Samsung: Company Overview and Current Operating Position
Analyse the International Business Strategy of Samsung Electronics.
The most important objective of pursuing this study is to critically evaluate the international business strategy of as adopted by Samsung Electronics. The company which originates from Korea has today emerged as one of the largest companies which have capabilities of outshining corporate giants like Apple Inc.(Worstall, 2012). This makes the choice of Samsung to be very apt as the company has not only expanded beyond its national frontiers but also has been successful to manage a large product / service portfolio to a greater extent. The study reviews Samsung Electronics on multiple aspects especially those related to its organizational design and culture, global market entry strategies, global operations, production and supply chain management and global human resource management. The study also determines varied management issues and opportunities to which Samsung is exposed to thus developing recommendations to overcome the same.
Samsung, the Korean company which made a humble beginning as a small trading company in 1938 has today evolved as a world-class modern corporation. By the end of 2014, Samsung operated in more than 84 countries through over 213 offices across the globe and employed some 320, 000 people(Samsung Electronics , 2015). The company’s portfolio spans electronics, heavy industries, financial services, chemicals, services and others. Its businesses are wide-ranging that extend over semiconductors, advance technology, skyscraper and plant construction, fashion, petrochemical, medicine, hotels and much more(Samsung Electronics, 2014).
At Samsung, talent and technology are directed beyond accomplishing the economic goals to also contribute towards creating a better global society(Samsung Electronics , 2015). Excellence is among the core values of the company which is evident from the fact that in 2015 Samsung Electronics occupied 13th position in Fortune Global 500(Samsung, 2016; Fortune Global, 2016).
Under the leadership of Mr. Oh-Hyun Kwon, Vice Chairman and CEO, the company has topped the charts in the overall mobile phone and smart-phones segments during Q3 2015 holding market shares of 19.0% and 23.2% respectively as per rankings of the research firm Counterpoint(Guha, 2015).Despite getting a tough competition from its rival Apple, the company has still managed to be the world’s largest mobile vendor(Mathew, 2015).
As a brand, Samsung has recently been ranked at 7th place in Interbrand’s “Best Global Brands 2015.” The progress of the brand is evident from that it stood at 17th place during 2011(Samsung Electronics, 2015). Samsung’s current market position can be attributed to its core values, planned business moves, tight control over supply chain activities, and its strategy to reap advantages of experience curve economies (Simonin, 2014).
At Samsung, the organizational design was primarily influenced by the typical Korean culture, often represented by disciplined, authoritarian and bureaucratic management styles. Such an organizational design facilitates top management’s imposition of vision on the rest of the company thereby easing control over activities (Stachowicz-Stanusch, 2010). But such an organizational design not only negatively affected the economic goals of the company; it also drew lot of external criticism to the company declaring it to be non-innovative and laggard(Stachowicz-Stanusch, 2010; Chun, 2015).
Organizational Design and Control Issues
The company therefore took a revolutionary decision to modify its organizational design from being an efficiency-focused to a more innovation oriented organization. The once risk aversion philosophy has been replaced by an organizational design which promotes continuous experimentation and innovation. Over the years, it has inculcated an organizational culture of developing in-house expertise (Glowik, 2016). The company operates on a non-union philosophy which was actually the idea of its founder, Mr. Lee ByungChul(Yoo & Kim, 2015). Since 2013, Samsung has been reorganized into three key divisions: IT& Mobile Communications, Consumer Electronics, and Device Solutions as depicted in the figure below.
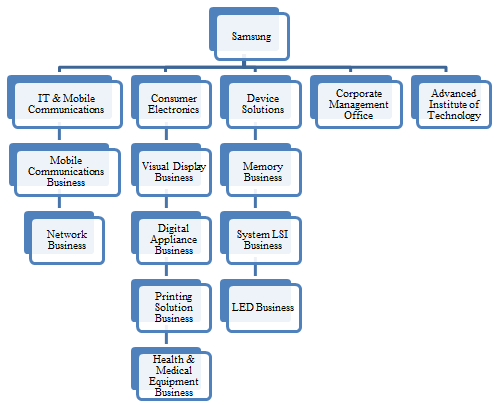
Figure 1Organizational Design of Samsung
Source: (Samsung Electronics , 2015)
These three major divisions of the company operate independent of each other. The company asserts that this not only aids in achieving operational synergies but also strengthens the individual capabilities of these divisions. But, in reality the company still has an organizational design which is vertically structured and too hierarchical. The commands in the company flow from top to bottom which not only delays decision-making but also acts as a source of discontentment among the workforce. Its autocratic organizational design is probably the reason that company took too long to understand the value of innovation(Worstall, 2012).However it cannot be denied that vertical integration strategy of the company enables cost-efficiency which helps the company in winning competitive advantage.
On the basis of literature contributed by Burns and Stalker (1961) cited in Chun(2015)Samsung is a mechanistic organization which is characterized by high horizontal and vertical differentiation, strict hierarchical structure, centralized decision-making and high formalization of roles and responsibilities.
Samsung has a diverse global portfolio and therefore enjoys an extensive global coverage. While choosing a new marketplace, Samsung basically aims at achieving economies of scale. A thorough market research is conducted and those markets are selected where the company can get cheaper factors of production and sell mostly standardized products with limited localization (Levine, 2015). Samsung prefers cost-leadership over differentiation strategy while operating internationally. In fact the company has been widely criticized for its strategy to copy rivals. Out of the four common foreign market entry strategies: licensing, joint venture, exporting and sole venture, the company mostly employs joint venture approach (Glowik, 2016). Samsung believes in forming strategic relationships which has aided the firm in emerging as a world-class leading technological firm (Levine, 2015). Its diversified portfolio helps in risk aversion at many times when there are adverse situations in any of the partner nations (Levine, 2015).
The entire operational control and manufacturing system in Samsung is vertically integrated which assists the company is excelling in its supply chain (Degun, 2014). The operations management and control in Samsung Electronics is governed by the basic Japanese approach wherein innovation was concentrated upon(Jung, 2014). Though quality compromise was strictly prohibited but organization was encouraged to be more cost effective. The operations revolved around low-cost manufacturing systems along with being customer centric (Jung, 2014).The overall value chain of Samsung is depicted in figure below:
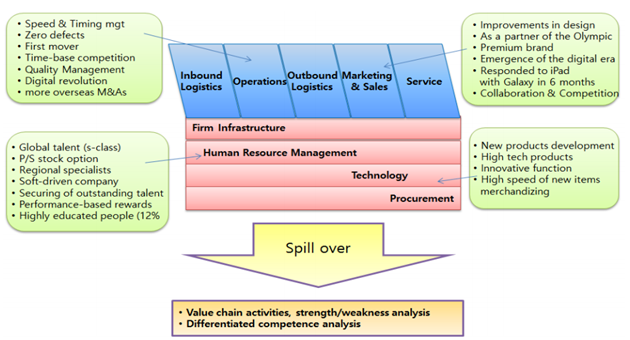
Entry Strategies and International Competitive Strategies
Figure 2 Operational Value Chain in Samsung Electronics
Source: (Jung, 2014)
For ensuring sustained operational control over its activities, Samsung Electronics has a continually reviews it business against the disclosure control policy annually and thus takes corrective actions in cases of deviations (Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd, 2009). Another way of monitoring operations in Samsung Electronics is managing the overall value chain thus generating significance for organizational stakeholders. A culture of continuous improvement of process was also entrusted through operational control (Jung, 2014).
The production in Samsung electronics is supported by six sigma approach that was adopted in 1993 by overhauling the overall management approach towards production(Mo Yang et al, 2007). Though initially Six Sigma was adopted only to manage the quality of final products but in due course of time it became one of the most significant business principles for Samsung Electronics. Later based on ‘quality movement’ within the organization and its subsidiaries across the world, quality enhancements were ensured even in business processes too. The eventual outcome was provision of quality outputs to the consumers, supporting innovations through new product developments, escalated profits and rising customer loyalty(Sabri, 2015).
Supply chain management (SCM) in Samsung Electronics has been one of the major pillars that have supported organizational growth beyond leaps and bounds. Multiple technologies related to SCM plays a dominant role in managing its supply chain thereby integrating its international activities along with supporting innovations. The most significant SCM technology deployed by Samsung electronics is the advanced planning and scheduling (APS) systems which was adopted in 1990s but yet is considered to be highly successful(Mo Yang et al, 2007). Continuous innovations have been made within the system to support external and internal environmental changes. The supply chain of Samsung Electronics is depicted in figure below:
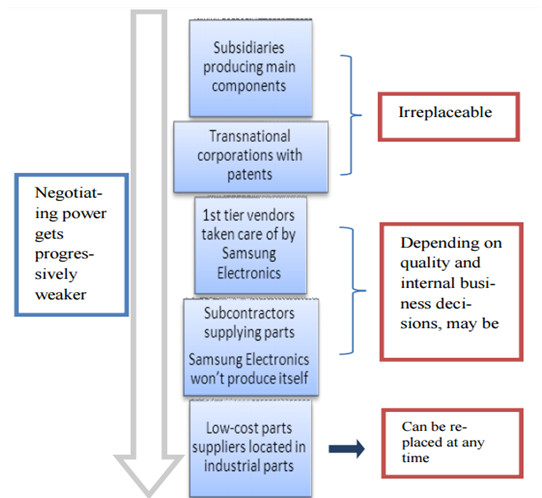
Figure 3Layers in Samsung Electronics’ supply chain and their importance
Source: (Han et al, 2013)
The supply chain of Samsung is developed in a manner that most of its production are absorbed within the Samsung groups and by its affiliate inustries. It is evident from the fact that production by Samsung Thailand is sold to Samsung in European countries as well as that in Brazil and Korea (Christiansen, 2015). Thus it operates as a highly integrated system wherein it acts as a producer as well as consumer in many circumstances.
One of the major issues within this supply chain is that, Samsung Electronics lays more emphasis on domestic companies rather than on international or transnational organizations associated with the same. Though quality is given due importance but discrimination is also practiced which affects the supply chain ethically thus having negative implications of supply chain partners of Samsung(Han et al, 2013). Another major issue identified with the supply chain of Samsung is that its non-adherence to social and environmental standards. Though a larger extent the company has resorted to environmental conservation but it fails to integrate the same with supplier management programs thus resulting in ineffective implementation of such approaches. Further it also forbids the company from taking maximum advantage of environmental certifications like ISO 14001 which results in increased risks of being subjected to social issues(Lee & Kim, 2009). In Samsung electronics to optimize benefits from Six Sigma and SCM both were amalgamated to drive organizational sustainability and support innovations.
Operational Control, Production and SCM
Irrespective of having highly effective and efficient supply chain and production systems it is important for Samsung to improve the same to retain its leadership position in international markets. It is thus recommended that Samsung needs to deploy a more obedient approach that would streamline issues present within existing supply chain as well as incessantly monitor the activities within the chain. Another major issue that is discrimination needs to be curbed which is possible only when the company resorts to a fair trade policy(Wilkinson, 2007). It is also significant for Samsung Electronics to have a codified regulatory system that will be equivalent for all the firms and supply chain associates based on their position and dealings with the company. Such a system would enhance the trust of supply chain partners in Samsung and thus motivate to them to conduct fair business along with being loyal to the company.
It is also recommended to Samsung to resort to reverse logistic that will help the company in overcoming environmental sustainability issues as well as minimize wastages(Sarkis et al, 2010). Through reverse logistics, Samsung will be able to support recycling, reuse and recovery of its used products thus helping in environmental conservation.
Considering the fact that HR management has been a significant issue for Samsung not within its company but within supplier companies it is critically essential for Samsung to design stringent measures to curb such practices. This is possible when the integrity management policy as determined by Samsung is also enforced upon the varied organizational suppliers. Further it is also important for Samsung to conduct HR audits at supplier firms on a regular basis with the help of a special team created solely for this purpose(Farndale et al, 2010). The team would operate as an external individual group and conduct audit thus certifying suppliers in accordance to Samsung’s norms. This will help Samsung to overcome blind belief on suppliers and their audit reports thus safeguarding its employees as well as goodwill.
Conclusion
Samsung has been operating with excellence in international markets which is clearly visible through its growth graph which it has achieved within a very short span of time. With an expansive geographically diversified portfolio, it is intricate for Samsung to manage its international business. But through proactive approaches amalgamated with an incessant urge to achieve leadership position has been the driving force of Samsung’s success. By defying traditional approaches and developing innovative management system Samsung has been able to outshine its competitors. However to manage dynamics of international business and gain long run sustainability it is critically significant for Samsung to be proactive in its approach and thus manage hindrances effectively.
References
Samsung Electronics . (2012). Samsung Electronics Sustainability Report 2012 . Seoul: Samsung Electronics .
Adnan. (2016). Mergers and acquisitions helping Samsung boost business oversea. Retrieved June 7, 2016,
Bloomberg. (2011). Samsung Electronics Co. buys out Sony's stake in LCD joint venture. Retrieved June 7, 2016,
Cheng, J., & Lee, M. (2015). Samsung Shareholders Back $8 Billion Merger, in Blow to U.S. Hedge Fund. Retrieved June 7, 2016,
Christiansen, B. (2015). Handbook of Research on Global Supply Chain Management. Hershey: IGI Global. .
Chun, J. (2015). How Samsung Electronics’ Organizational Structure and Culture Affect Its Innovation. Denmark: Ibp Union.
Farndale, E., Paauwe, J., & Boselie, P. (2010). An exploratory study of governance in the intraâ€Âfirm human resources supply chain.
Fortune Global. (2016). Fortune Global 500. Retrieved June 6, 2016,
Glowik, M. (2016). Market Entry Strategies: Internationalization Theories,
Guha, R. (2015). Samsung leads the Indian mobile market share in Q3, 2015: Study. Retrieved June 6, 2016.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2017). Samsung Electronics' International Business Strategy: Analysis Essay.. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-strategy-analysis-of-samsung-electronics.
"Samsung Electronics' International Business Strategy: Analysis Essay.." My Assignment Help, 2017, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-strategy-analysis-of-samsung-electronics.
My Assignment Help (2017) Samsung Electronics' International Business Strategy: Analysis Essay. [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-strategy-analysis-of-samsung-electronics
[Accessed 20 May 2025].
My Assignment Help. 'Samsung Electronics' International Business Strategy: Analysis Essay.' (My Assignment Help, 2017) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-strategy-analysis-of-samsung-electronics> accessed 20 May 2025.
My Assignment Help. Samsung Electronics' International Business Strategy: Analysis Essay. [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2017 [cited 20 May 2025]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/international-business-strategy-analysis-of-samsung-electronics.
