Describe about the Implementation and Monitoring of WHs Policies and Procedures?
WHS policies takes care the health and safety issues of an organization. It regulates the hazards and risk control of the organization so that the employees working there are safe and following the rules and regulations and maintaining the measures taken by the organization.
Implement & Monitor WHS Policies, Procedures and Programs
Elements and Performance Criteria
Explanation of the work team, relevant provisions of WHS Acts, regulations and codes of practice-
The WHS Acts has commenced their new law on January 1, 2012 and coordinated with OH&S laws in many territories of Australia.
Safe Work Australia has advanced the transitional principles which set out the arrangements in the way the existing safety legislation and safety health are induced into the new health system.
WHS regulator of every state and territory has developed recourses to support their administration along with the transition.
There are many Codes of Practices (A-Z practices) which have been implemented. Few of them are- 1. How to safely remove Asbestos
- How to manage and change Asbestos in workplace.
- Managing Electrical Risks in workplace.
WHS Policies of an organization-
The workers have to be ensured about their own safety. The officers have to take the responsibilities about the safety of the organization also. The officers have to keep their knowledge up to date about WHS.
Procedures used by these organizations-
Training and induction are held for new employees. Additional training are conducted for existing employees
Programs held by organizations like
How to take steps against sexual harassment, bullying this types of programs are taken so that there is no commotion in the office environment and there is no absenteeism and people are advised not to entertain this type of acts.
Steps taken by organizations to identify hazards and their outcomes of risk assessment and control are-
- At first the hazard has to be spotted out.
- After spotting the risk the people and performance team has to be informed.
- Problems are fixed.
- Results are evaluated.
This is the basic work process of every organization to spot and solve the problems and to take actions according to their own WHS company policies.
Consultation and Cooperation needed for managing health and safety risks in the workplace are-
- Best practices for health and safety risks.
- Consultations about health and safety risk.
- Consultations about occupational health and safety risk
- Checking’s of better negotiation practices.
Best practices for managing work area hazards –
- By best teamwork and collaboration, best result is expected.
- There is appealing and confinement for better positive and skilled workers.
- People in the workplace should be open to any type of changes.
- Less number of disputes should take place.
- Dispute between the employer and the employee should as negligible as possible.
Every organization ensures that the health and safety issues are consulted directly and they also ensure that they are meeting the demanded legislative expectations. Health and safety risks are not only the main things there are other issues also which comes under health issues like bullying , emotional harassment etc. Two codes of practice are implemented in workplaces like-
- Preventing and controlling fatigue in work areas.
- Blocking and responding to bullying in work areas.
Management can consider any one responsible for these issues if they are unable to take reasonable steps to prevent such types of acts.
Tracking and solving these types of matters can be done through many procedures-
- Through meeting face to face.
- Through telephonic conversations.
- Through emails and also by other writing communications.
- Through newsletters and other internal company’s brochure and memos.
For holding this types of meeting few agendas has be maintained like planning out the meeting, determining the tasks which are involved in this meeting, informing the people who will be attending the meeting and monitoring and learning the outcomes of the meeting ('Ratified Australian Veterinary Association policies January/February 2012', 2012).
To identify the WHS training needs, the training need analysis have to be conducted to find out the training gap. In this process there should review details of past trainings attended by the learners and what gaps the learners are facing now on those details the gaps will be found out and then the training will be given and for this training the budget will also be determined(Burwell and Davidson, 2007).
Provide information to the work team about WHS policies and procedures
Ways through which WHS training gaps will be indentified are-
- Incident survey forms.
- Accidental survey forms.
- Statistics report on incidents and accidents.
- Reports by Managers.
- Assessment report by colleagues.
- Assessment report by consumers and clients.
After analyzing the training need and skill audits, the arrangement for training for required team members after consultation is done.
Few reasons for training for the team members are-
- Insufficient knowledge about using the equipments safely.
- Introducing new machineries in the workplace.
- Lack of knowledge in using equipments as they do not use them regularly.
- Introductions of new polices in the organization.
- Resolving the issues of bullying and harassments.
After identifying the training need then it can be decided that the trainings will be given on the basis of on job, off job, coaching, mentoring.
When the trainings will be given few points can be included are-
- Job function of WHS roles.
- Industry experts giving presentations.
- Holding formal workshops.
For giving these trainings few things should be noted that – whether there are sufficient staffs for training or not, required budgets is available or not for conducting the training or not, availability of resources is there or not.etc
Training needs cannot be avoided. So, all WHS training needs should be addressed as soon as possible. If by any reason it cannot be addressed then few measures should be taken for the safety of the employees (Aspland and Datta, 2011).Ways through which training needs can be conducted are – on job training, off job training, mentoring, coaching, education through online etc. Through this kind of training it can be ensured that the learning objectives are implemented among the employees and it is benefitting the employees and also the organizations ('Editorial Policies and Procedures', 2009).
Training falls under the ongoing costs of the organization. WHS training needs is serious as its includes the safety of the employees and training on WHS and workplace safety should be taken seriously(Watson et al., 2009).Number of deaths is increasing every year in Australian workplace and claiming for compensation is also increasing along with the cost of training. So the organizations should keep in mind that while giving training they should also ensure about the safety of the workers and this will affect the direct costs and indirect costs of the organizations (Wye et al., 2009).
Some indirect costs are- Time loss, interruption in work because of idle time, absenteeism because workers are feeling unsafe, loss in the production, absenteeism because of stress, counseling costs because the workers are facing traumas etc(Lexchin and O'Donovan, 2010).
Hazards in work area according to WHS policies and procedures, and WHS legislative and regulatory requirements
In workplaces physical hazards is most common. There are many other hazards which take place in work areas like economic hazards, chemical hazards and biological hazards.
In work places physical hazards take place like – continuous noise pollution, exposed electrical cords, working on heights etc.
Economic hazards take place when there is stress in the work area and these type of hazards are not recognized easily because it does not affect the body easily.
Chemical hazards take place if any chemical in kept open in the open air then people are breathing in that air and that chemical is going in the body through breathing(JORQUERA, 2007).
A hazard can cause a injury and harm people, stuffs or environment. It is threat for all. After training when the team members are open to hazards then they can involve themselves in saving people from accidents in the organizations(Jones and Martain, 2013). Reports are maintained on the accidents so that the company can take measures on those accidents and the organization should also ensure their level of commitments towards the safety of the workplace. Reports are shown to the stakeholders and the management that the organization is following the rules as it is in the WHS principles. Everything should be monitored and upgraded to keep the health and safety issues intact in the organization (Altmann, 2007).
Information about the organization's WHS policies, procedures and programs
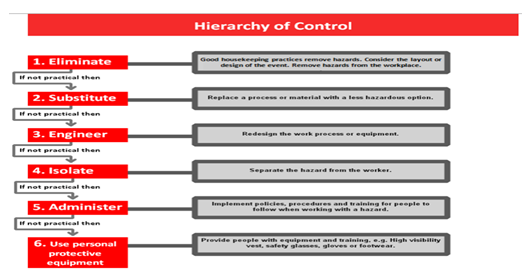
Figure -1 (Hierarchy of Control)
The managers and the staff should regulate the procedures by addressing and reporting the risks in the workplace environment. Orders on risks assessments are carried out to ensure the safety where risks, hazards could take place(Long et al., 2012). New technologies are introduced so that the company can miss the occurrence of accidents and incidents in the near future. Making the staffs introduce to the new technologies so that if any hazards occur they can take immediate actions. For planning the safety of the employees it is very important to have the guidelines and sometimes the changes are neglected for the safety of the customers(Swinburn, 2008).There should be new and clear set of rules, guidelines should be introduced for the sake of the safety of the workers. For risk assessment hierarchy control is one of the good plans and it helps to identify the risks and steps should be taken to minimize those risks ('The Adelaide Statement on Health in All Policies: moving towards a shared governance for health and well-being', 2010).
It is not possible to block each and every hazard but by risk assessment control it can be minimize the chances of hazards. By few factors the amount of risks can be assessed are-
- Regulating the likelihood- how the risk can occur and at what level injury can take place.
- Regulating the impact- if the injury takes place then how bad will be the impact.
Risk management should be performed when there are high risks under the regulations of WHS.eg- hazards taking place through electricity and noise comes under high risk factors and there are codes of conducts for solving this type of hazards (Dillow, 2009).
- Monitoring the safety measures for the employees.
- Whenever there are any hazards or risk the team should report there.
- It should be maintained in a report how many people are getting exposed in the risks.
- There should not be any chances of failure because from one failure it will lead to another.
- Actions should be taken to minimize the chances of destroying by hazards.
- Reports on accidents – Reports on any incidents where the employees are getting hurt and any damage of equipments.
- Reports on incidents – Reporting of all major and minor incidents should be maintained .It can be minor illness also.
- Registration of injuries- All major and minor injuries should be recorded.
- Registration of first aid- All first aid related issues should be registered.
Incidence rate- The number of cases each person is facing in a given period of time. When then sum of person-time of risk population is in the denominator then the person time is known as incidence rate.
Average lost time- The loss of time faced by the workers everyday during working hours due to safety issues.
Frequency rate- It is the rate at which the workers are getting injured and this indicates the safety level of the organization.
Conclusion:
Overall it can be said that the WHS policies and regulations are looking after the overall health and safety issues of the employees working there and also of the organizations(Seale, Kaur and MacIntyre, 2012). WHS is giving trainings to employees so that they can solve any health and safety issues occurring to them and their colleagues and any hazards destroying the environment of the organizations (Ratified Australian Veterinary Association policies January/February 2012, 2012).
References
Altmann, G. (2007). Journal policies and procedures. Cognition, 102(1), pp.1-6.
Aspland, T. and Datta, P. (2011). Insights into the School Reporting Policies Across Australia for Students with Special Needs. curric teach, 26(2), pp.73-83.
Burwell, J. and Davidson, R. (2007). An evaluation of safety policies and procedures in Australian magnetic resonance imaging departments. Journal of Medical Radiation Sciences, 54(2), pp.4-7.
Dillow, R. (2009). A Review of “Model Policies and Procedures for Not-For-Profit Organizations”.Journal of Business & Finance Librarianship, 14(3), pp.312-315.
Editorial Policies and Procedures. (2009). Animal Genetic Resources Information, 45, p.121.
Jones, R. and Martain, S. (2013). HRM fundamentals. Nollamara, W.A.: HRVET.
JORQUERA, J. (2007). Safety procedures of coagulation factors. Haemophilia, 13, pp.41-46.
Lexchin, J. and O'Donovan, O. (2010). Prohibiting or ‘managing’ conflict of interest? A review of policies and procedures in three European drug regulation agencies. Social Science & Medicine, 70(5), pp.643-647.
Long, M., Aitken, J., Seddon, C. and Torres, A. (2012). Professional practice & work health and safety. Russell Lea, N.S.W.: Better Teams Publications.
Ratified Australian Veterinary Association policies January/February 2012. (2012). Australian Veterinary Journal, 90(4), pp.107-114.
Seale, H., Kaur, R. and MacIntyre, C. (2012). Understanding Australian healthcare workers' uptake of influenza vaccination: examination of public hospital policies and procedures. BMC Health Services Research, 12(1), p.325.
Swinburn, B. (2008). Obesity prevention: the role of policies, laws and regulations. Australia and New Zealand Health Policy, 5(1), p.12.
The Adelaide Statement on Health in All Policies: moving towards a shared governance for health and well-being. (2010). Health Promotion International, 25(2), pp.258-260.
Watson, R., Brand, C., Watson, R. and LoGiudice, D. (2009). Delirium in the elderly. A survey of environmental policies and procedures in Melbourne hospitals. Australian Health Review, 33(4), p.656.
Wye, P., Bowman, J., Wiggers, J., Baker, A., Knight, J., Carr, V., Terry, M. and Clancy, R. (2009). Smoking Restrictions and Treatment for Smoking: Policies and Procedures in Psychiatric Inpatient Units in Australia. PS, 60(1), pp.100-107.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2016). Implementation And Monitoring Of WHS Policies And Procedures: Essay On Elements And Performance Criteria. (70 Characters). Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/implementation-and-monitoring-of-whs-policies-and-procedures.
"Implementation And Monitoring Of WHS Policies And Procedures: Essay On Elements And Performance Criteria. (70 Characters)." My Assignment Help, 2016, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/implementation-and-monitoring-of-whs-policies-and-procedures.
My Assignment Help (2016) Implementation And Monitoring Of WHS Policies And Procedures: Essay On Elements And Performance Criteria. (70 Characters) [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/implementation-and-monitoring-of-whs-policies-and-procedures
[Accessed 31 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Implementation And Monitoring Of WHS Policies And Procedures: Essay On Elements And Performance Criteria. (70 Characters)' (My Assignment Help, 2016) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/implementation-and-monitoring-of-whs-policies-and-procedures> accessed 31 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. Implementation And Monitoring Of WHS Policies And Procedures: Essay On Elements And Performance Criteria. (70 Characters) [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2016 [cited 31 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/implementation-and-monitoring-of-whs-policies-and-procedures.
