Background
Discuss about the Service Marketing for McDonald.
The report focuses on the service organization- “McDonald’s” and in this regard presents the blueprint of this organization. The rationale for studying this organization is its popularity and personal preference. Its front stage and back stage functions are described along with its decisive moments. The assignment illustrates the determinants of satisfaction/dissatisfaction for this service organization and using the relevant theories it discusses the service quality measurement and quality gaps in McDonald. Further, the paper presents the service recovery strategy plan for this organization to deal with various critical incidents.
McDonald’s is the popular and the largest restaurant in the world. This fastest growing global food service retailer is serving food and drink to less than one percent of the world’s population (Crawford 2015). This service organization has thirty thousand restaurants in one hundred and twenty countries. It attracts millions of customers with it high quality food both of vegetarian and non-vegetarian selections, excellent brand recognition and highly experienced management (Mehta and Mehta 2013). According to Thornton et al. (2016), McDonald’s capitalizes on global opportunities with its unique global infrastructure and advanced operational system. It has earned the high score regarding individual learning, diversity and inclusion, people-centricity, and organizational learning.
In this section, the organization and the service blueprint is presented which shows the operations carried out in McDonald’s and is same for all the outlets. The service blueprints act as a platform, which is designed for effective decision-making (Block et al. 2013). It is recognized as a "customer-focused process" to identify the factors to deliver high quality service. This is a tool that helps determine ways to perform superior service and create optimal experiences for the clients (Namkung and Jang 2013). The figure below represents the blueprint of McDonald’s. It is used to ensure all the factors are in place. It is used to detect the areas of service failure. It shows the various internal actors and inter-relationships between their various actions in customer service. The service blueprint constructed includes five aspects of the proposed service. These are consumer actions, front stage and backstage elements (discussed in subsequent sections), physical evidence and support processes (Yang 2012).
The physical evidence is the external appearance of the restaurant and includes the layout, décor, bins, tables and chairs, the electronic board displaying menu, and lighting, which are called as onstage elements. These are the first thing that a visitor observes at first glance. The backstage elements of the restaurant are the pots and pans (Dabholkar 2015). The support process in McDonald’s is mainly comprised of the payment system.
Blueprint of the Organization
Figure: McDonald’s service blueprint
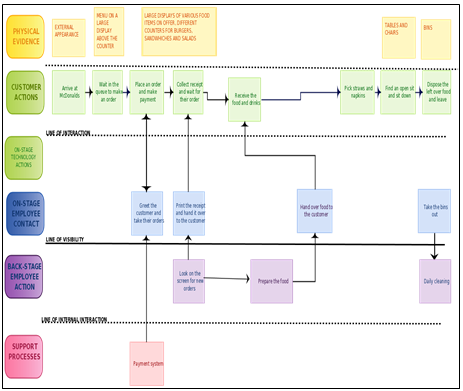
(Source: Yang 2012)
The front stage operations of the restaurant involve customer actions, onstage technology actions, and onstage employee contact (Smagghe 2014). The customer actions in the restaurant involve selecting the food item from the large display of menu over the counter and stand in the queue to place an order. The customer makes payment, gets the order receipt and wait for the food to be prepared. They receive their order after which they pick up napkin and straws, choose the appropriate place to sit and leave the restaurant after they have finished, disposing of the plates in the dustbin. The role of the customer service staff is to greet and communicate with the visitors and assists them through a provision of information on new offer or combo meals or in making a food choice, followed by billing and payment. They need to provide the invoice of the transaction and includes the payments through coupons or vouchers. Some of the onstage staff is engaged serving the food and in cleaning the bins and cans and safekeeping (Yang 2012). The staff is also instructed to collect customer feedback to meet their expectations. The detailed flow chart is given below. The front stage and the backstage functions occur simultaneously in the restaurant, and the interrelationship is illustrated in the above-given blueprint.
Figure: McDonald's front stage functions

(Source: created by author)
The backstage functions of McDonald’s involve maintenance of fresh stock of food (import of food products, daily purchase of fresh vegetables such as tomato and lettuce), monitoring the storage (frozen/frosting) conditions (proper refrigeration of perishable goods and soft drinks), safekeeping, updating online services (indirect staff-customer interaction) and menu boards, and cleaning of dining place and kitchen. The backstage members are chefs, prep staff and the cleaning crew (Bernhardt et al. 2013). Both the front and back stage staff are well trained to provide outstanding hospitality services and delivers food in less than one minute. The product managers involved in the backstage operations design websites with eye-catching images and attracting colors. They also introduce unique pricing strategy such as happy meal to improve the sales volume (See figure given below). Some of the staff is engaged in décor and lighting to increase the footfalls (Alheritiere et al. 2016).
Figure: McDonald’s backstage functions

(Source: created by author)
The “moments of truth” occurs at a very instant when a contact (directly or indirectly by mail, phone or website) is made with the customer who then forms an opinion about the organization (Thornton et al. 2016). The opinion formed may be positive or negative depending on the client experiences. The ambiance in McDonald, appearance of staff, hospitality, and more are all the “moments of truth” (Rowley and McMurtrey 2016). The positive moments of truth include staff’s attitude of politeness towards the visitors, clean environment, high quality of food, food variety, culture and very small waiting time which creates a positive image in mind of any customer of McDonald. Further, customers are pleased with the easy accessibility of all the outlets of McDonalds located in the popular areas with less traffic volume. The other positive moment of truth for the organization and its customers is the promotional pricing strategy that offers the discount of $20 on breakfast meals. The value pricing and bundling strategies increased customer’s base. For example, happy meal, family meal has enhanced the sales volume. The organization has been successful in creating outstanding customer experience by understanding the “nature of entire service delivery process and its various stages exposed to the customers." For example, the customers are greeted by the guard and then by the staff at the counter every time of order placement, cleaning the table, and client interacting with the staff. These created the opportunity for the organization to win the customers in the long run as well. McDonald’s self service-concept (placing an order and cleaning the left out food) is acknowledged by millions of customers (Bernhardt et al. 2013). Mc Donald involves in both exterior customer orientation and internal customer focus. It provides the customers to view its back operations creating more transparency in the process. This helped the organization create a successful service brand. This is evident, as most of the customers prefer eating at the restaurant than taking the parcel home (Cao and Kim 2015). Further McDonald has robust marketing strategies, its advertisements ending with “I’m loving it," emotional expressions and eye-catching images attract millions of customers (Crawford 2015). In service marketing, managing this moment of truth offers a great challenge to the organization.
Moments of Truth for this Service Organization
According to Block et al. (2013), the most important aspect of the competitive business environment is customer satisfaction. “Service quality” is the factor critical to success in fast food restaurant (Alheritiere et al. 2013). The service quality measurement is used to perceive the client satisfaction of the services provided by the organization. Literature review presented with different instruments used to study service quality gap such as “Expectancy-disconfirmation model” (developed by Oliver in 1981), “SERVQUAL” (developed by Zeithaml in 1985), “Answer Tree method” and others to study the quality gaps (customer’s expectation and perception) in McDonalds (Dabholkar 2015). The research findings revealed that the three major determinants of client satisfaction at McDonald are "tasty food, good value and restaurant cleanliness." Additional factors are a location of store, attitude of staff, brand, and product promotion. Customers were mainly dissatisfied with product prices at McDonald. These instruments have high reliability and validity. The theory of Expectancy-disconfirmation model is based on the fact that “customers form their satisfaction with a target service by direct comparisons between their expectations and perceptions” (Rowley and McMurtrey 2016). The theory of SERVQUAL model is also the same. The Means-end-model theory states that the “perceived value of the customer" significantly affects the customer satisfaction. Alternately the "Behavioral intentions model" is used to determine customer satisfaction by assessing the behavior and intentions of customers (Mehta and Mehta 2013).
The negative image in the mind of customers related to McDonald's includes the issues related to food content. The literature review provides evidence where this organization has been held responsible for increasing obesity in the US. It was found from the research findings of Zhao et al. (2014) that McDoanld’s fast food contains high calories, fat and salt. Customers were dissatisfied when the organization was identified to use Trans-fat and beef oil that is harmful to health. The food inspectors investigated two of the special food items of McDonald, "Big macs and Chicken McNuggets” and found them toxic (Cao and Kim 2015). Consuming this food may have serious health implications. According to Smagghe (2014), McDonald continues to sell this item in some of its outlets. Customers in Australia, UK, and the US have stopped eating at McDonald turning health conscious (Belk et al. 2014). The organization has been found accountable for a slaughter of hundreds of cows every year and destruction of rain forest for a production of beef. There has been a growing number of complaints against McDonald for failure in maintenance of hygiene and nutrition. It was accused of promoting food containing risk factor for cancer (Ramirez Millan 2014). This practice of the organization was considered unethical. The packaging system of McDonald is not environmentally friendly as it contains HFC-22 and is found to contribute to the ozone depletion, destroying mineral resources and natural habitats by cattle ranching (Namkung and Jang 2013). These issues have changed customer’s perception and expectation of McDonald. The organization is implementing practices to meet the demands and expectations of the customers by focusing on its current market trends to improve customer satisfaction.
Determinants of Satisfaction/Dissatisfaction for this Service Organization
McDonald envisions giving its customer the “world’s best quick service restaurant experience." The recovery plan to deal with some of the critical issues detailed above is discussed in this section.
Firstly, McDonald must change its menu and incorporate balanced food taking consideration of the growing health issues. It must enhance the quality of food and taste. Secondly, the organization must improve its brand image by robust advertisements and by publishing its latest reports of food investigation that reflects the healthy content of foods (Dabholkar 2015). Thirdly, McDonald must adopt green packaging solutions to demonstrate its eco-friendly attitude. Fourthly, it must revise its policies and continue with its three key strategies which are-
- Focus more on recent market trends
- Focus on customer’s emotional, psychological and social perspectives and build strong relationship with them to meet their expectation
- Delivering its customers “optional excellence” in each restaurant understanding their expectations
- Leverage its strengths by using innovative plans and technology
- Expand its business and brand popularity to achieve enduring profitable growth (Alheritiere 2013).
Fifthly, McDonalds must engage in market research as well frequent customer feedback practices on a regular basis. Sixthly, the business must participate in health promotion and environment protection campaign to fulfill its corporate social responsibility. Finally, the business must also evaluate the implemented changes on a regular basis (Crawford 2015).
Conclusion
The last decade showed that McDonald had undergone several changes. It can continue to be the winner in the market by overcoming its challenges and implementing right strategy. A quality service should mean exceeding client’s expectation. The paper has discussed the history of McDonald along with its functions and the challenges in the market. The quality gaps in this organization have also been discussed. It has highlighted how the organization plans to overcome its challenge.
References
Alheritiere, A., Montois, S., Galinski, M., Tazarourte, K. and Lapostolle, F., 2013. The worldwide relation between the number of McDonald's restaurants and the prevalence of obesity. Journal of internal medicine, 274(6), pp.610-611.
Belk, K.E., Woerner, D.R., Delmore, R.J., Tatum, J.D., Yang, H. and Sofos, J.N., 2014. The meat industry: Do we think and behave globally or locally?.Meat science, 98(3), pp.556-560.
Bernhardt, A.M., Wilking, C., Adachi-Mejia, A.M., Bergamini, E., Marijnissen, J. and Sargent, J.D., 2013. How television fast food marketing aimed at children compares with adult advertisements. PLoS One, 8(8), p.e72479.
Block, J.P., Condon, S.K., Kleinman, K., Mullen, J., Linakis, S., Rifas-Shiman, S. and Gillman, M.W., 2013. Consumers’ estimation of calorie content at fast food restaurants: cross sectional observational study.
Cao, Y. and Kim, K., 2015. How do customers perceive service quality in differently structured fast food restaurants?. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 24(1), pp.99-117.
Crawford, A., 2015. McDonald's: A Case Study in Glocalization. Journal of Global Business Issues, 9(1), p.11.
Dabholkar, P.A., 2015. How to improve perceived service quality by increasing customer participation. In Proceedings of the 1990 Academy of Marketing Science (AMS) Annual Conference (pp. 483-487). Springer International Publishing.
Gerhardt, S., Hazen, S. and Lewis, S., 2014. Small Business Marketing Strategy Based on McDonald's. ASBBS Proceedings, 21(1), p.271.
Mehta, G.B. and Mehta, S.S., 2013. An observational field study of consumer behavior at mcdonald’s. Business studies journal, p.19.
Namkung, Y. and Jang, S.S., 2013. Effects of restaurant green practices on brand equity formation: Do green practices really matter?. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 33, pp.85-95.
Ramirez Millan, M., Wallace, L. and Conner, E., 2014. Net Zero Energy Analysis For Mcdonalds usa, LLC.
Rowley, B. and McMurtrey, M.E., 2016. McDonald's and the Triple Bottom Line: A Case Study of Corporate Sustainability. Journal of Strategic Innovation and Sustainability, 11(1), p.33.
Smagghe, D., 2014. Comment on letter to the editor from F. Lapostolle:‘Worldwide relation between the number of McDonald's restaurants and the prevalence of obesity’. Journal of internal medicine,276(2), pp.199-200.
Thornton, L.E., Ball, K., Lamb, K.E., McCann, J., Parker, K. and Crawford, D.A., 2016. The impact of a new McDonald's restaurant on eating behaviours and perceptions of local residents: A natural experiment using repeated cross-sectional data. Health & place, 39, pp.86-91.
Yang, S.K., 2012. A study of customer participation on job satisfaction, organizational commitment and turnover intention.-The case of McDonald’s Employees in Taipei.
Zhao, M., Downey, G. and O’Donnell, C.P., 2014. Detection of adulteration in fresh and frozen beefburger products by beef offal using mid-infrared ATR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Meat science, 96(2), pp.1003-1011.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2018). Service Marketing For McDonald: Blueprint, Moments Of Truth, Determinants Of Satisfaction/Dissatisfaction. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/service-marketing-mcdonald.
"Service Marketing For McDonald: Blueprint, Moments Of Truth, Determinants Of Satisfaction/Dissatisfaction." My Assignment Help, 2018, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/service-marketing-mcdonald.
My Assignment Help (2018) Service Marketing For McDonald: Blueprint, Moments Of Truth, Determinants Of Satisfaction/Dissatisfaction [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/service-marketing-mcdonald
[Accessed 01 June 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Service Marketing For McDonald: Blueprint, Moments Of Truth, Determinants Of Satisfaction/Dissatisfaction' (My Assignment Help, 2018) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/service-marketing-mcdonald> accessed 01 June 2025.
My Assignment Help. Service Marketing For McDonald: Blueprint, Moments Of Truth, Determinants Of Satisfaction/Dissatisfaction [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2018 [cited 01 June 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/service-marketing-mcdonald.
