylene which is made from ethane gas.
The first task to identify the functional requirements is; the requirements pertaining to what the product will have to do, how product responds to a stimulus, how product behavior which depends on the structure. At design process, it is always important to put the focus on physical features of the product, it is important to look at how the product function in operation. A design problem could include functional requirement specified in numerous bizarre ways as well as constraints and characteristics. Example of badly specified functional requirements includes; maintaining toughness in bending, minimize material cost, manufacturing cost not exceeding 10% of the unit cost. Well specified functional requirements include the product must resist bending and excess heat must be dissipated to the ambient air (Dardyshire, 2010, p. 65).
Identify properties for the product and select most appropriate materials and processing methods
The properties of products are classified as physical and chemical and physical are further grouped as thermal, mechanical, magnetic and optical
- Toughness and this is the capability of a material to grip energy deprived of rupturing.
- Ductility
- Thermal conductivity which is a quantity of heat flow through a material.
- A melting point which is the hotness at which a material turns from solid to liquid.
- Flammability which is the ability of the material to suppress combustion.
- Resistivity which is the capability of a material to oppose or resist the electric charge.
- Fatigue Strength which is the extreme stress amplitude in fatigue below which a material can bear an infinite number of stresses.
The most common manufacturing processes include casting, forming, machining, joining processes, heat treatment and finishing. The most preferred method for this product is the casting.
This is always the first step in manufacturing. Here, the material in the form of a liquid is emptied into the mold then it is permitted to undergo solidification by the reaction such as plastic or cooling such as metals. The filling of mold can be done gravitational force or beneath pressure and the mold cavity is organized so that it has the wanted properties and shapes. The cavity is made oversize in order to compensate the contraction of metal as it cools down to room temperature. The patterns are made oversized in order to achieve this.
Investigating the Impact of Metal Alloys and Polymers on Parent Material Properties
Sand casting which is used in making large parts. The metal which is molted is emptied into mold cavity made out of the synthetic or natural sand. The sand cavity is formed using pattern usually made of metal or wood and it is enclosed in a flask. The core is a sand shape inserted into the mold to produce to produce the internal features of that part such as internal passages or holes. In order to form desired cavities, cores are placed in the cavity (Funatani, 2009, p. 67).
The product imposed by processing has some limitation since processing of materials involves heating thus affecting their structure and properties of the product. A material particle can be displaced to other positions by a relative motion or by an overall motion to the rest of material, formed by thermal, mechanical and chemical forces. Therefore, the shape of the material is maintained by the relative motion while a shape of deformation of the product is caused by the relative motion.
Fiber reinforced polymer composite is the widest spread type of polymer composite used currently and without these reinforcements, poor mechanical properties will be offered by the polymer. The fiber is providing increased stiffness and the strength of a product while the matrix, on the other hand, is responsible for covering the reinforcement thus protecting them from chemical and mechanical damage. They also protect the product from crushing which may be caused as a result of deformation. The matrix materials also act as a load-transferring media because they transfer the load in an orthogonal direction from the fiber axis.
In spark-plug, electrodes typically comprise of high nickel alloy but when it comes to an insulator, they are made of aluminum oxide ceramic. A dramatic effect can be caused by spark plug performance by the insulator material thus it is necessary to reduce the leakages in electricity or flashover from the terminal of the plug and to the shell. The material which can also be used instead of aluminum oxide ceramic is the Sillimanite which can be produced artificially or found in its natural state.
- A copper-based material where copper is the largest constituent and a plurality of precipitates which include phosphorus and iron. The precipitates and copper help in strengthening the copper matrix so that the core material is a precipitate strengthened copper alloy. The core is surrounded by nickel-based material where nickel is the single largest constituents of the nickel-based material
Using metal matrix composite, the aluminum matrix is used to synthesize composite showing high strength. Carbon reacts with aluminum to generate a compound known as aluminum carbonate which is soluble in water and brittle. The matrix is usually a lighter material and provides a compliant support for the reinforcement and the composite are created by combining various materials to form a new material that retains essential properties from the original element. Production of a composite is done by reinforcing a resin material.
Product Design Constraints and Material Selection
An aluminum metal is heated in the crucible and a motor blade placed in the crucible to in obtaining a uniform molten metal. At a controlled rate, the reinforcement is poured above the melt surface to ensure a continuous feed. A homogeneous composite is produced after generating a uniform mixing of reinforcement particles (Croft, 2009, p. 56)
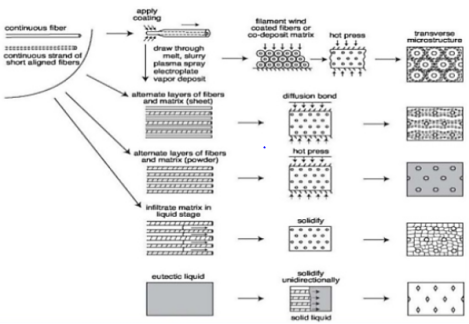
Fig: Showing process of MMC
The best method to apply in case copper was required to have ductile and malleable properties is annealing method since it is heat treatment method which alters both chemical and physical properties in order to increase the ductility and reduce the hardness of the material. In this method, a material is heated above its recrystallization temperature then cooling. In annealing, atoms travel in the crystal lattice while the amount of dislocations drops thus causes an alteration in hardness and ductility. Diffusion of atoms takes place within the copper so that the material improvements towards its state of equilibrium. The movement of atoms affect the eradicating and redistributing the dislocations in metals because the heat provides the energy required to break the bonds thus increasing the rate of diffusion. The properties can be achieved in copper by heating the copper metal then allowing it to cool at the temperature of the room in still air. Copper can be cooled by slowly in air or faster by quenching it in water.
Surface delamination. This s a situation where a tinny surface layer shows up on a material as a result of polluted material and this layer looks like coatings. This is caused by foreign material finding their means into molten plastic isolated from finished goods (Charity, 2015, p. 225).
Weld lines. They are really appearing in the part where a molten plastics encounter each other while flowing at dissimilar portions of the mold. They are triggered by insufficient bonding of two or more fronts when there is half-done solidification.
Warping. These are deformation which occurs in different parts of the molded component when there is shrinkage. On-uniform cooling of mold material causes warping
Burn Marks. This is discolorations like colored rust which is formed on the injection molded prototypes surface (Charity, 2015, p. 412)
Jetting. This is where the plastic which is molten fails to stick to the mold surface as a result of injection speed.
Sink marks. These are small depressions or craters which in areas of injection molded prototype which is thicker. It is always triggered when the cooling time is inadequate for plastic to cool completely (Charity, 2015, p. 122)
Conclusion
Many armed forces use the ballistic helmet in order to protect them from getting injuries such as traumatic brain injury. There are modern materials currently used in making the helmet namely;
There are numerous causes controlling the material response to ballistic effect and the chief source of kinetic energy absorption is the straining and breakage of secondary and primary fibers. Therefore, an important role is played by the fiber tensile in foreseeing the effect response resulting from the ballistic fibers. In modern body armor system, synthetic fiber established by DuPont in1965 have been used during manufacture. Helmet made using this material offers better comfort and higher protection since it has the high tensile strength (Brooks, 2016, p. 312).
Carbon nanotubes are examples allotropes of carbon comprising of nanometer diameters, tubular structure large length to diameter ratio. Carbon nanotubes have good energy absorption of heat, lightweight and high strength. The ballistic limit taken for carbon nanotubes is higher meaning that it is the best material for ballistic application than any other material. For ballistic operations, polymer matrix Nano-composites where a polymer matrix is reinforced by Nano-particles like carbo Nano-tubes and this material has high energy absorption capabilities (Berns, 2008, p. 211).
- Unpressurized light aircraft
The best material to use in light aircraft is aluminum since it is strong and lightweight. Aluminum alloy does not corrode easily unlike steel. The problem only arises at high temperature where they lose strength. Based on the cost, aluminum alloy is cheap compared to carbon fiber.
- A mid-altitude commercial passenger carrying the plane
The best material to use in commercial passenger carrying plane is carbon fiber reinforced polymer or graphite. Commercial aircraft made of carbon fibers embedded in an epoxy resin can be stacked in numerous ways to maintain integrity during flight. The carbon fiber material is strong as aluminum but has the weight (Bahadori, 2014, p. 100).
- High altitude, high-speed military specialization
The best material to use in building military aircraft is titanium since it is a light alloy able to withstand virtually external damage from heat, chemical, industrial, environmental and corrosive contaminants. Titanium can also be used in making hot sections of the engine since it has a high melting point which is 1668 degrees Celsius and it is also lighter compared to steel but the problem is that it is costly (Alinn, 2012, p. 124).
References
Align, J., 2012. Material Science and Metallurgy. s.l.: Hauffe Grupe.
Bahadori, A., 2014. Corrosion and Material Selection. s.l.:HarperCollins.
Berns, H., 2008. Ferrous Materials. s.l.:Sanoma.
Bogdanovic, V., 2012. Sheet Metal Forming Processes and Die Design. s.l.: Scholastic.
Brooks, C., 2016. Principles of the Heat Treatment of Plain Carbon and Alloy Steels. s.l.: Random House.
Charity, B., 2015. Materials Characterisation. s.l.: Thomson-Reuters.
Croft, A., 2009. Heat Treatment of Welded Steel Structures. s.l.: Sanoma.
Derbyshire, A., 2010. Mechanical Engineering. s.l.: McGraw-Hill Education.
Funatani, K., 2009. Metallurgical Process Design. s.l.:Simon & Schuster.
George, R., 2011. Wear of Materials. s.l.:Ridders Digest.
Goebbels, K., 2009. Materials Characterization. s.l.: OLMA Media Group.
Gupta, M., 2008. Microwaves and Metals. s.l.:Informa.
Schmitz, C., 2015. Aluminum Recycling. s.l.: Pearson.
Thelning, K., 2013. Steel and its Heat Treatment Bofors. s.l.: China Publishing Company.
Totten, G., 2006. Steel Heat Treatment. s.l.: Adventure Works Press.
williams, D., 2008. Hydroforming for Advanced Manufacturing. s.l.: Wolters Kluwer.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2019). Types And Effects Of Heat Treatment On Parent Material Properties. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/properties-behavior-of-the-parent-material.
"Types And Effects Of Heat Treatment On Parent Material Properties." My Assignment Help, 2019, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/properties-behavior-of-the-parent-material.
My Assignment Help (2019) Types And Effects Of Heat Treatment On Parent Material Properties [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/properties-behavior-of-the-parent-material
[Accessed 23 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Types And Effects Of Heat Treatment On Parent Material Properties' (My Assignment Help, 2019) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/properties-behavior-of-the-parent-material> accessed 23 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. Types And Effects Of Heat Treatment On Parent Material Properties [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2019 [cited 23 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/properties-behavior-of-the-parent-material.
